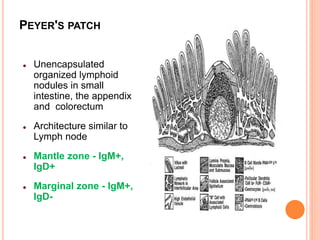
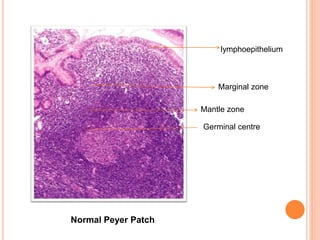
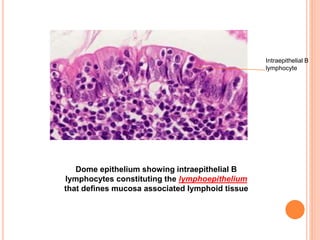
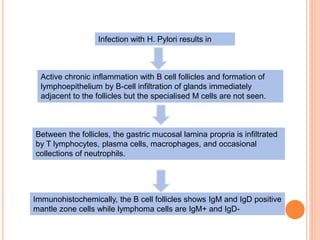
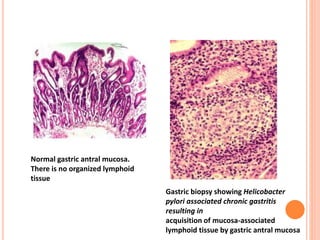
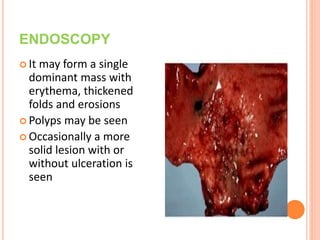
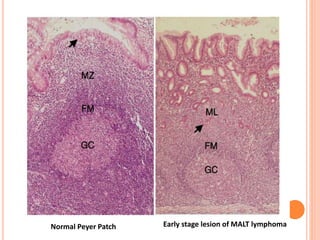
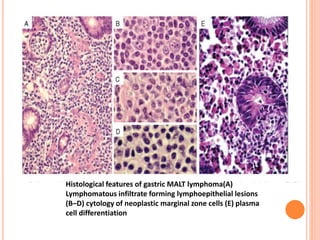
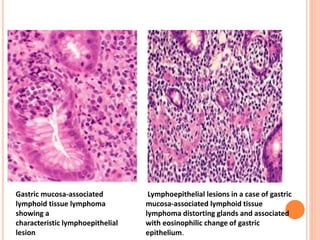
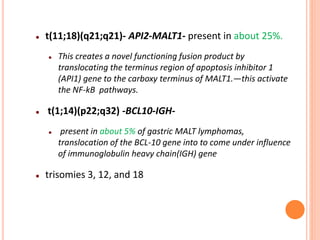
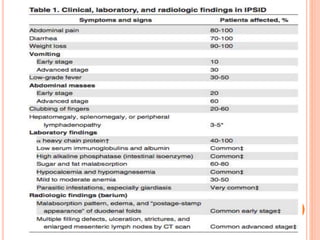
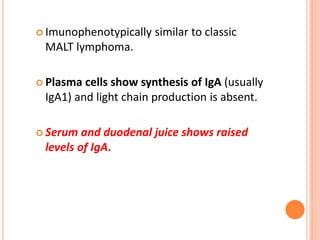
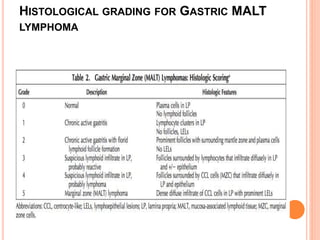
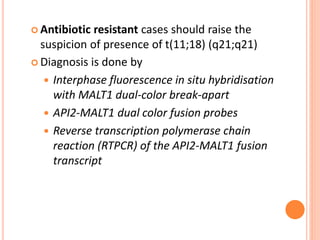
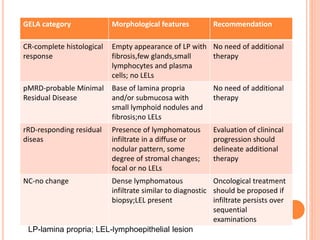
MALT lymphoma arises from mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue (MALT) found along mucosal surfaces. It most commonly involves the stomach and is often associated with H. pylori infection. Histologically, it ranges from resembling normal MALT to displaying lymphoepithelial lesions and infiltration of lymphoma cells. Immunohistochemistry shows B-cell markers and molecular testing can identify translocations involved in pathogenesis. IPSID is a subtype associated with C. jejuni infection seen in certain regions. Staging involves extent of involvement from mucosa to large masses with cytologic atypia.