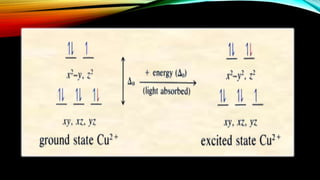
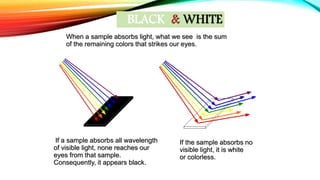
Crystal Field Theory (CFT) explains the color properties and magnetic characteristics of transition metal complexes by describing the bonding between ligands and metals through the splitting of d-orbitals in the presence of ligands. The striking colors of these complexes result from d-d electronic transitions, where electrons jump between split d-orbitals when excited by photons. However, CFT has limitations, including its inability to account for orbital splitting beyond d-orbitals and the order of ligands in the spectro-chemical series.







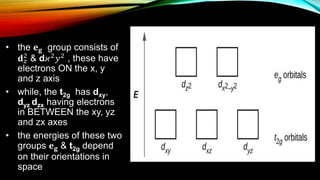
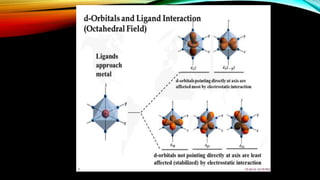
![• d-orbitals are degenerate
• BUT, when ligands get
attached and are uniformly
distributed; their energy gets
higher
• IF, the ligands are oriented at
the axes i.e. x, y and z, the
degeneracy gets removed and
the d-orbitals split into two
groups [ 𝐞 𝒈 & 𝐭2𝑔]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/crystalfieldtheory-180531063839/85/Crystal-field-theory-10-320.jpg)

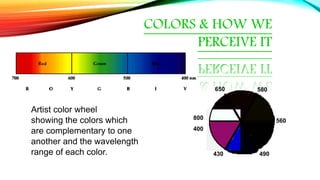
![COMPLEX INFLUENCE ON
COLOR
[Fe(H2O)6]3+
[Co(H2O)6]2+
[Ni(H2O)6]2+
[Cu(H2O)6]2+
[Zn(H2O)6]2+
800
430
650 580
560
490
400](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/crystalfieldtheory-180531063839/85/Crystal-field-theory-17-320.jpg)



