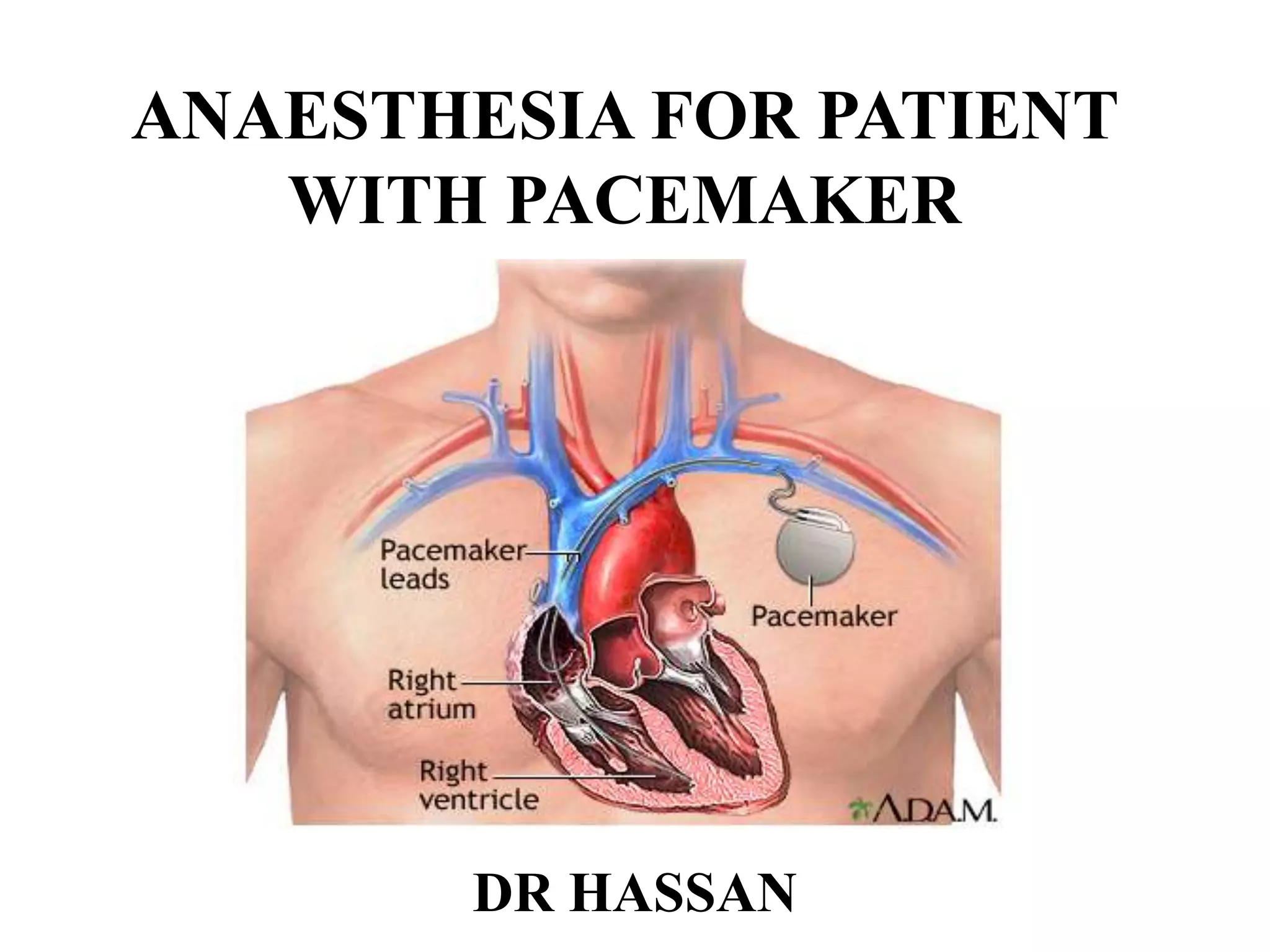
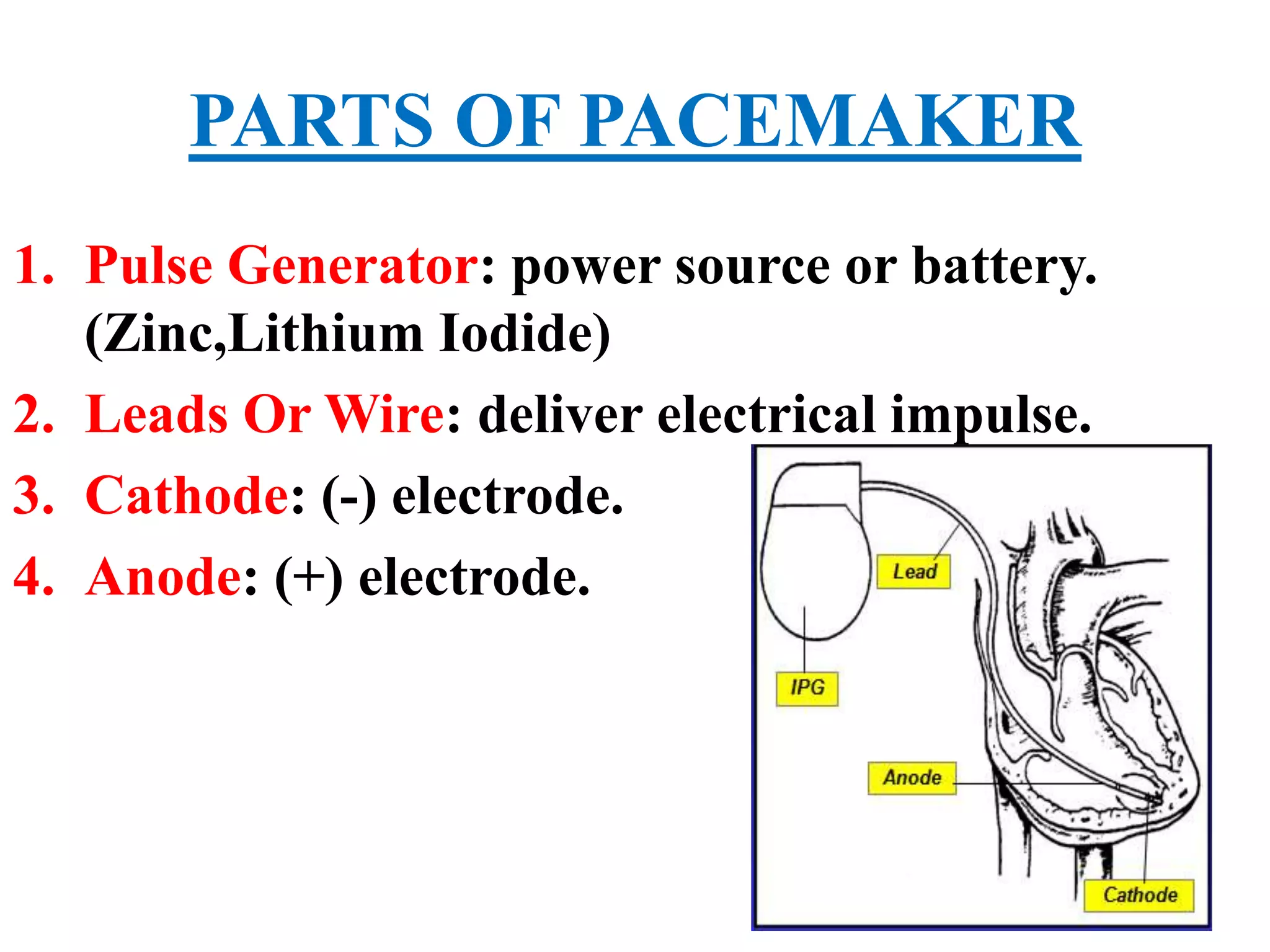
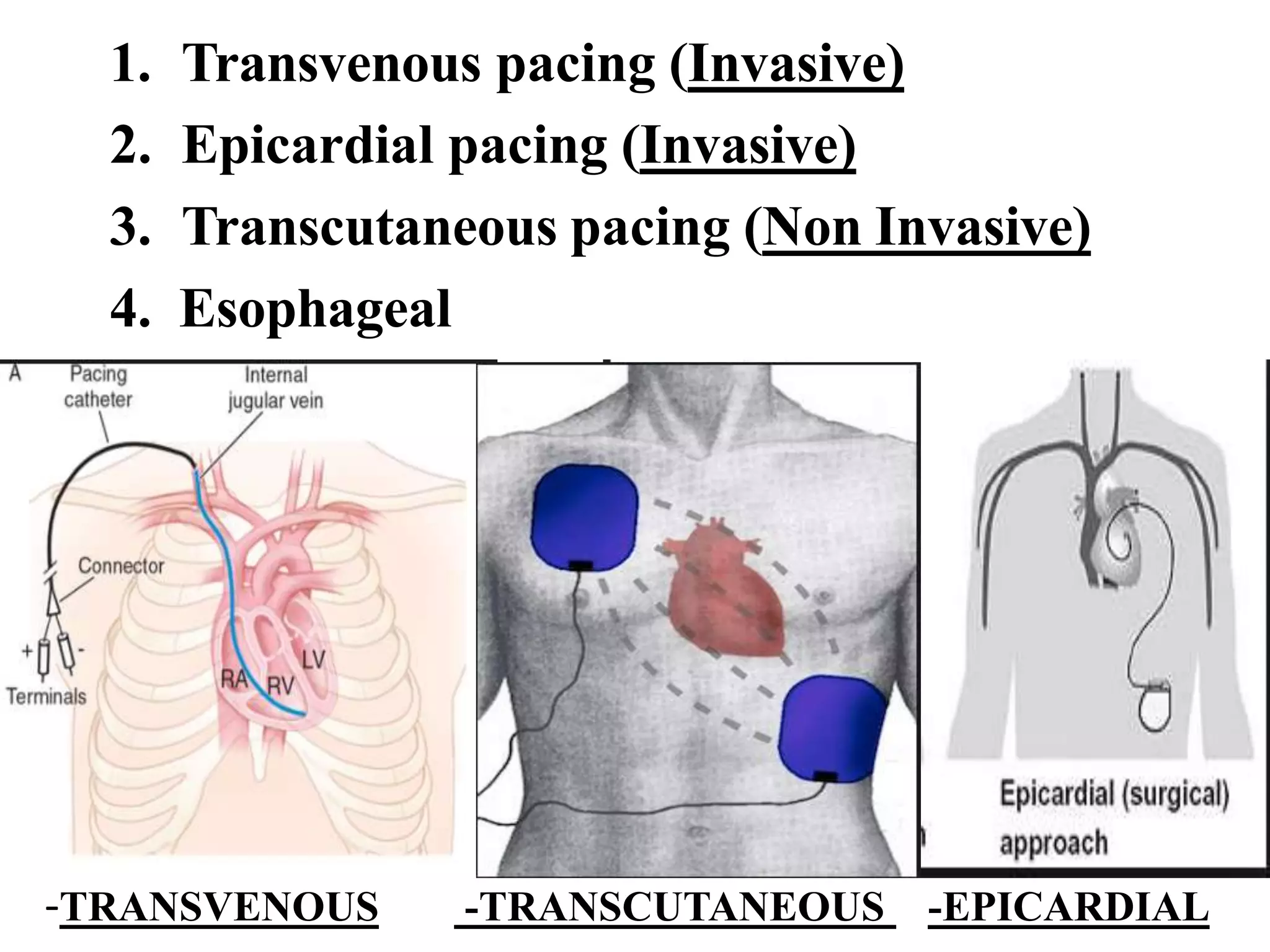
