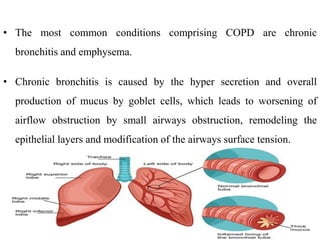
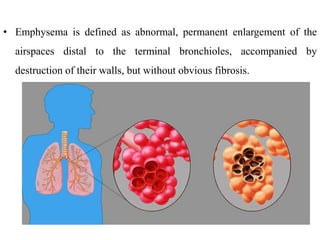
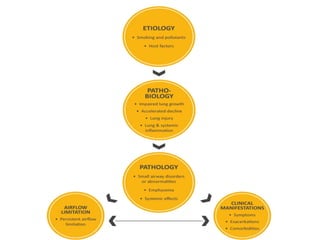
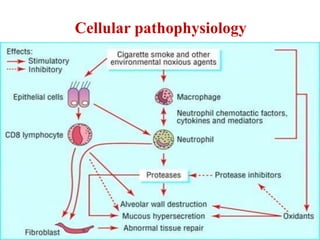
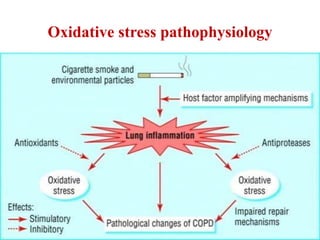
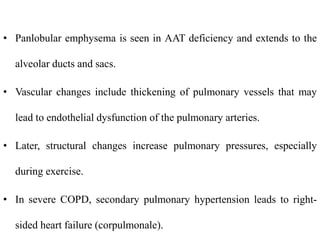
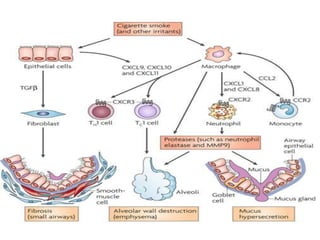
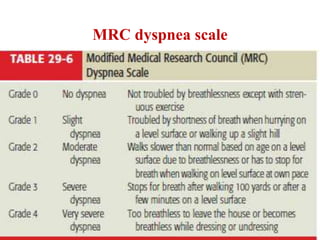
Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) is characterized by irreversible airflow limitation caused by progressive lung inflammation and damage, primarily due to tobacco smoke and environmental factors. It is a leading cause of morbidity and mortality worldwide, with symptoms including chronic cough and dyspnea that can escalate, requiring careful diagnosis and management strategies. Treatment includes smoking cessation, pulmonary rehabilitation, bronchodilators, and corticosteroids, aimed at improving lung function and quality of life.