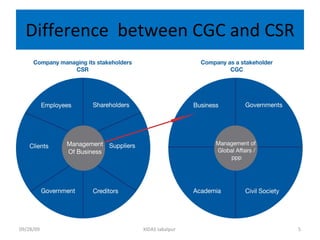
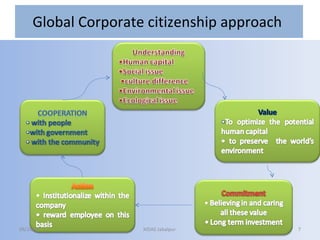
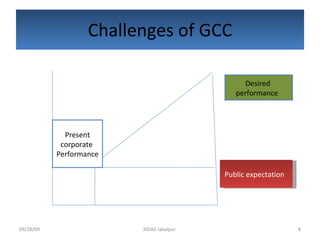
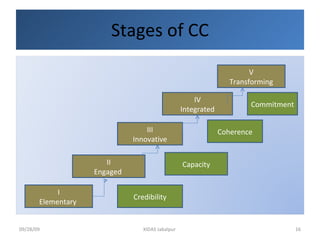
Global corporate citizenship refers to companies acting as stakeholders in society alongside governments and civil society. It involves companies minimizing harm and maximizing benefits to stakeholders while ensuring strong financial results. As global challenges have increased regarding transparency, accountability, and trust, corporate citizenship now requires a strategic, integrated approach endorsed at top levels of companies.