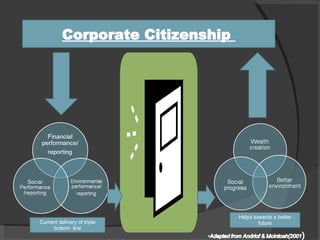
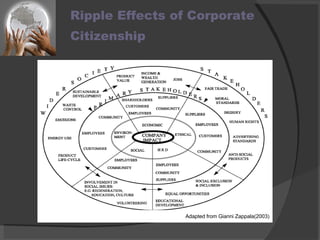
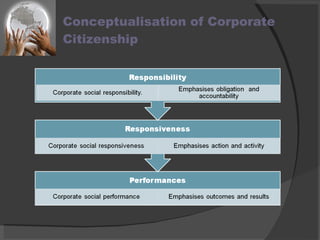
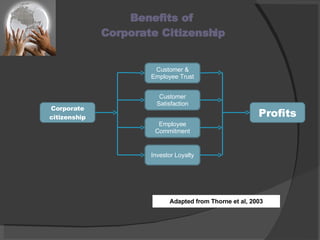
The document discusses the concept of corporate citizenship as an evolution of corporate social responsibility, emphasizing its role in addressing societal expectations and responsibilities within the global economy. It outlines the definitions, historical evolution, benefits, and features of corporate citizenship, highlighting its focus on stakeholder engagement and social impact. The conclusion stresses the importance of corporate citizenship for businesses in creating a sustainable future while fostering trust and accountability in their operational environments.