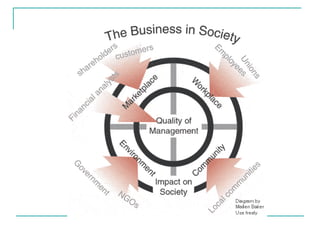
Corporate social responsibility (CSR) originated in the late 1960s and early 1970s after multinational corporations formed the term "stakeholder". CSR aims to embrace responsibility for a company's actions and encourage a positive environmental and social impact. It also helps guide an organization's mission and values. CSR involves operating businesses ethically and contributing to economic and social development. While approaches to CSR vary by country, common practices include community development, philanthropy, education programs, and environmental initiatives. However, some criticize CSR as a distraction from ethical issues or for being used for commercial benefit rather than true social responsibility.