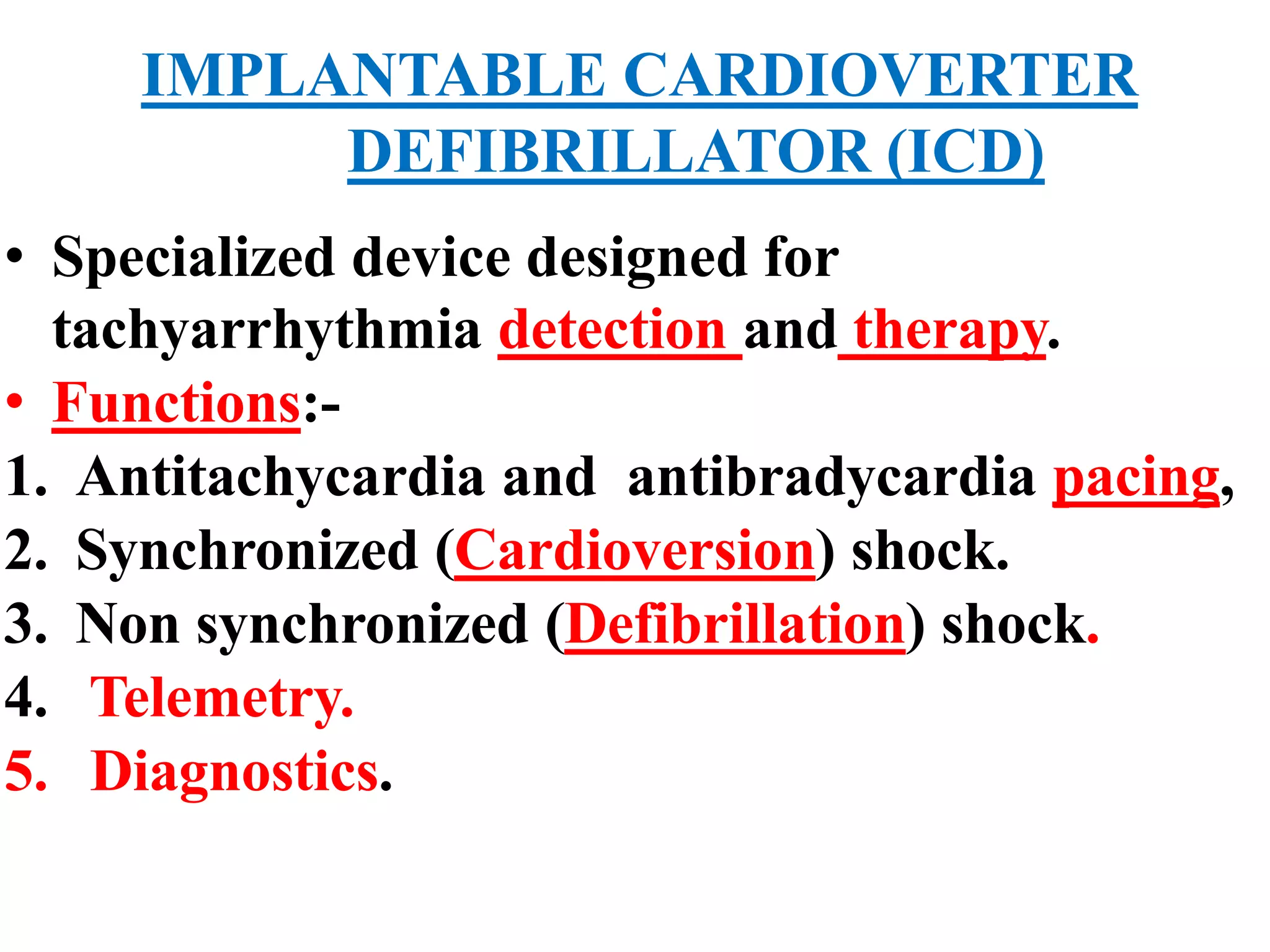
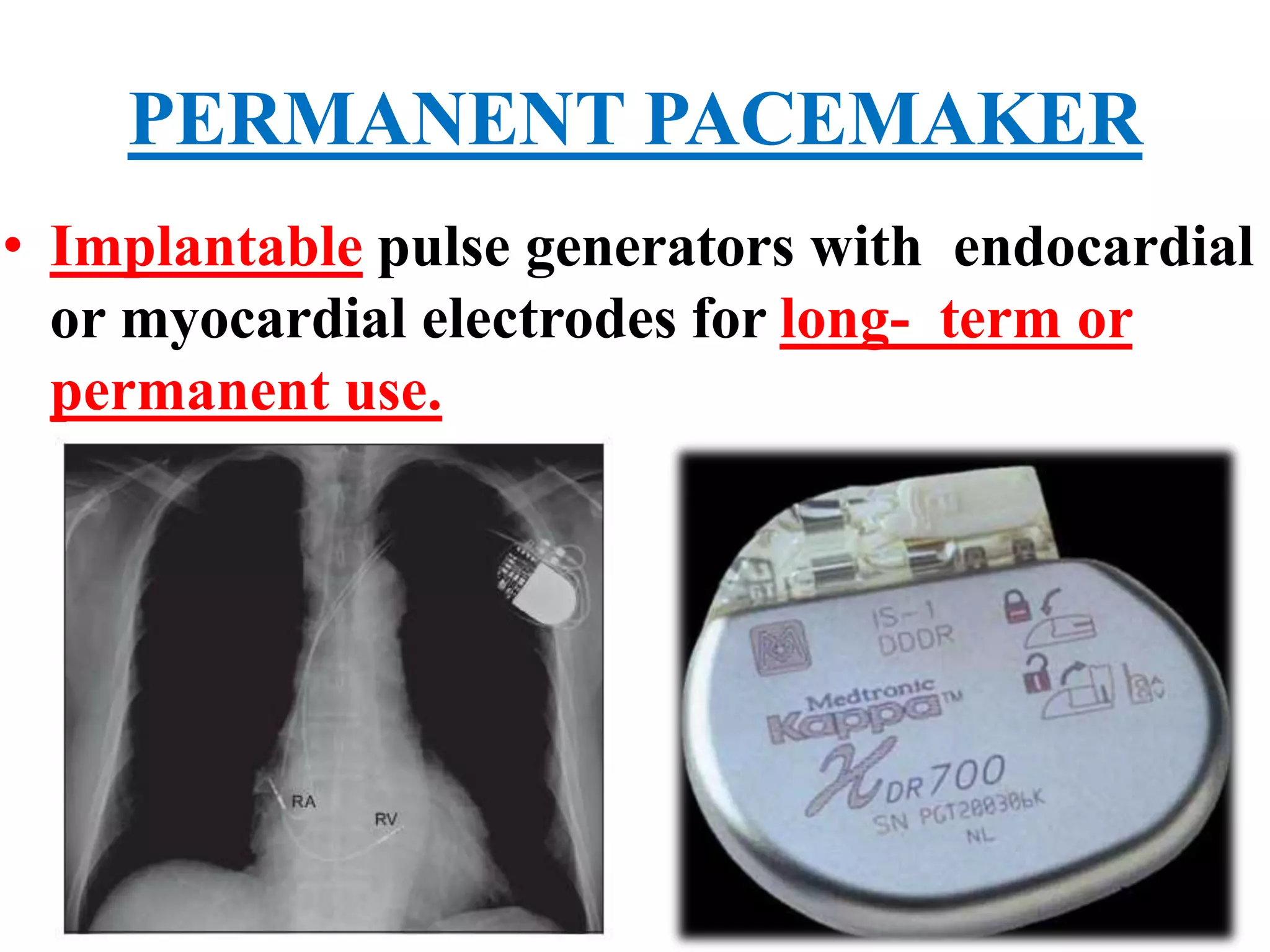
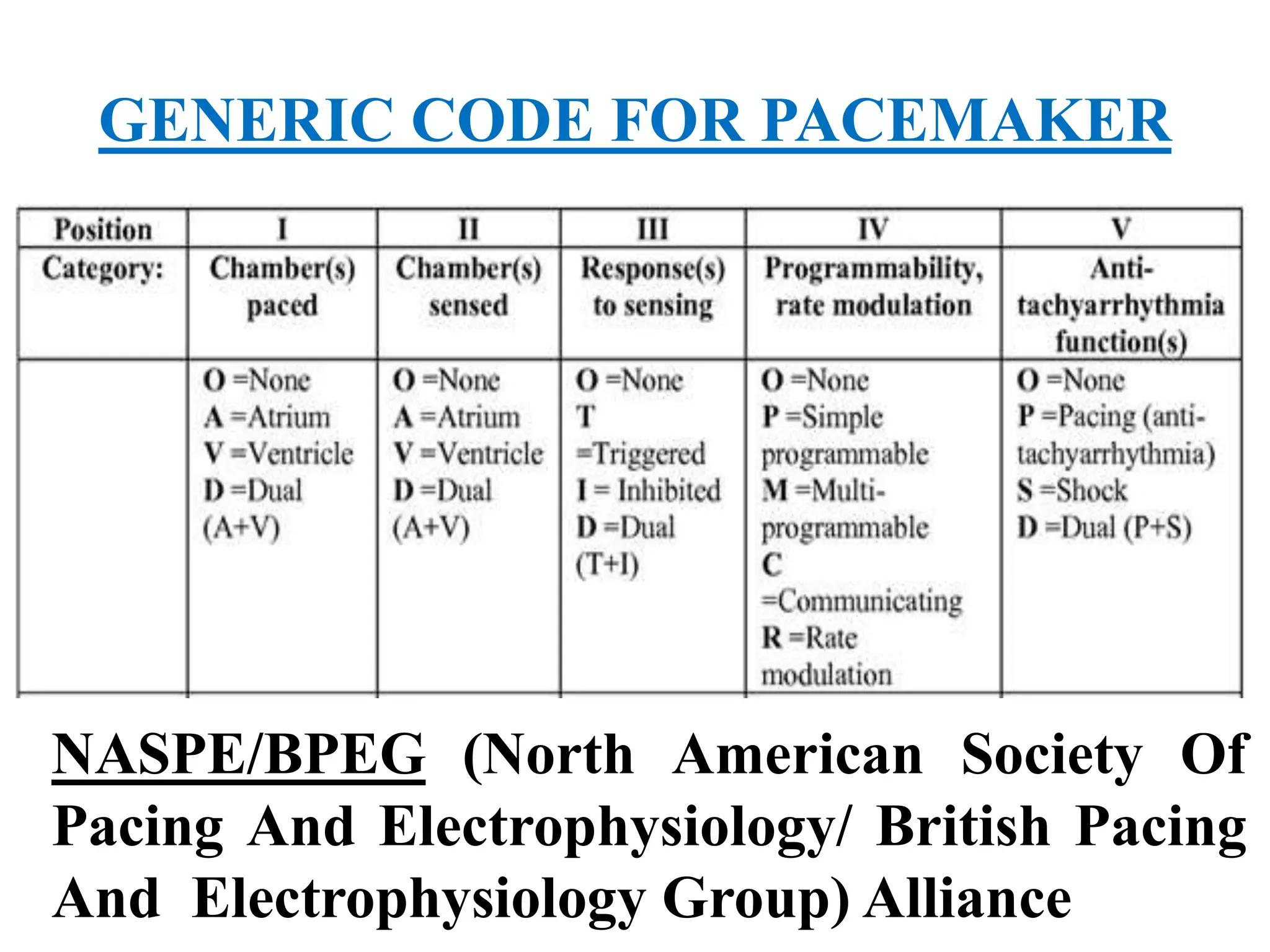
