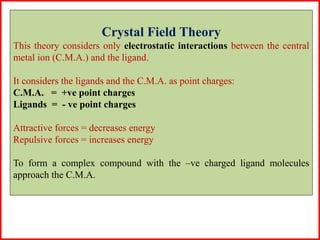
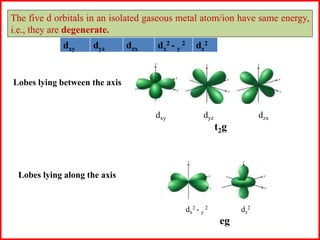
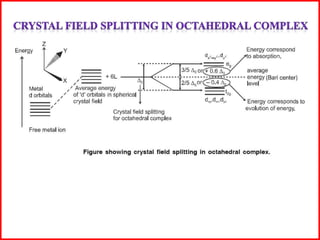
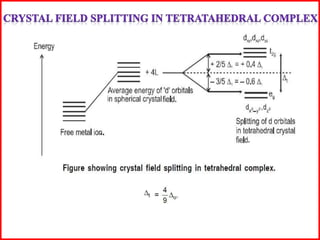
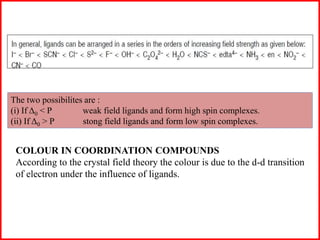
This document summarizes Crystal Field Theory, which considers the electrostatic interactions between metal ions and ligands. It describes ligands and metal ions as point charges that can have attractive or repulsive forces. This causes the d orbitals of the metal ion to split into two sets with different energies - t2g and eg orbitals. The type of splitting and whether complexes are high or low spin depends on the ligand field stabilization energy and pairing energy. Color in coordination compounds is also explained by d-d transitions under ligand influence. Factors like the metal ion, ligands, and complex geometry affect crystal field splitting. However, the theory has limitations like not accounting for other metal orbitals or fully explaining ligand strengths.