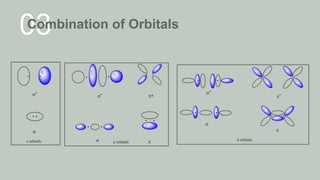
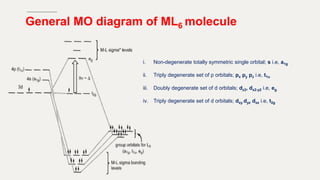
Molecular orbital theory (MOT) is an alternative model to valence bond theory that explains how atomic orbitals from different atoms combine to form molecular orbitals. The linear combination of atomic orbitals (LCAO) method considers the probability of finding electrons in atomic orbitals from different atoms. According to the LCAO method, molecular orbitals are formed from constructive and destructive interference of atomic orbitals. MOT can be used to explain bonding in homonuclear diatomic molecules like N2 and O2, heteronuclear diatomic molecules like CO and NO, and polyatomic molecules like CO2 and SF6. It can also describe bonding in octahedral transition metal complexes like hexaaquoferrate(II) ion





![05
Examples of MOT
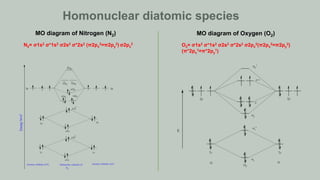
Homonulear diatomic species
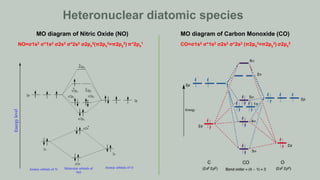
Heteronuclear diatomic species
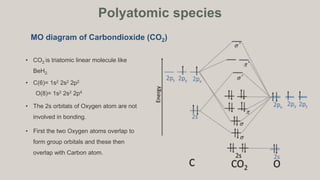
Polyatomic species.
a. CO2
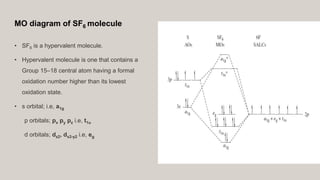
b. SF6
Octahedral complexes of 1st transition series.
a. Hexaaquo ferrate (II) ion: [Fe(H2O)6]2+](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/molecularorbitaltheory-210709132852/85/Molecular-orbital-theory-7-320.jpg)

![• Fe is in +2 oxidation state.
• Fe (26)= [Ar] 3d6 4s2
Fe2+ = [Ar] 3d6 4s0
• There are 18 electrons in all, two from each
water molecule and six from Fe2+ ion.
• The 1st twelve electrons are placed in lower six
bonding molecular orbitals a1g t1u and eg. The
remaining electrons are placed in the molecular
orbital of next higher energy.
14
Hexaaquo ferrate (II) ion: [Fe(H2O)6]2+](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/molecularorbitaltheory-210709132852/85/Molecular-orbital-theory-14-320.jpg)


