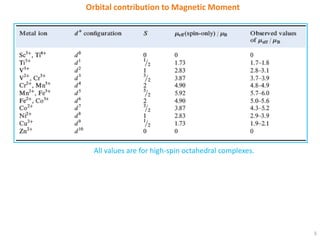
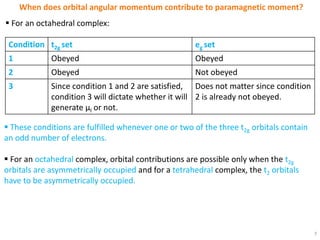
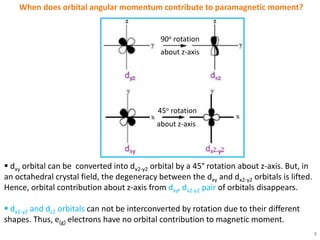
The selection rules that determine which electronic transitions are allowed or forbidden in transition metal complexes are the Laporte selection rule and spin selection rule. The Laporte rule forbids transitions that result in no change in orbital angular momentum, while the spin rule forbids transitions that change the overall spin of the complex. These rules can be relaxed by vibronic coupling in octahedral complexes or do not apply in tetrahedral complexes. Orbital contributions to paramagnetic moment only occur when the transition metal d orbitals are asymmetrically occupied, allowing electron circulation between degenerate orbitals.

![3
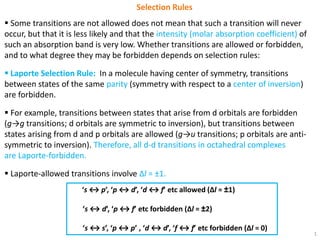
Selection Rules
Spin Selection Rule: The overall spin S of a complex must not change during an
electronic transition, hence, ΔS = 0.
To be allowed, a transition must involve no change in spin state. This is because
electromagnetic radiation usually cannot change the relative orientation of an
electron spin.
▪ [Mn(H2O)6]2+ has a d5 configuration and it is a high-spin complex. Electronic
transitions are not only Laporte-forbidden, but also spin-forbidden. The dilute
solutions of Mn2+ complexes are therefore colorless.
▪ Certain complexes like MnO4
- and CrO4
2- are intensely colored even though they
have metal ions without electrons in d orbitals. The color of these complexes are not
from d-d transitions, but from charge-transfer from ligand to metal orbitals.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lecture11-220920170419-d424ed90/85/La-Porte-Selection-rule-pptx-3-320.jpg)