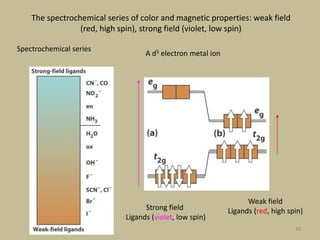
This document discusses crystal field theory (CFT), which interprets the chemistry of coordination compounds. Some key points:
1. CFT was proposed by Hans Bethe in 1929 and modified by J.H. Van Vleck in 1935 to allow for some covalency. It assumes electrostatic interactions between metal ions and ligands.
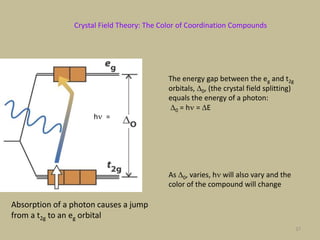
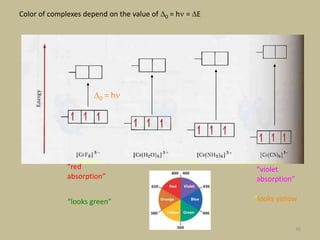
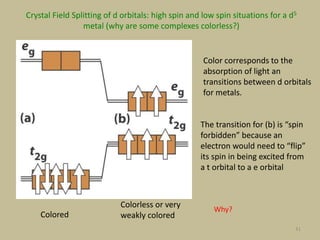
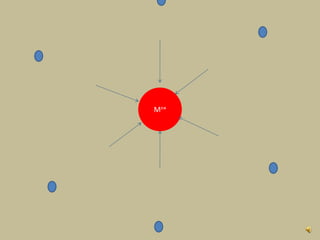
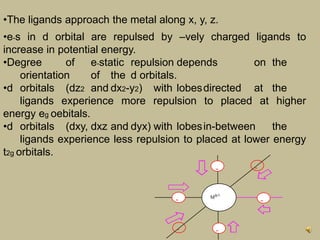
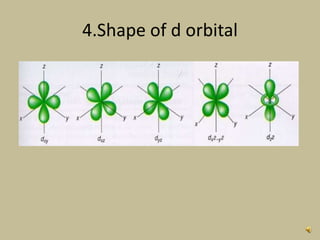
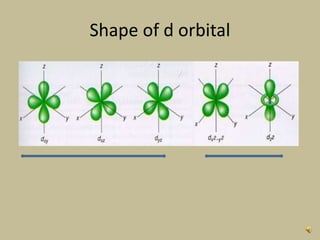
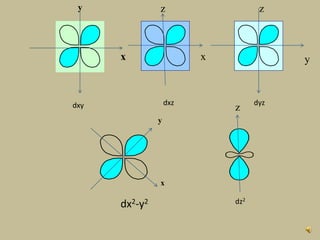
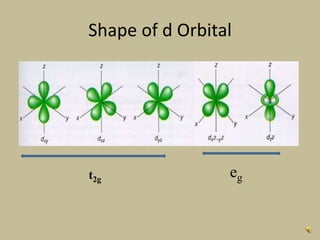
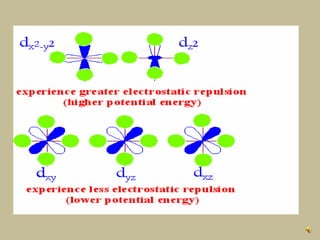
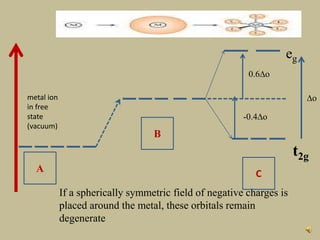
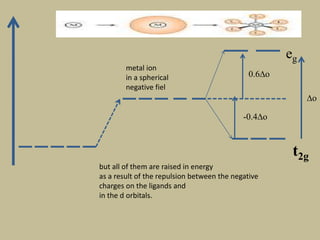
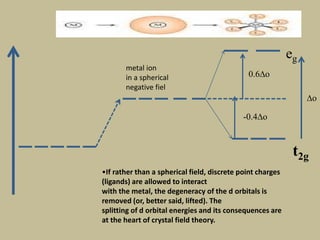
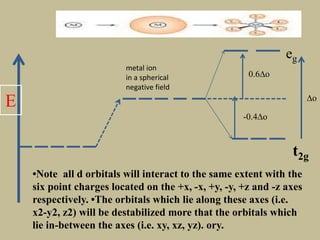
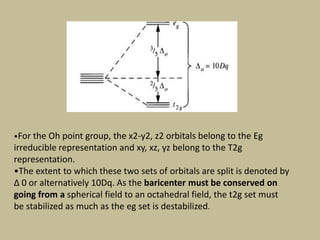
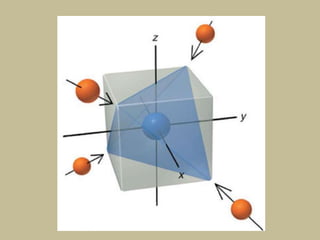
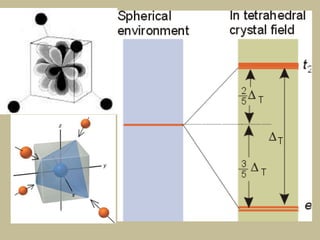
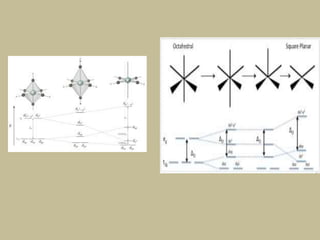
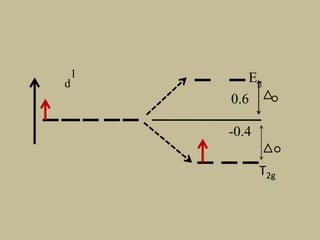
2. In an octahedral crystal field, the d-orbitals split into two sets - the lower energy t2g orbitals and higher energy eg orbitals. The splitting is called the crystal field splitting parameter Δo.
