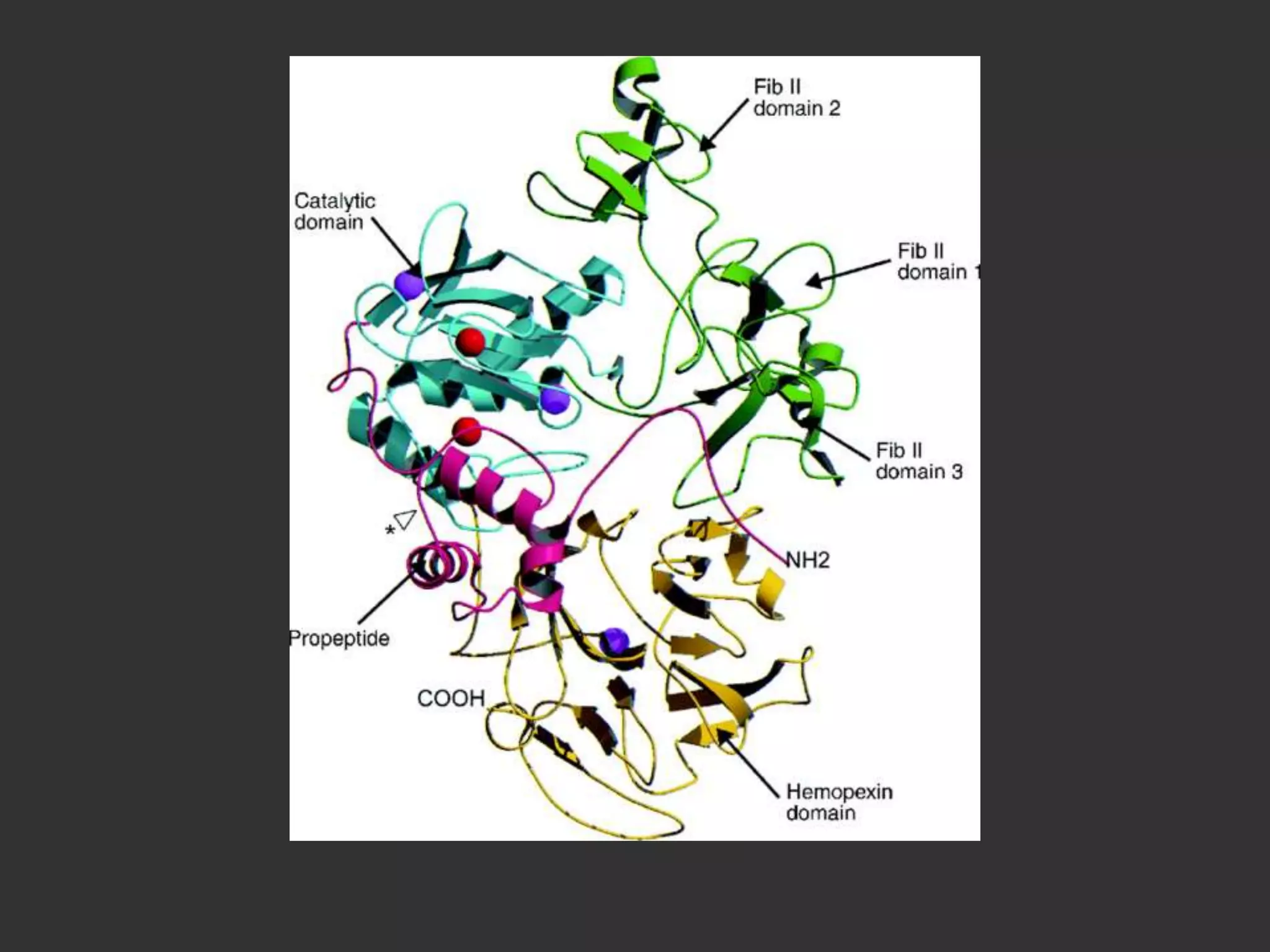
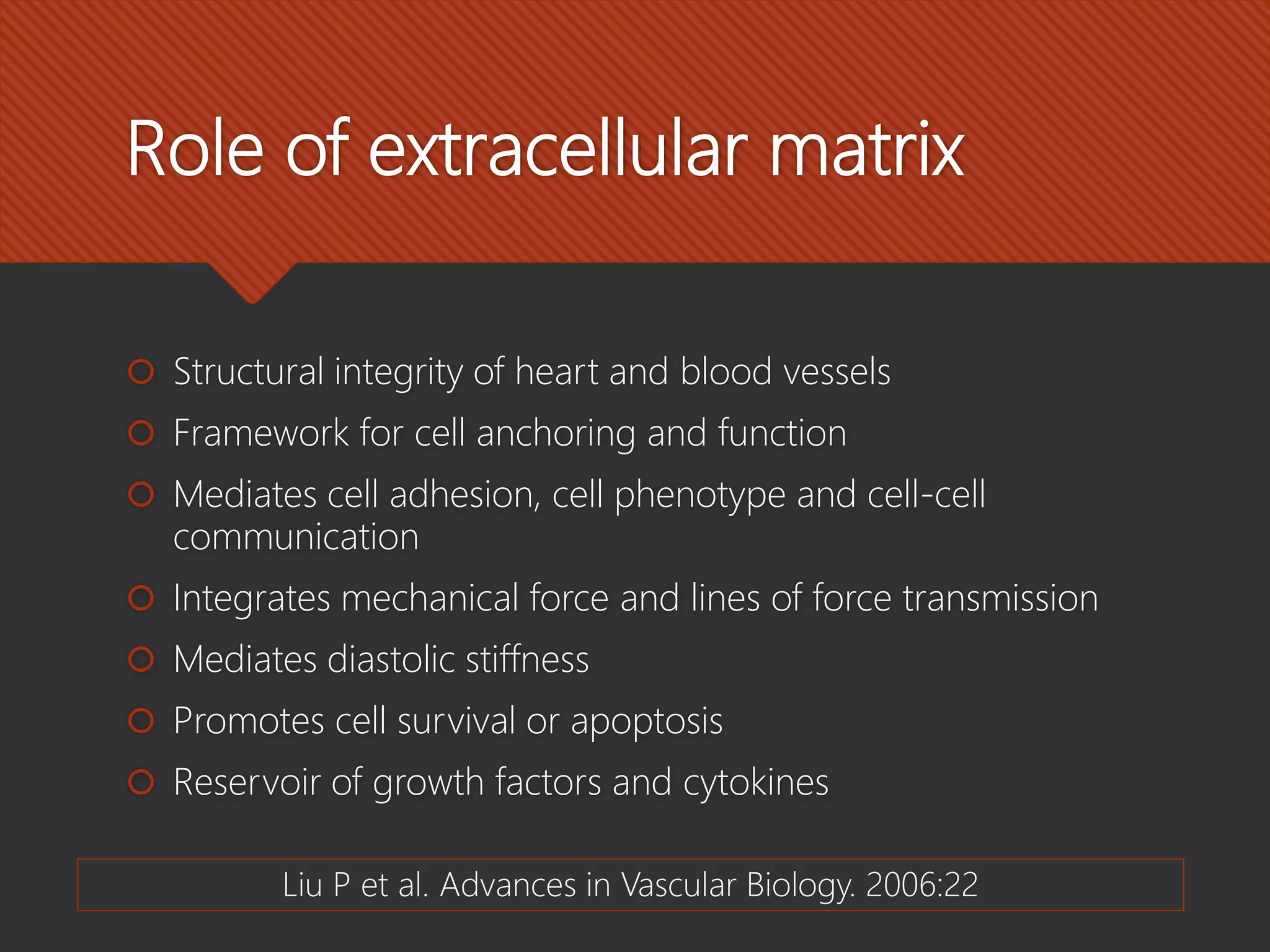
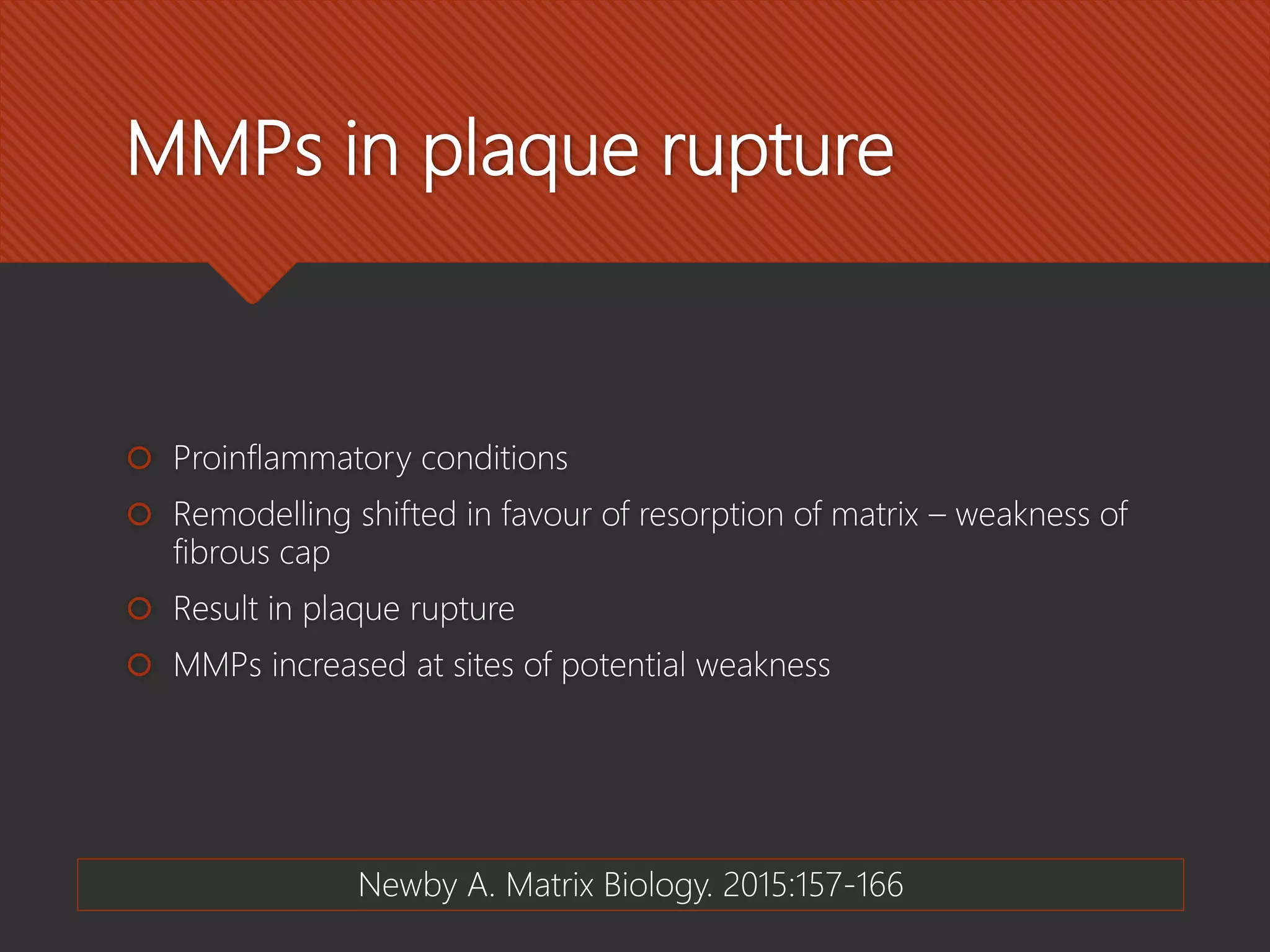
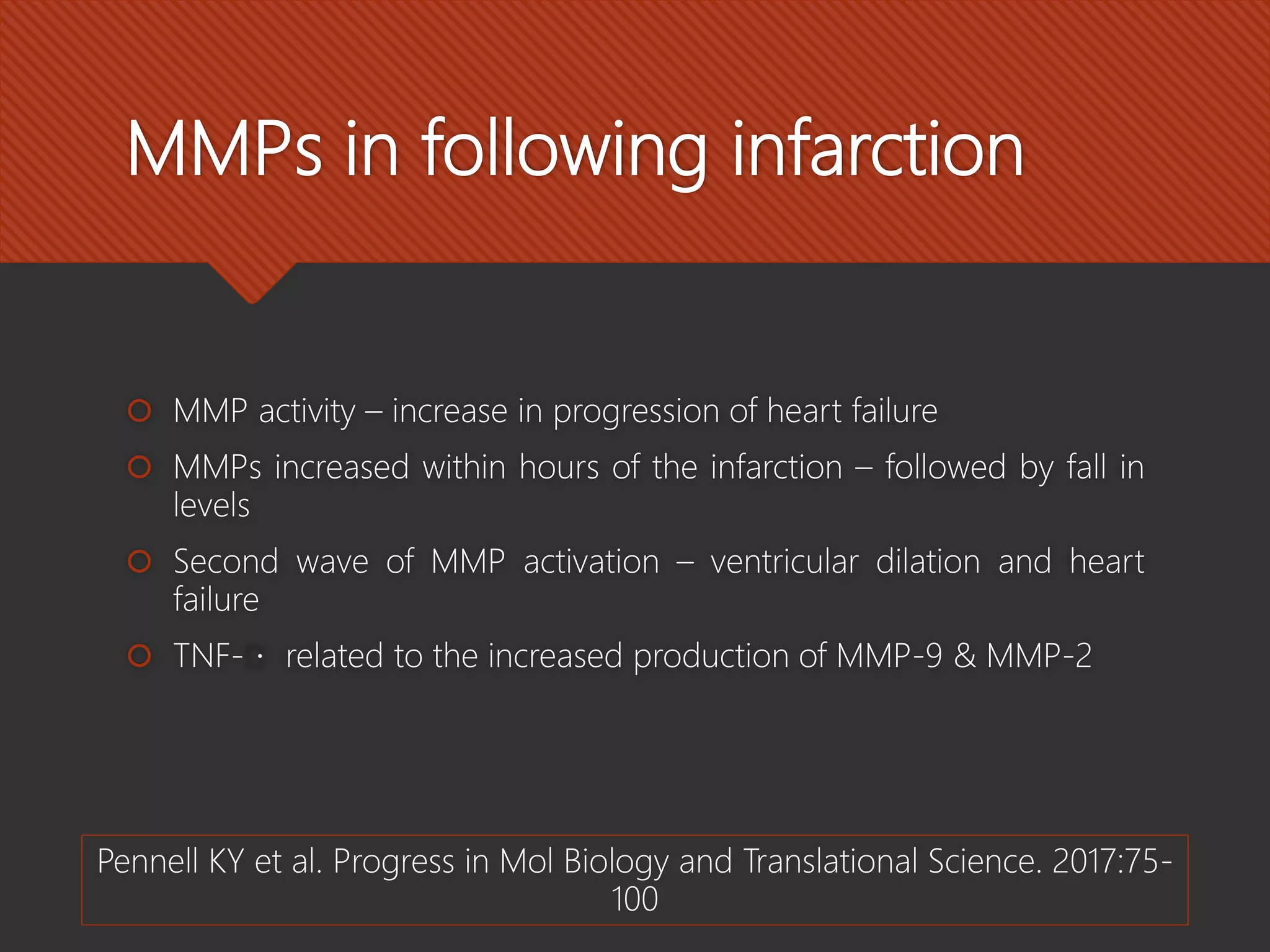
Matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs) are critical enzymes involved in cardiovascular disease, particularly in processes like atherosclerosis, plaque rupture, and heart failure. They play a role in the remodeling of the extracellular matrix, affecting structural integrity and cellular functions, while their activity can be influenced by various risk factors and tissue inhibitors. MMPs have potential as therapeutic targets and diagnostics, although they are not recommended as routine biomarkers due to insufficient predictive value.