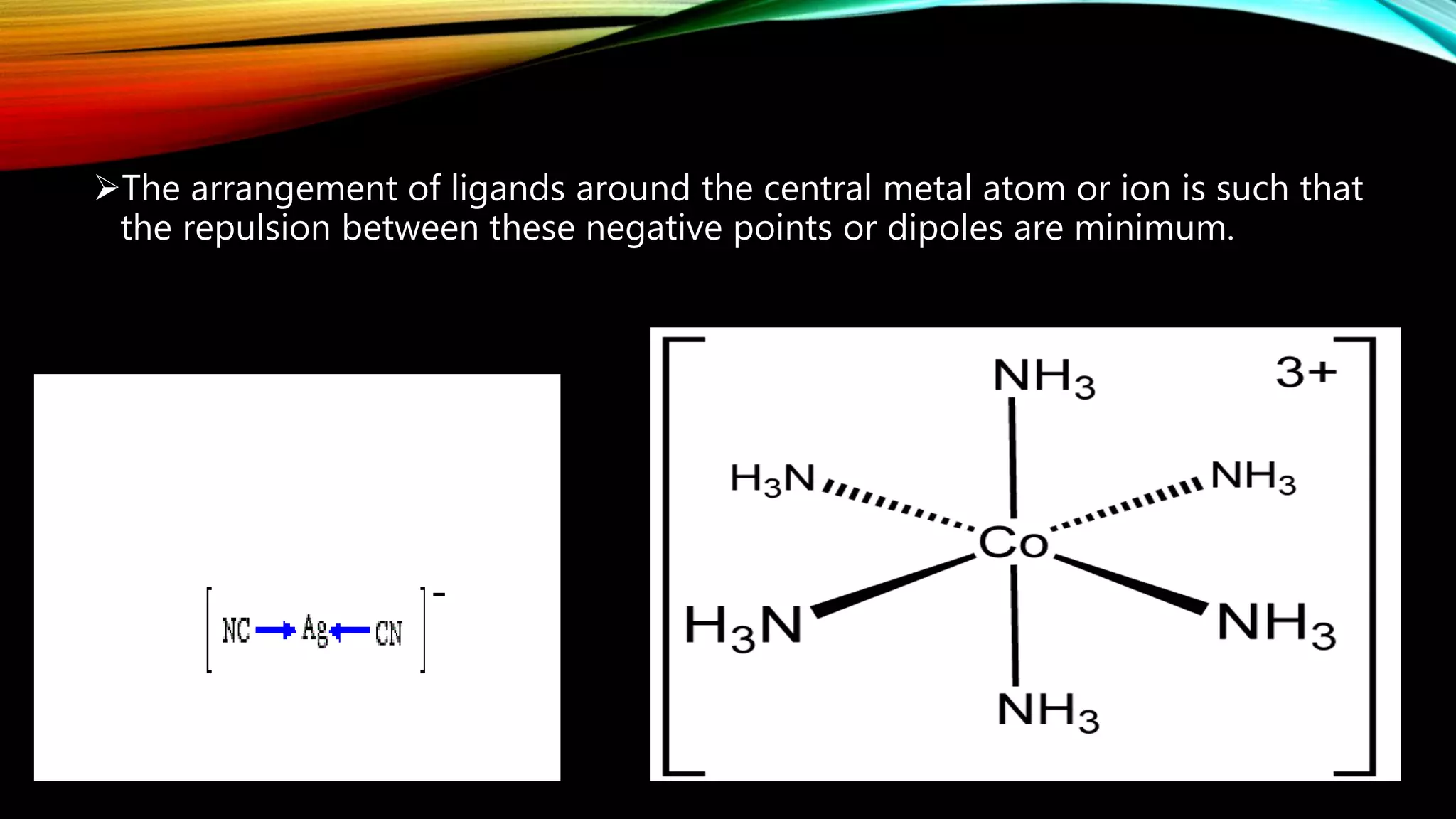
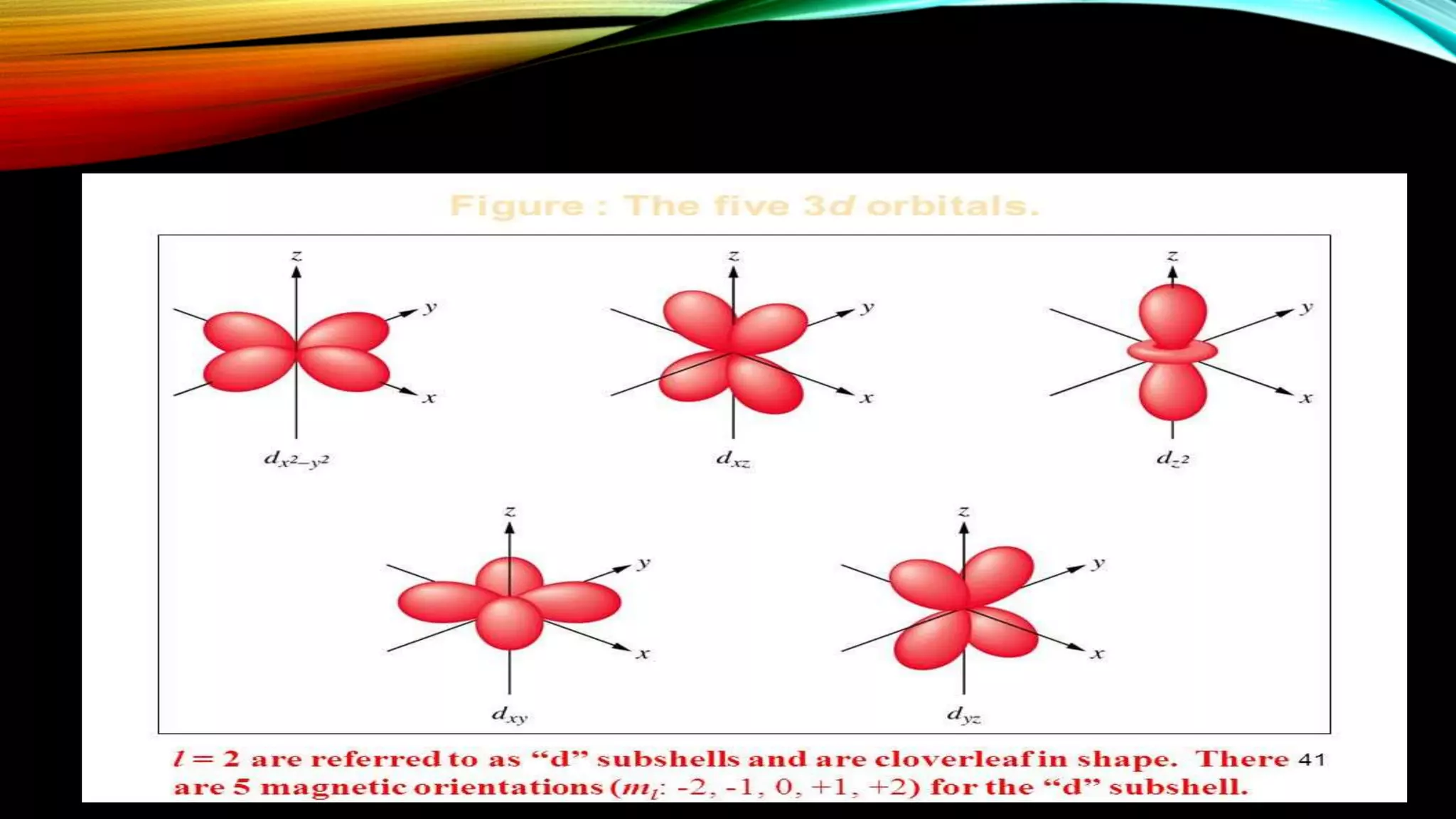
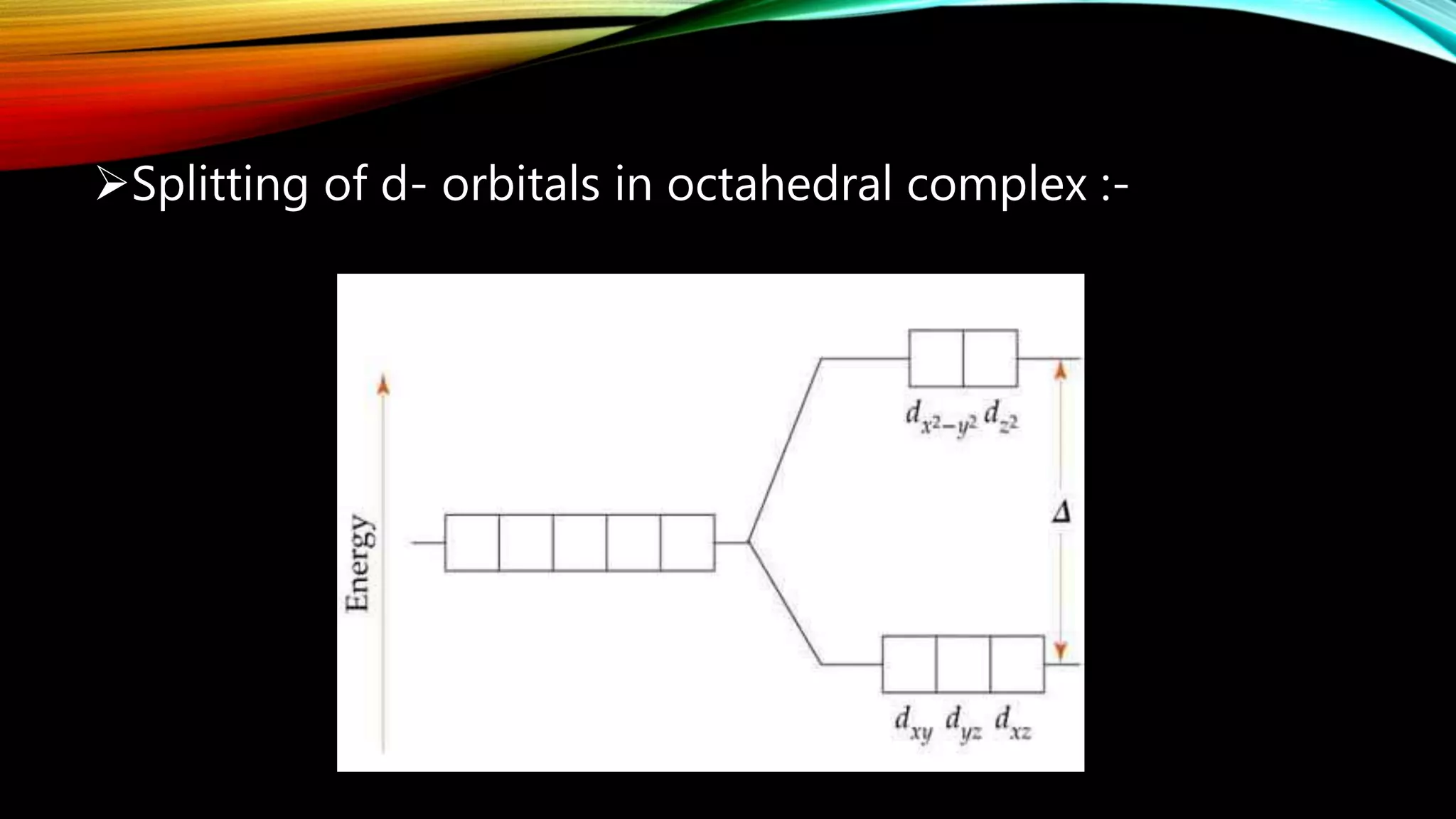
