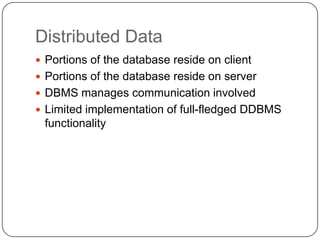
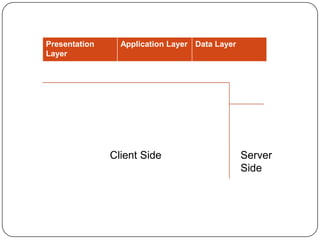
This document discusses different types of client server models. It describes logical layers including the presentation layer, application layer, and data layer. It then defines five common client/server models: distributed presentation, remote presentation, distributed logic, remote data, and distributed data. Each model divides responsibilities between the client and server differently. For example, remote presentation puts the presentation manager on the client and the application and data layers on the server.