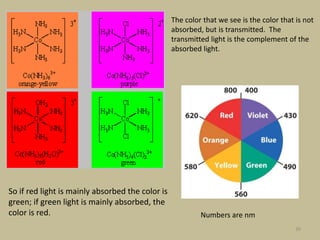
3. The color of coordination compounds depends on the size of this splitting, as the energy difference corresponds to the absorption of photons.





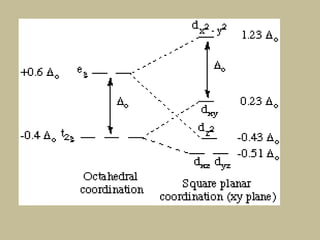
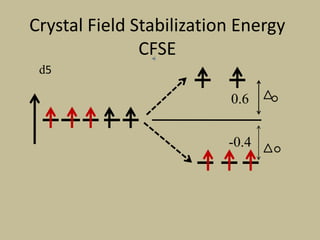
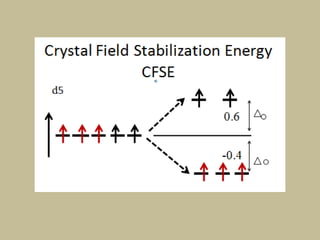
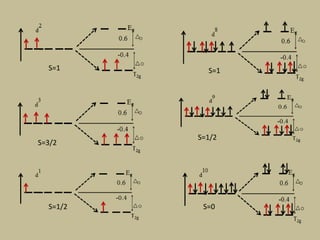
![CFSE = [(0.6 x number of eg electrons)
- (0.4 x number of t2g electrons)]Δ
CFSE = [(0.6 x 0)
- (0.4 x 5)]Δo
=-2 Δo
CFSE = [(0.6 x 2)
- (0.4 x 3)]Δo
= 0Δo](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/crystalfieldtheory-200821073940/85/Crystal-field-theory-31-320.jpg)

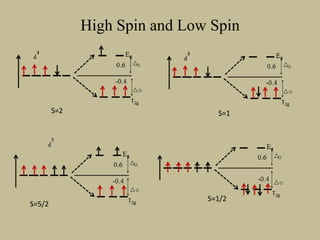
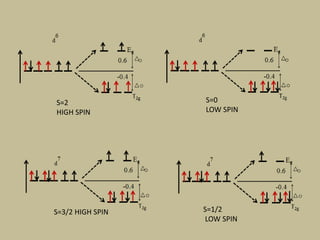
![33
Large splitting
Low spin
Small splitting
High spin
Energy gap larger than
advantage due to Hund’s rule
Energy gap small; Hund’s rule
applies
How many unpaired spins in Fe(CN)6
4- and in Fe(H2O)6
2+?
What is the charge of Fe in Fe(CN)6
4- and in Fe(H2O)6
2+?
Fe2+ in both cases Fe = [Ar]3d64s2; Fe2+ = [Ar]3d6
What kind of ligands are CN- and
H2O?
CN- is a strong field ligand and H2O
is a weak field ligand](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/crystalfieldtheory-200821073940/85/Crystal-field-theory-33-320.jpg)