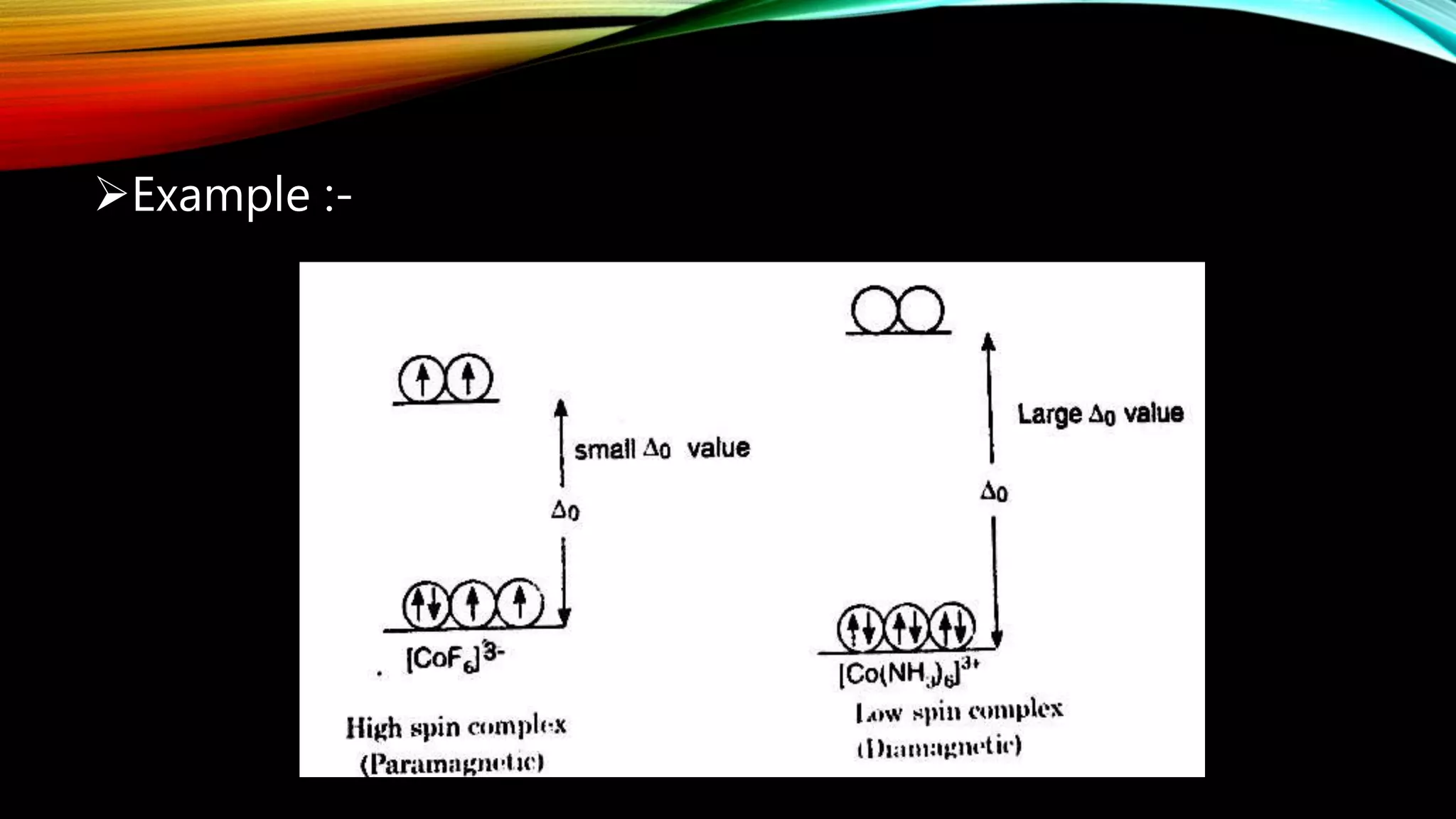
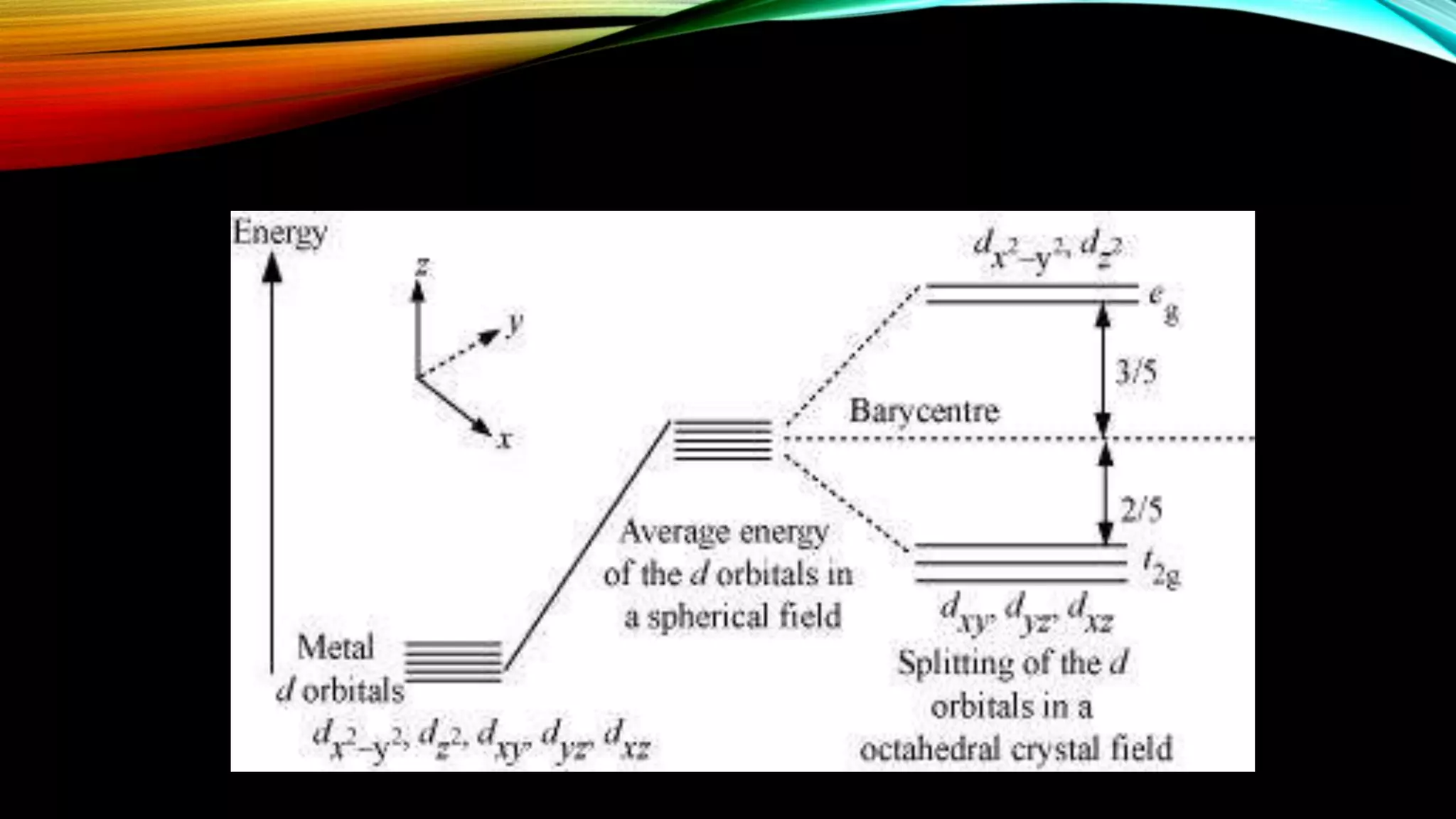
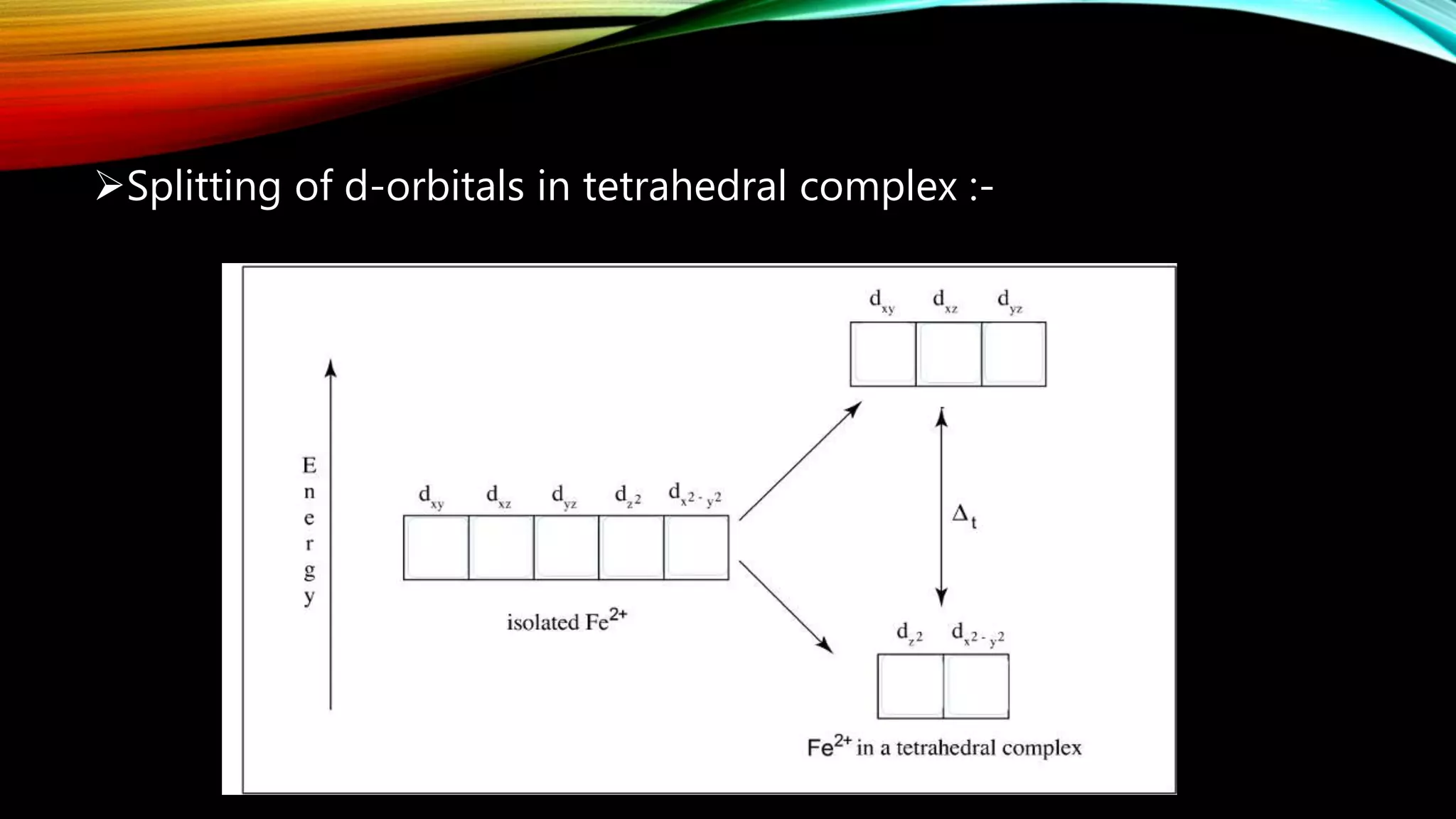
