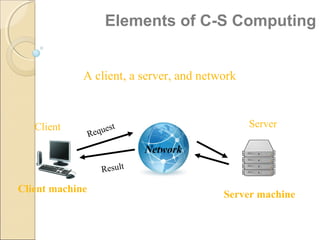
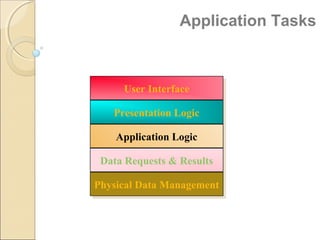
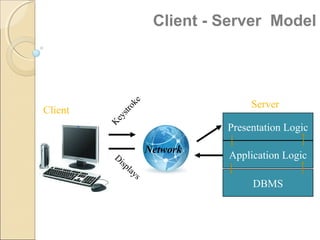
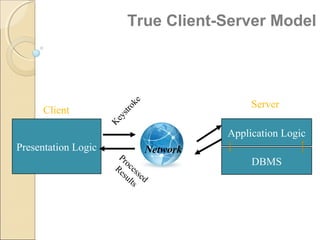
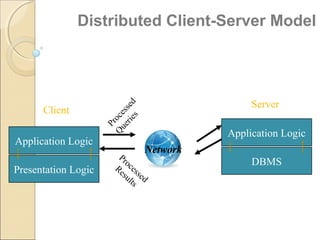
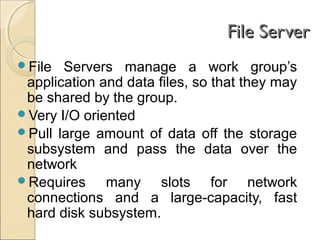
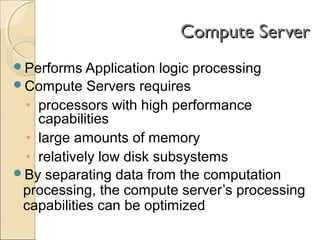
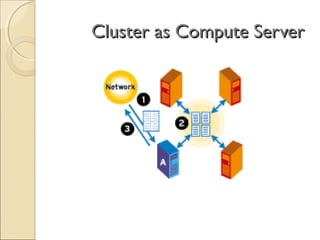
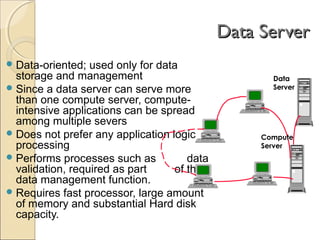
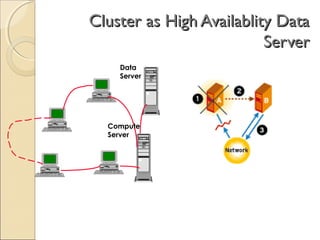
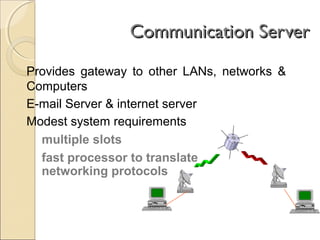
Client/server computing involves separating tasks between client and server machines. The client makes requests that are processed by the server, which returns results to the client. Key elements are the client, server, and network connecting them. Major focus is on the software handling tasks like the user interface, application logic, and data management between client and server. Different types of servers specialize in files, data, computing tasks, databases, and communication between networks.