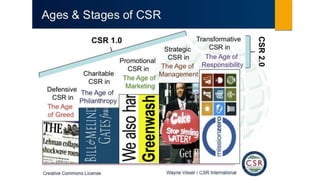
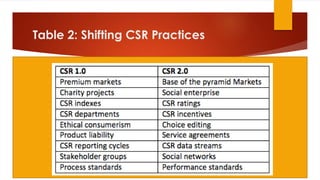
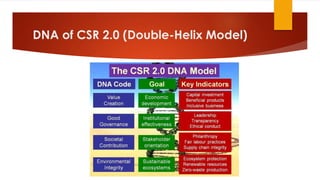
This document discusses the need to reinvent corporate social responsibility (CSR) for the 21st century by transitioning from CSR 1.0 to CSR 2.0. CSR 1.0 is described as outdated and ineffective at addressing major social and environmental challenges due to being incremental, peripheral to core business strategies, and not always economically viable. CSR 2.0 proposes five principles of creativity, scalability, responsiveness, glocality, and circularity to make CSR more transformational. It presents a new holistic model of CSR with four "DNA responsibility bases" of value creation, good governance, societal contribution, and environmental integrity. The document calls for businesses to embrace this new conception of responsible capitalism centered on long-term