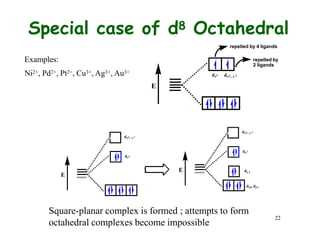
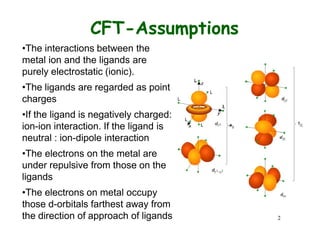
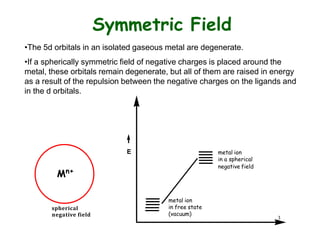
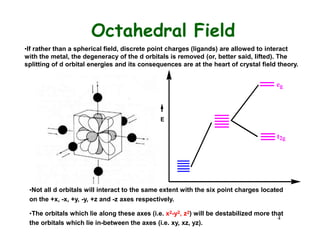
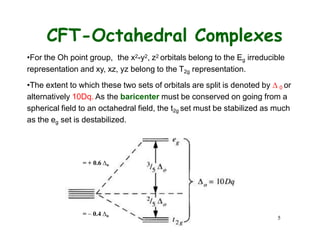
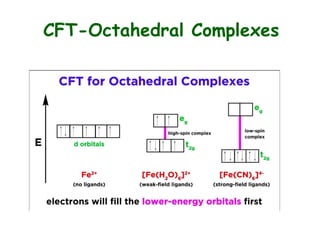
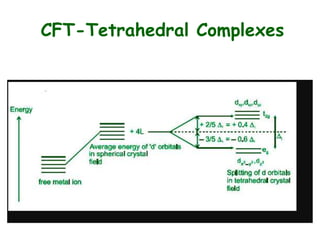
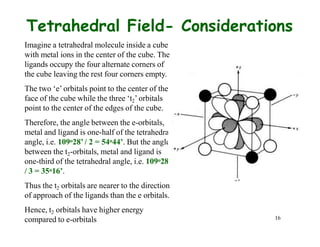
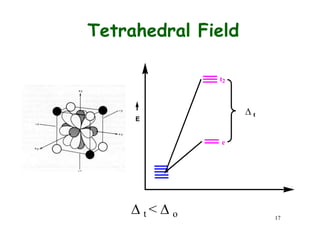
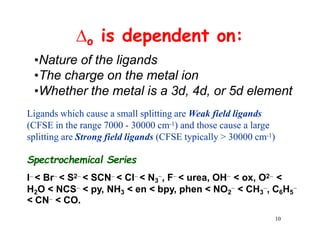
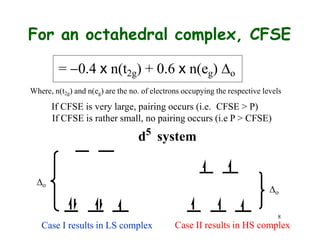
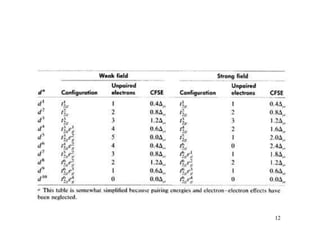
Crystal field theory (CFT) explains the splitting of d-orbital energies when a metal ion is placed in a ligand field. For an octahedral complex, the d-orbitals split into a lower-energy t2g set and a higher-energy eg set. The extent of this splitting, known as the crystal field splitting energy (CFSE), depends on factors like the nature of ligands. CFT can be used to understand properties like ionic radii variations, hydration enthalpies, and ligand field strengths. Tetrahedral complexes have a smaller CFSE than octahedral complexes.

![Illustration of CFSE
[Ti(H2O)6]3+ : a d1 complex and the e occupies the lowest energy
orbital, i.e. one of the three degenerate t2g orbitals. The purple
colour is a result of the absorption of light which results in the
promotion of this t2g electron into the eg level. t2g eg –> t2g eg
1 0 0 1
The UV-Vis absorption
spectrum reveals that this
transition occurs with a
maximum at 20300 cm-1 which
corresponds to o 243 kJ/mol.
(1000 cm-1 = 11.96 kJ/mol or
2.86 kcal/mol or
0.124 eV.)
6
Typical 0 values are of the same order of magnitude as the energy of a chemical bond.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cft1-230717135038-764886c3/85/CFT-1-pptx-11-320.jpg)

![9
CFSE vs Pairing Energy
Complex Config.
d6
d6
[Fe(OH2)6]2+
[Fe(CN)6]4
[CoF6]3-
[Co(NH3)6]3-
d7
d7
o, cm 1 P, cm1 spin-state
10,400 17,600 high-spin
32,850 17,600 low-spin
13,000 21,000 high-spin
23,000 21,000 low-spin](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cft1-230717135038-764886c3/85/CFT-1-pptx-14-320.jpg)
![11
[CrCl6]3- 13640 cm-1 163 kJ/mol
[Cr(H2O)6]3+ 17830 213
[Cr(NH3)6]3+ 21680 314
[Cr(CN)6]3- 26280 314
[Co(NH3)6]3+
[Rh(NH3)6]3+
[Ir(NH3)6]3+
24800 cm-1
34000
41000
163 kJ/mol
213
314](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cft1-230717135038-764886c3/85/CFT-1-pptx-15-320.jpg)
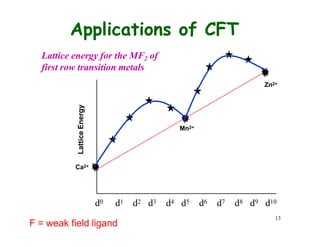
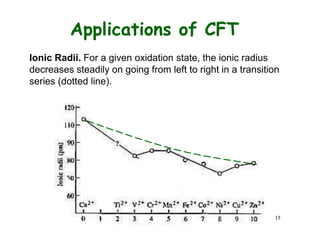
![14
Applications of CFT
Hydration Enthalpy. Let
us look at the variation of
enthalpy of M2+ ions
M2+(g) + 6 H2O(l) =
[M(O2H)6]2+(aq)
Ca2+, Mn2+, and Zn2+ have
do, d5, and d10, hence
CFSE is 0. Other metal
ions deviate from the
expected line due to extra
CFSE
H2O = weak field ligand](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cft1-230717135038-764886c3/85/CFT-1-pptx-18-320.jpg)