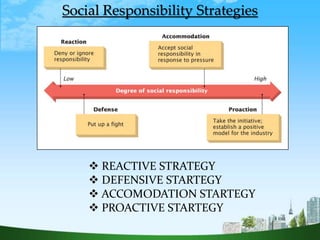
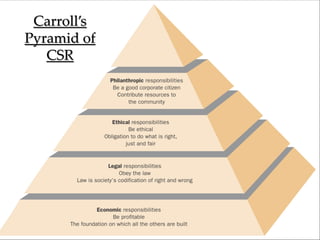
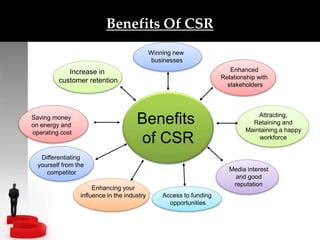
The document discusses Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR), defining it as a concept where organizations take responsibility for their societal and environmental impacts beyond legal obligations. It covers the history, types, and benefits of CSR, as well as its evolution in India, illustrating how CSR integrates into sustainable business strategies and emphasizes ethical practices. Ultimately, it concludes that companies must embrace CSR to enhance their reputation and meet rising expectations from society.