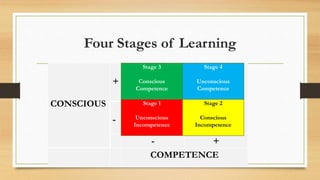
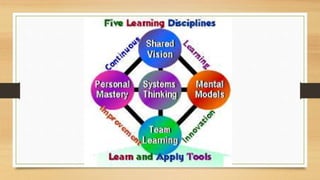
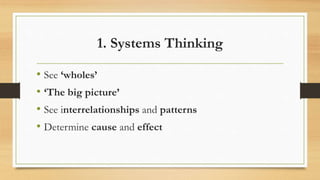
The document discusses the concept of a knowledge society, emphasizing its role in human and sustainable development through education, access to information, and inclusivity. It identifies three key pillars for enhancing knowledge value, fostering participatory approaches, and integrating knowledge policies, alongside recommendations for improving education and increasing ICT access. The text also advocates for lifelong learning, creativity, and collaborative knowledge sharing to address global challenges and promote social equity.