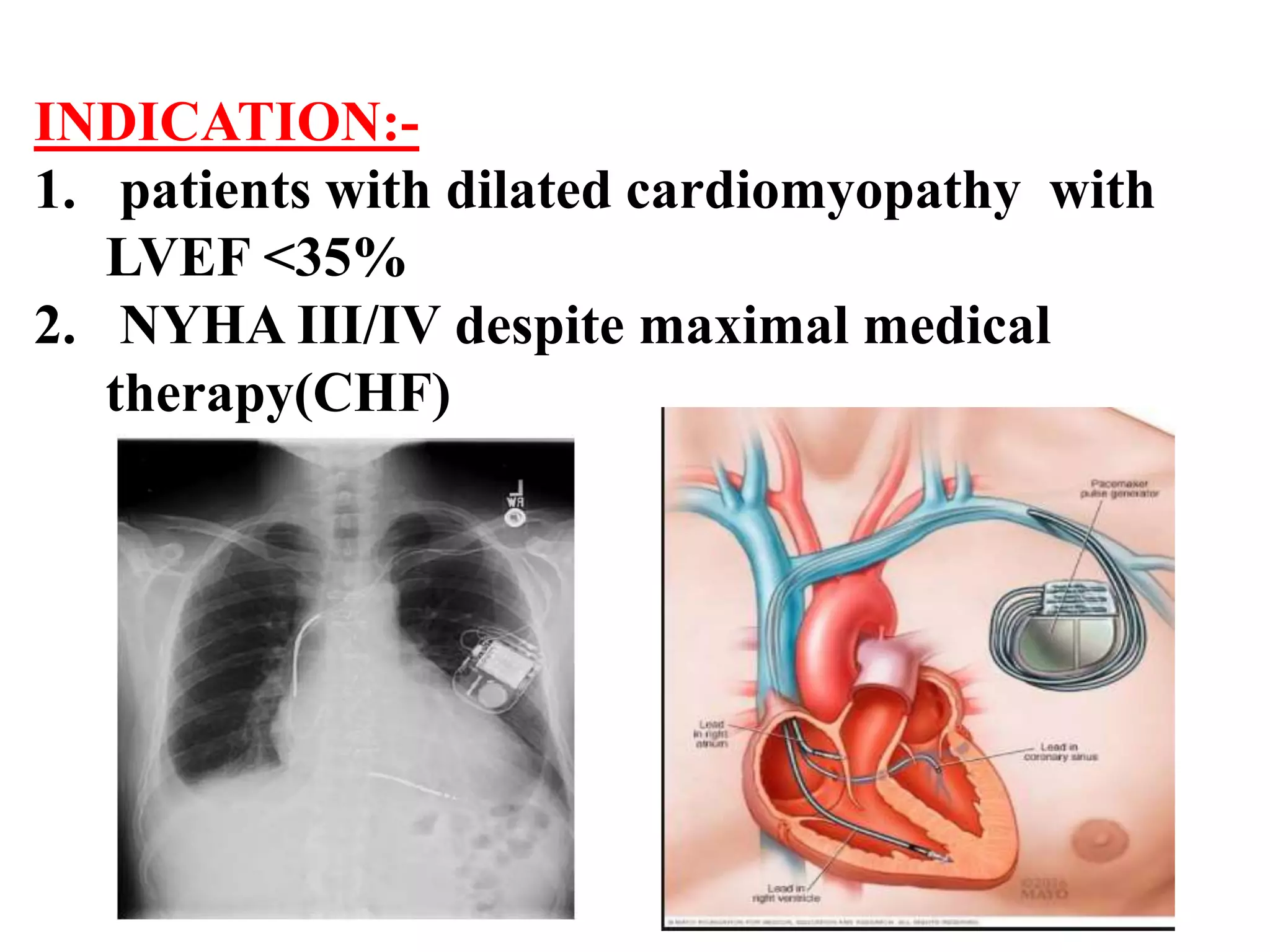
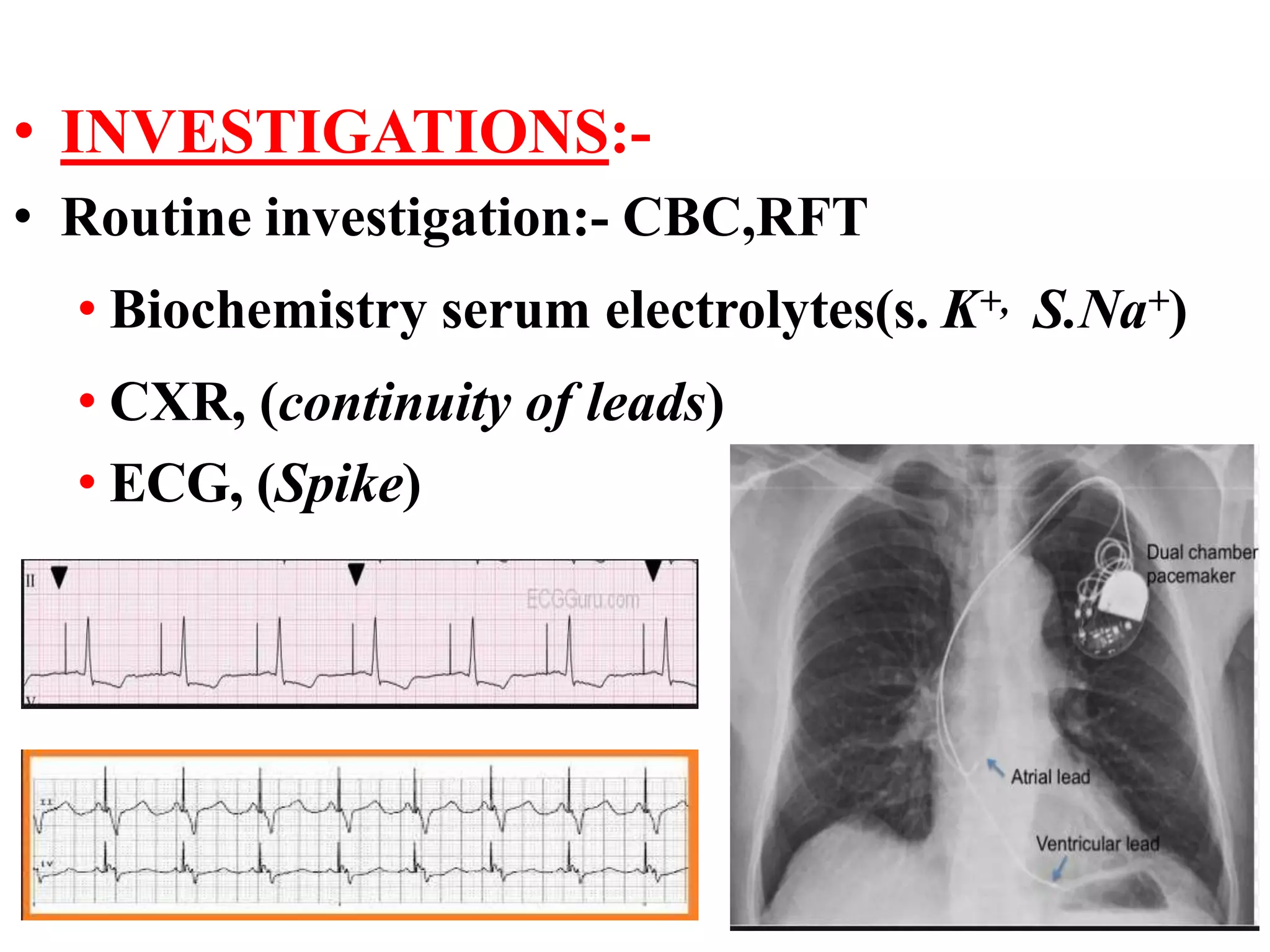
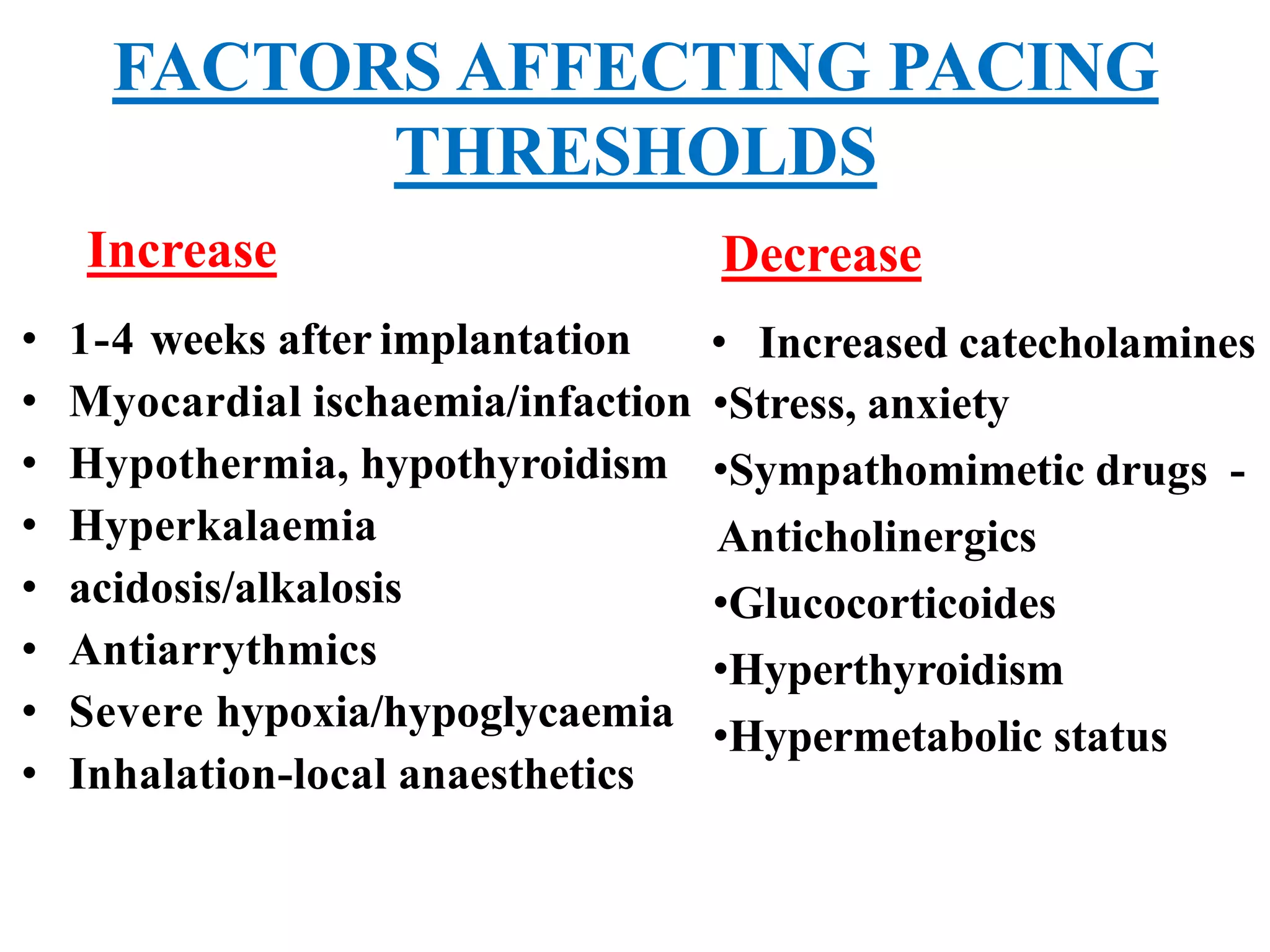