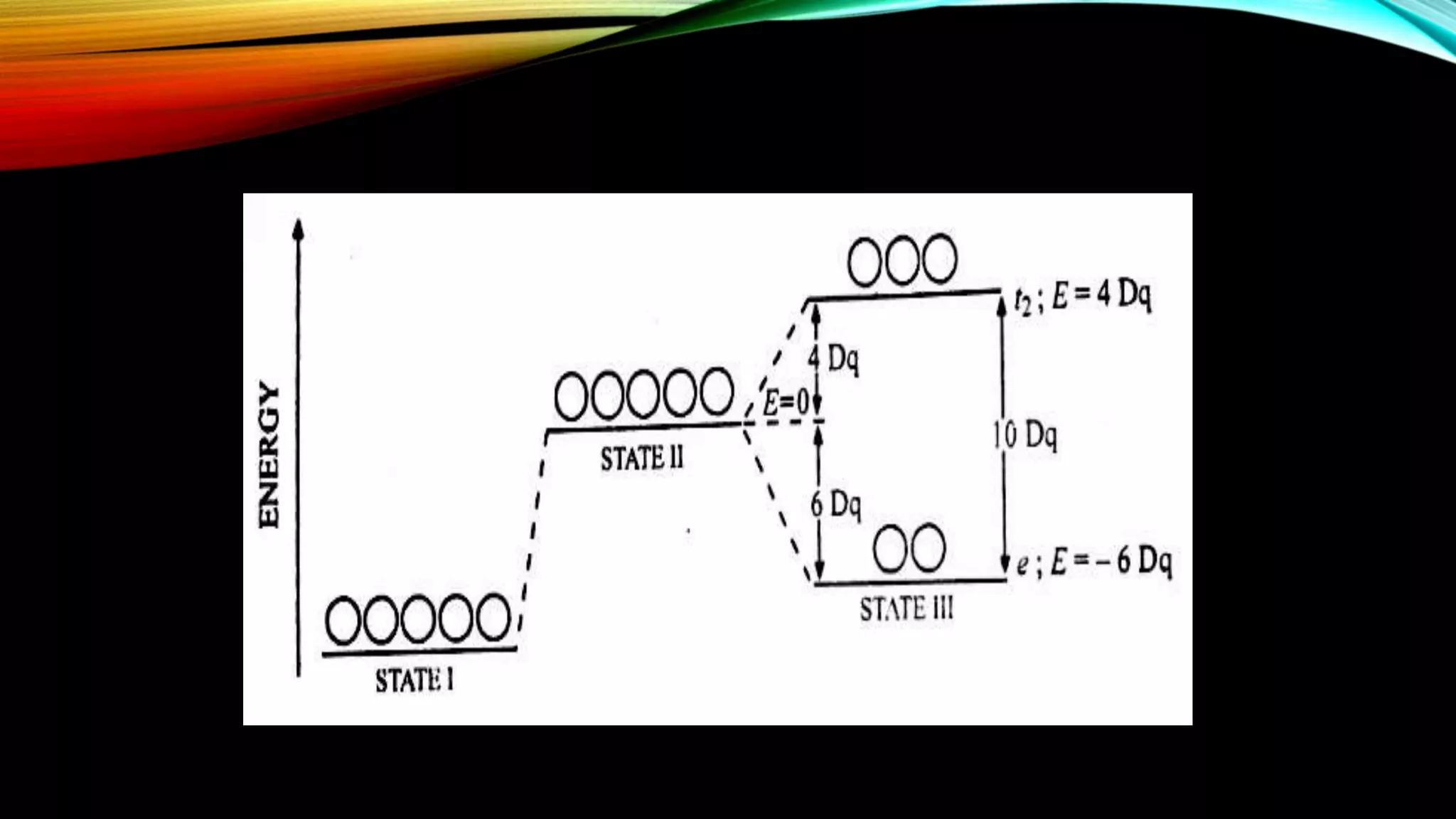
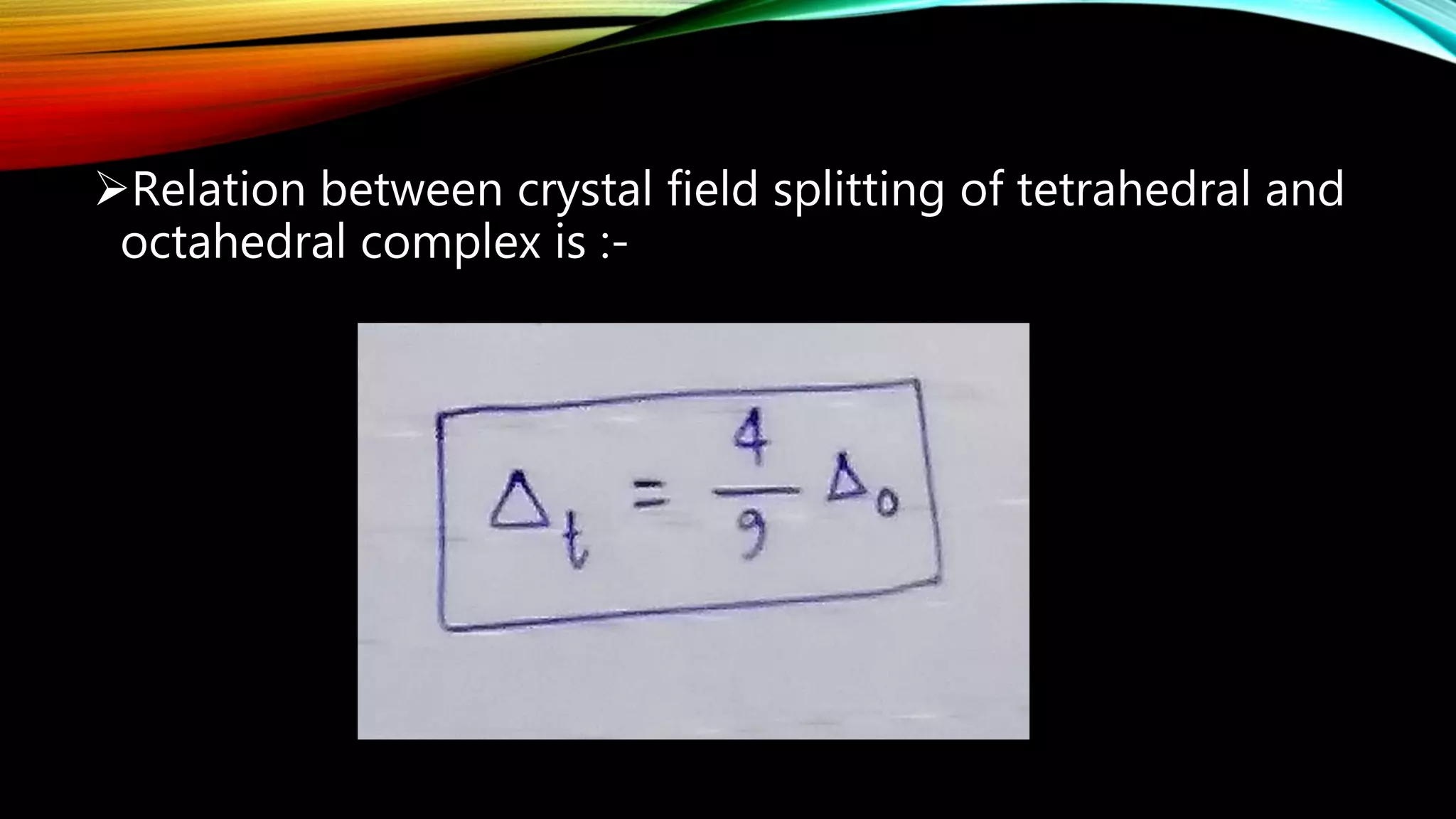
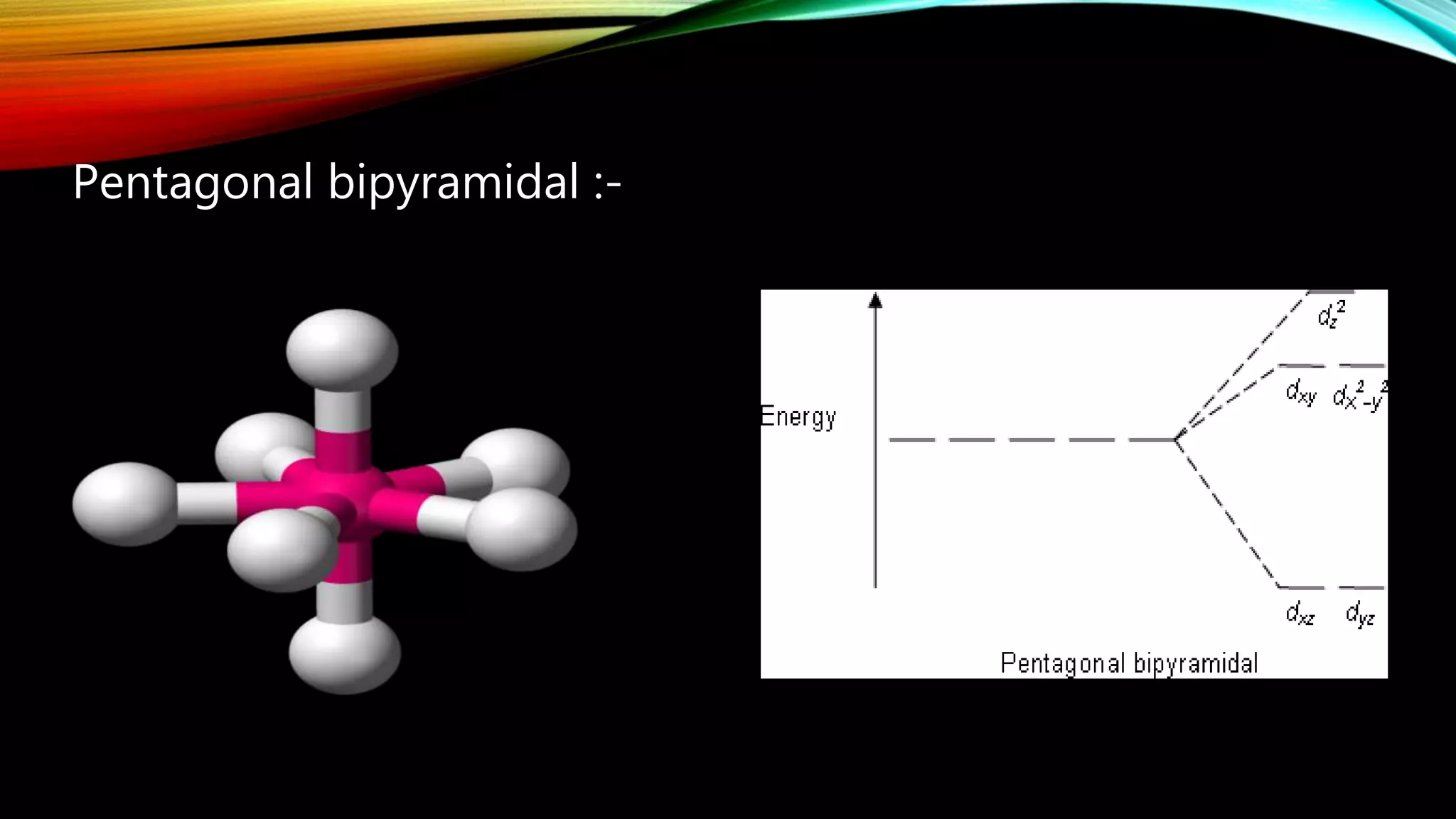
