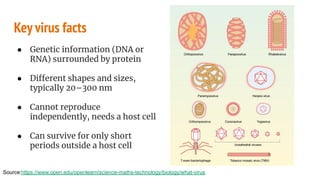
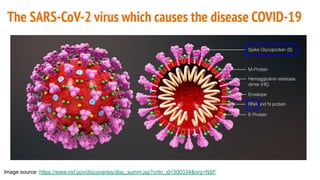
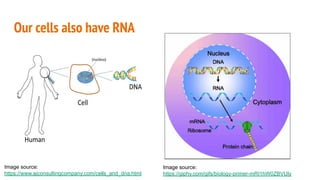
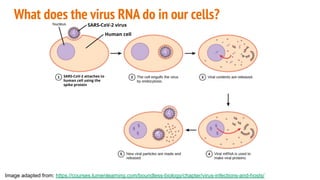
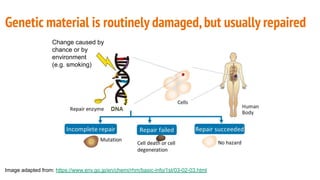
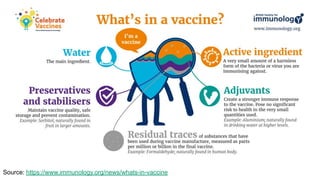
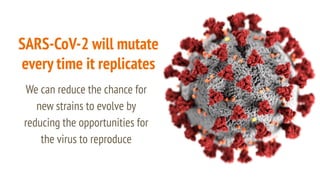
The document discusses COVID-19 variants and vaccines, highlighting key facts about viruses, particularly focusing on the SARS-CoV-2 virus and its evolution through mutations. It details how vaccines operate, their efficacy against different strains, and emphasizes the need for continued research and accurate information sources regarding COVID-19. It concludes by noting that SARS-CoV-2 will mutate regularly, and reducing virus reproduction opportunities can help mitigate the emergence of new variants.