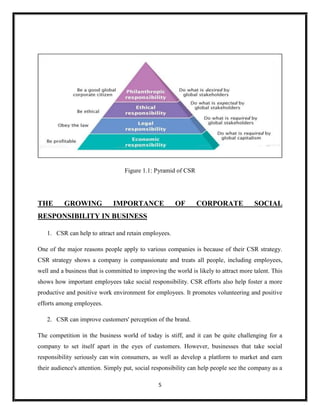
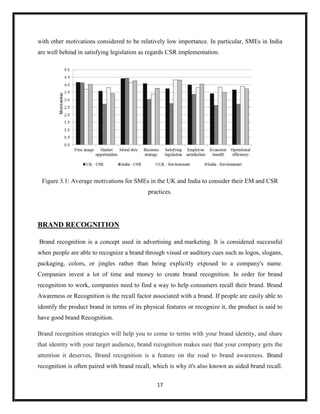
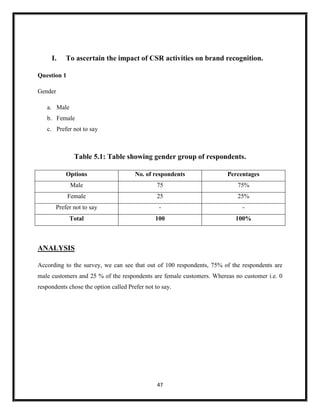
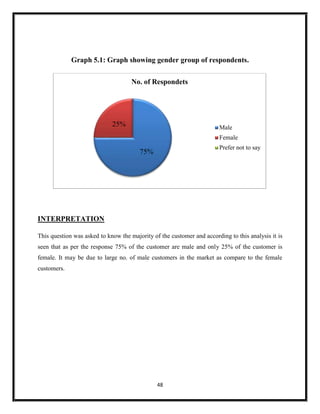
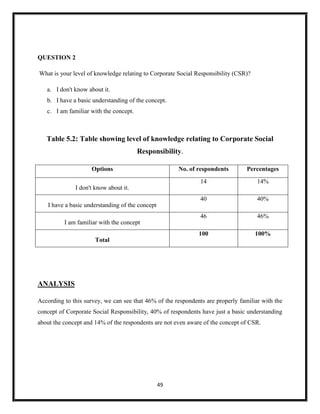
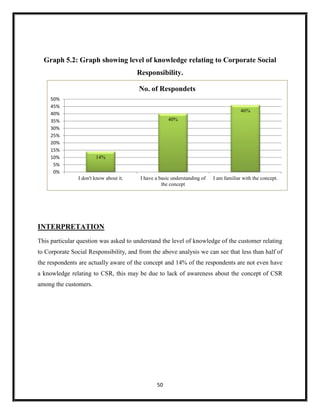
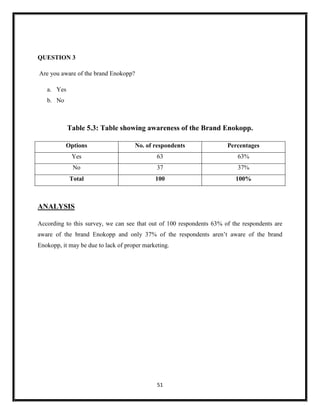
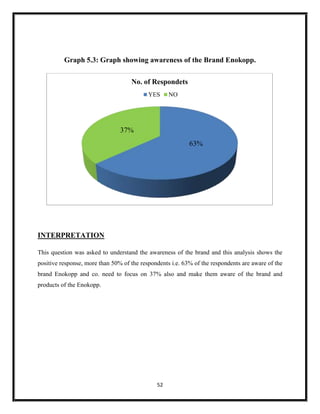
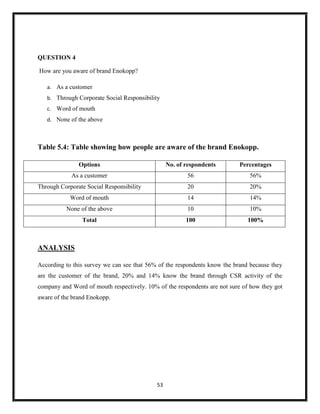
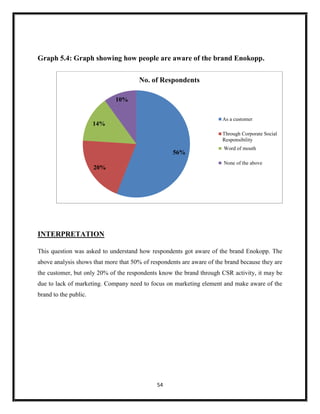
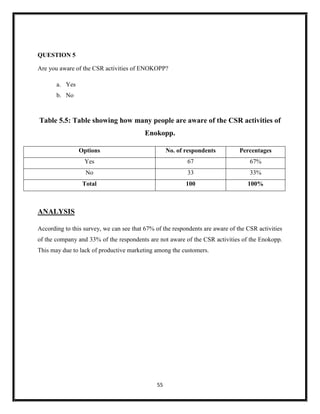
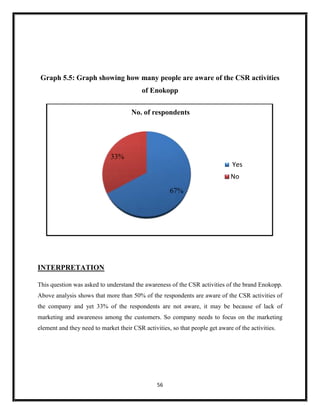
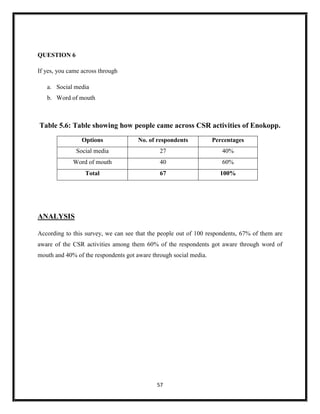
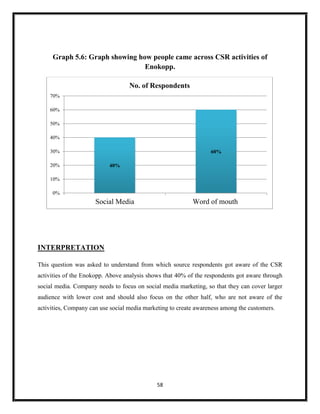
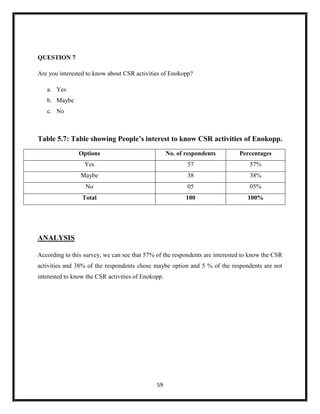
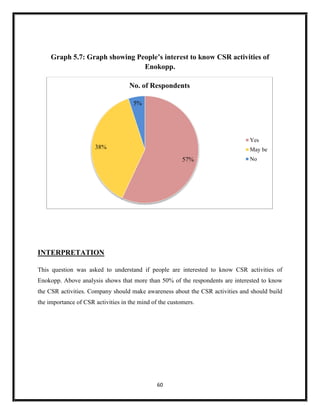
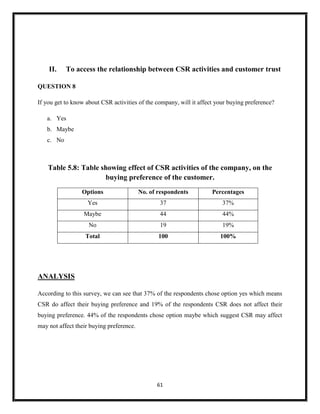
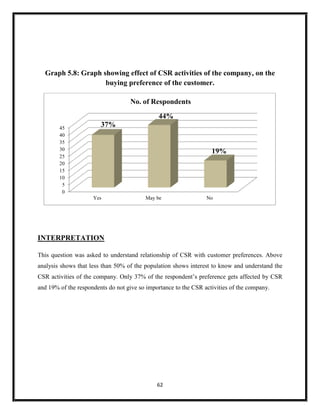
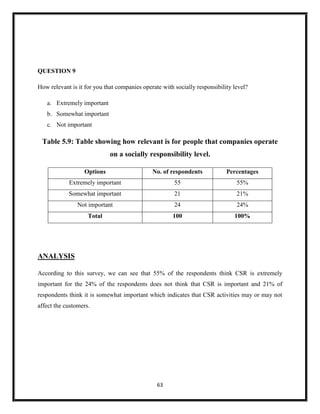
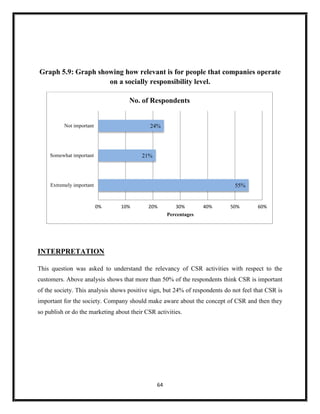