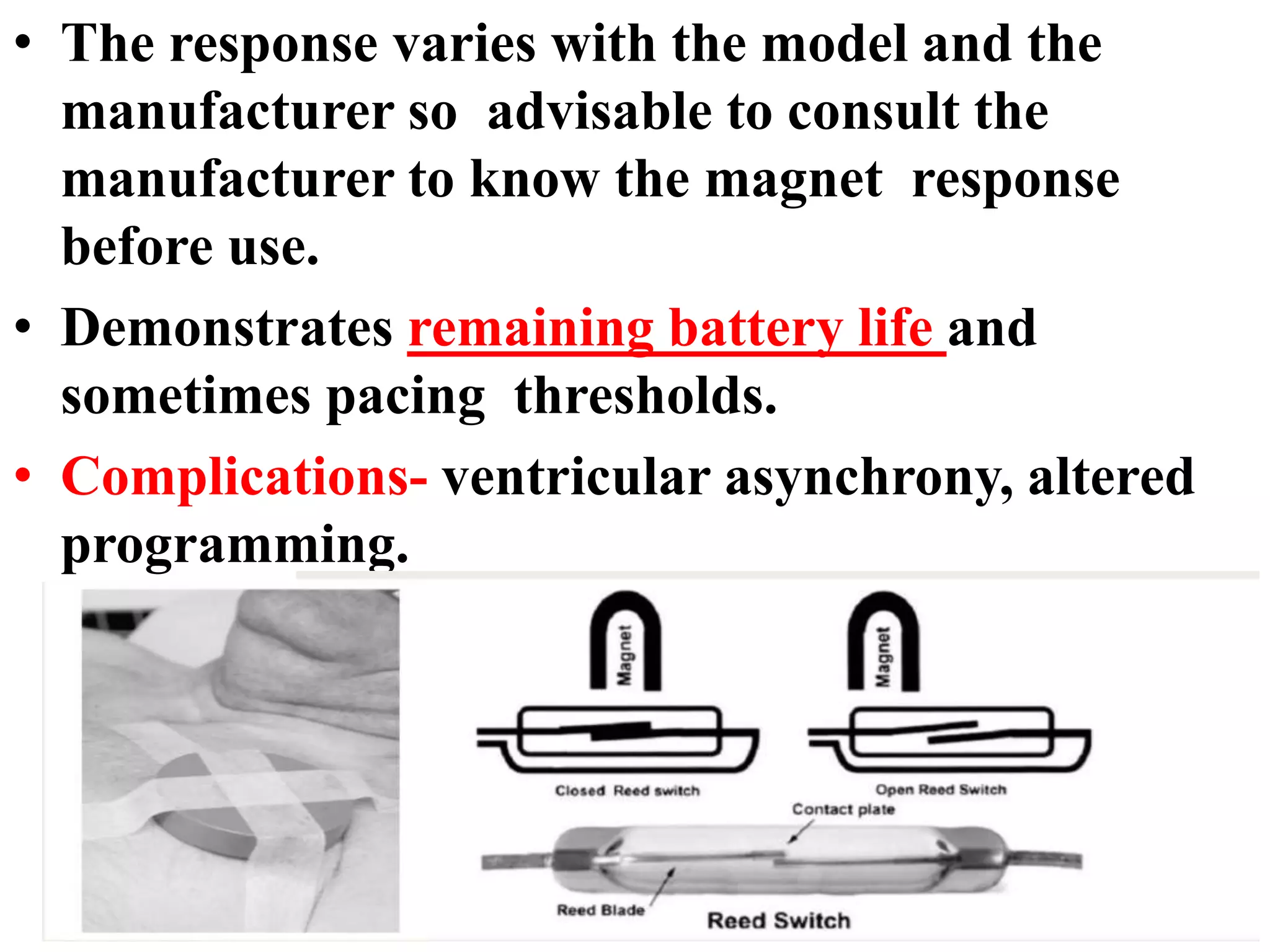
The document discusses the management of patients with pacemakers during anesthesia, outlining the evolution, types, and functions of pacemakers, as well as important preoperative evaluations and anesthetic considerations. It emphasizes the necessity of a multidisciplinary approach to ensure patient safety, particularly regarding pacing and the potential effects of electromagnetic interference during surgical procedures. Monitoring and protocols for managing complications related to pacemakers are also highlighted to prevent adverse outcomes.