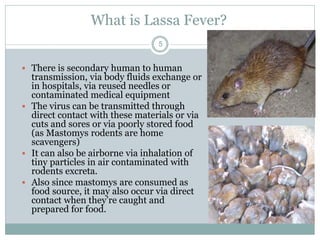
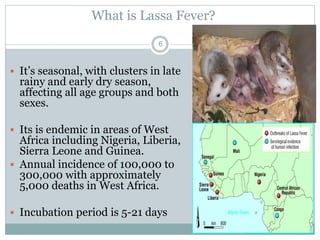
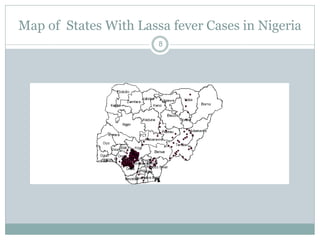
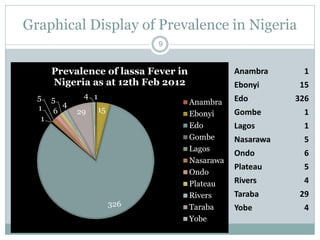
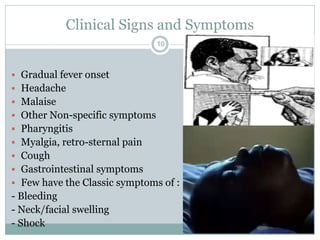
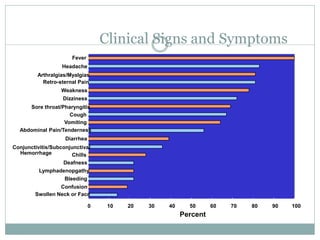
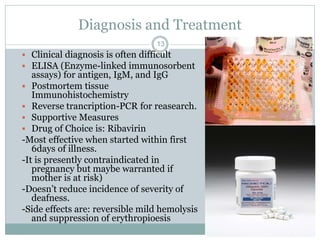
Lassa fever is a viral hemorrhagic fever caused by the Lassa virus and transmitted by rodents. It is endemic in West Africa, with an estimated 100,000-300,000 cases and 5,000 deaths annually. There is currently an outbreak in Nigeria affecting 12 states and 397 cases, resulting in 40 deaths so far. Clinical signs include gradual fever, headache, bleeding, and neck swelling. Diagnosis involves ELISA and PCR tests, and treatment is supportive care and the antiviral drug ribavirin. Preventing transmission involves avoiding contact with infected rodents and person-to-person spread through medical settings.