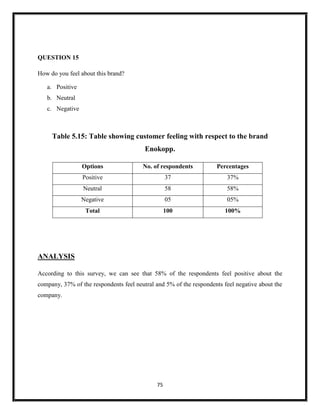
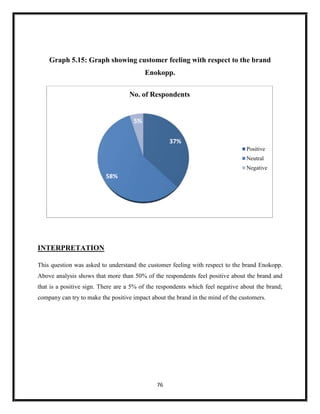
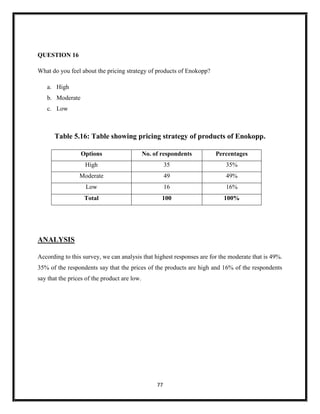
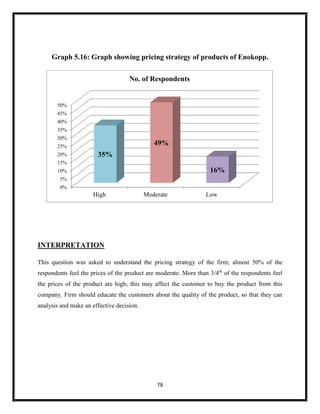
The document summarizes key aspects of corporate social responsibility (CSR) including:
- The meaning and definitions of CSR, how it has evolved from voluntary to mandatory practices.
- The objectives of CSR which include embracing responsibility, maximizing societal impact, and giving back to communities.
- Benefits of CSR for businesses such as increased employee engagement, improved brand perception, and enabling better customer engagement.
- New amendments to CSR rules in India including clarifying eligible CSR activities and treatment of unspent/excess CSR funds which must be transferred to specified funds.