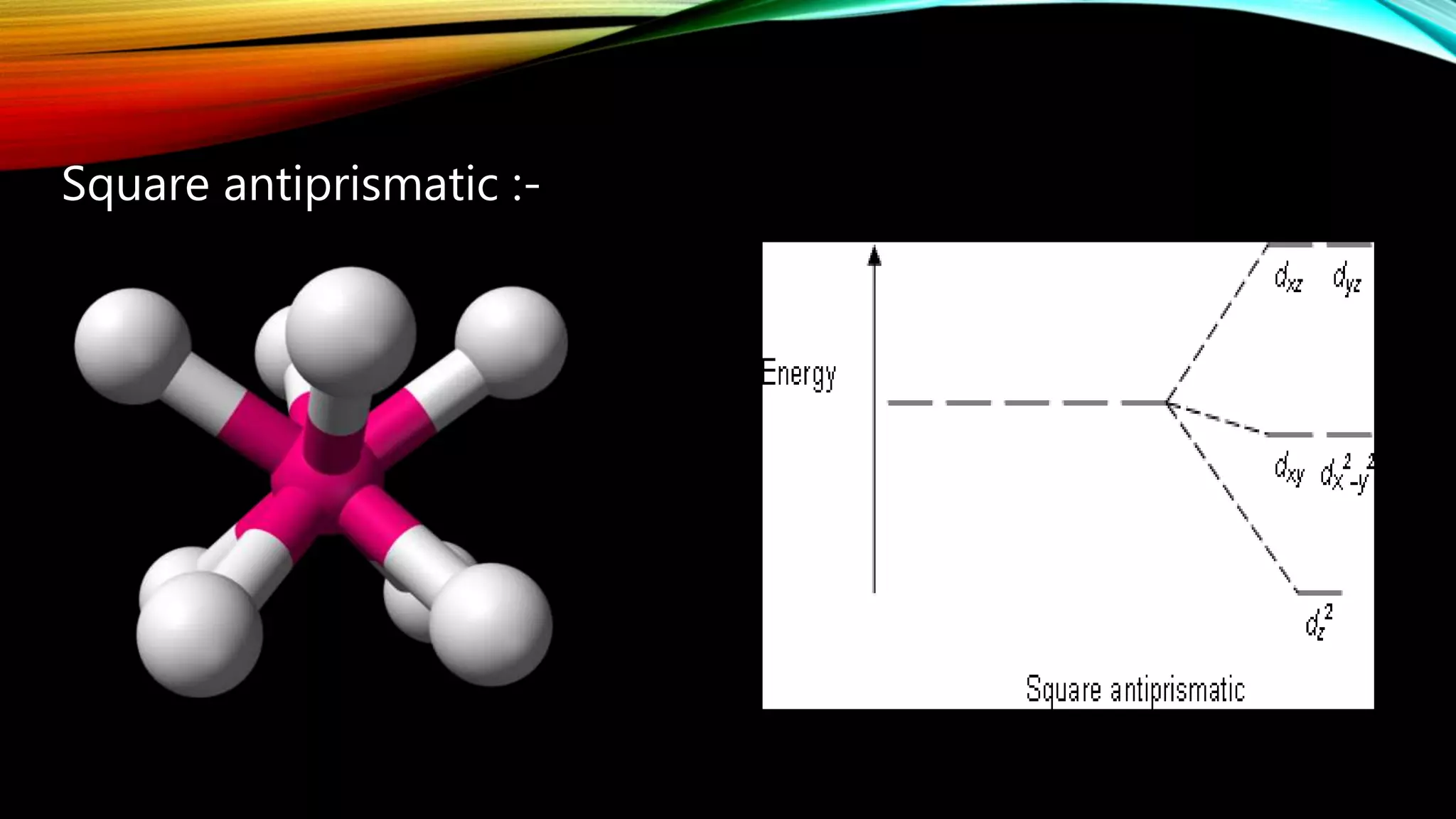
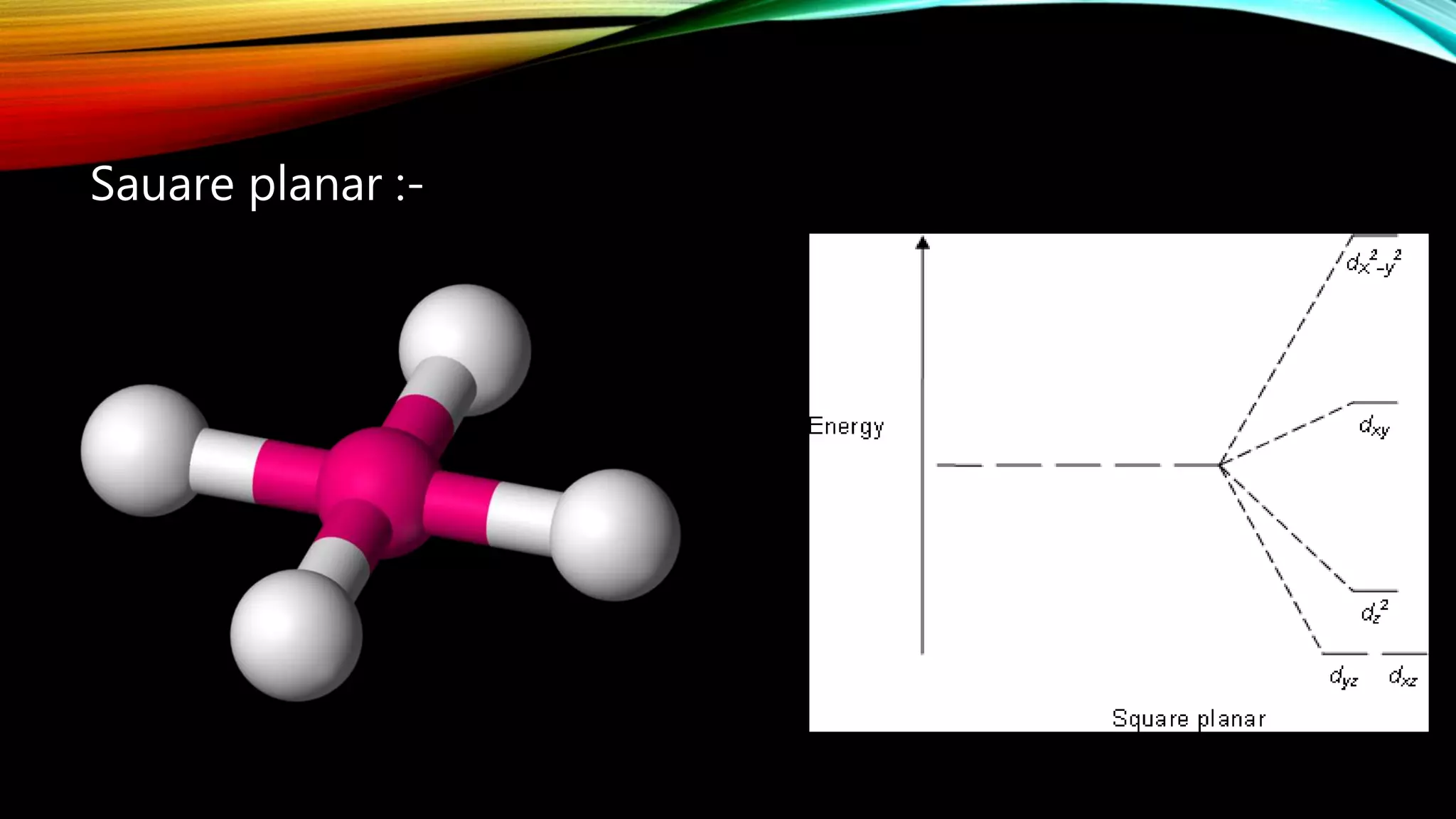
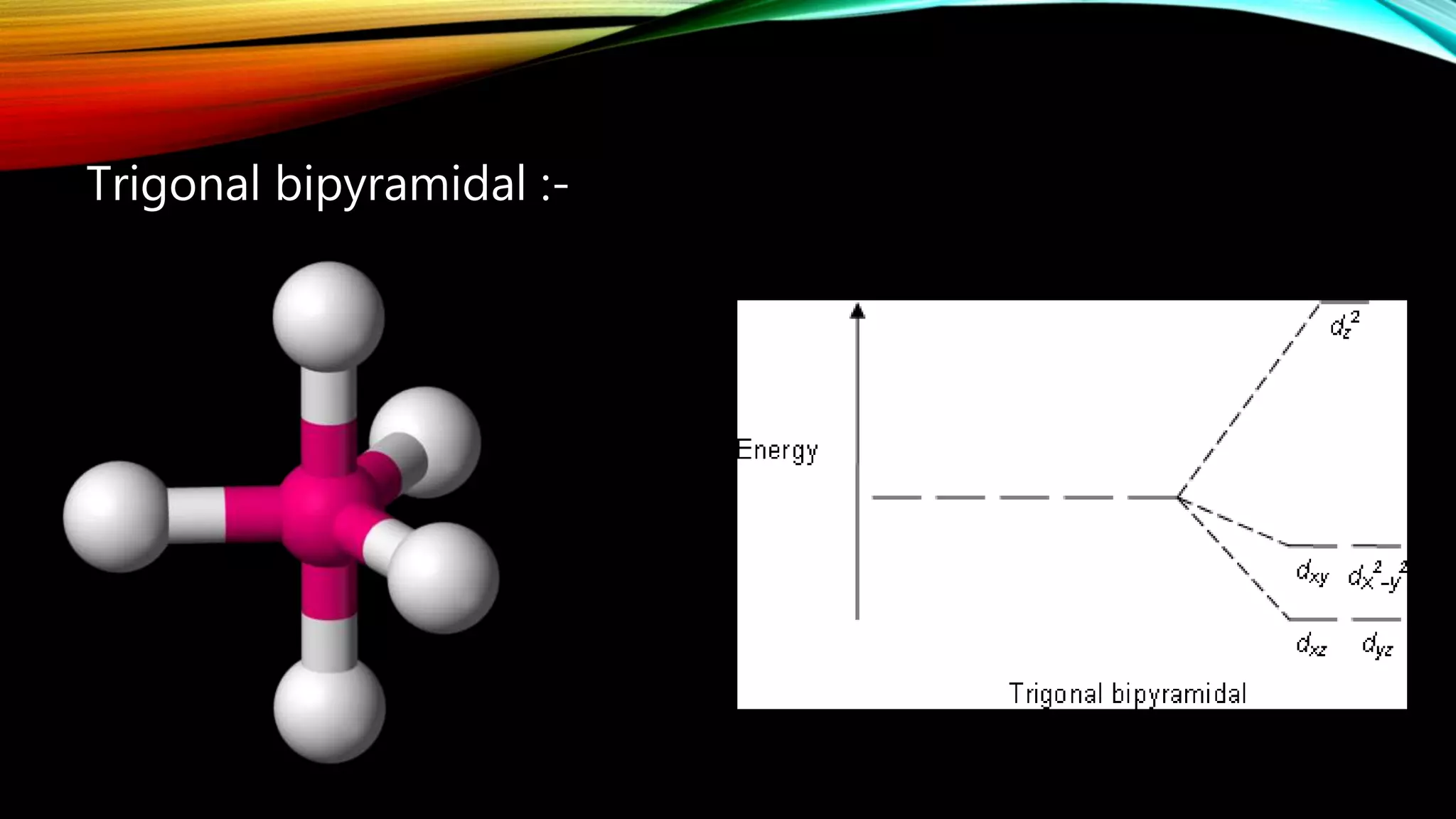
Crystal Field Theory (CFT), developed by Hans Bethe and John Hasbrouk Van Veck in the 1930s, is a bonding model describing the properties of transition metal complexes, such as colors and magnetism. CFT assumes ionic bonds between central metal atoms and ligands, which can be positive, neutral, or negative, and explains the arrangement of ligands to minimize repulsion. Additionally, CFT addresses d-orbital splitting in complexes and is utilized to explain spin states, magnetic properties, and colors of complex compounds.