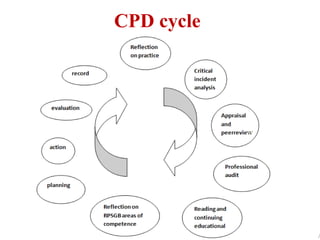
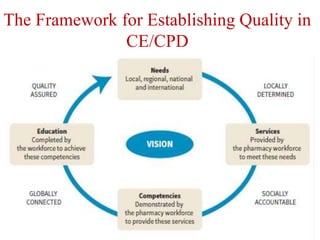
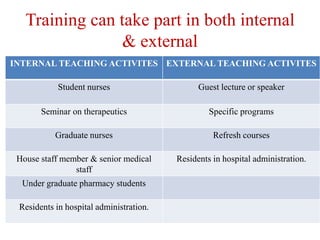
Continuing professional development (CPD) programs help pharmacists maintain competence through lifelong learning. CPD involves a cyclical process of reflection, planning, action, evaluation and recording. It aims to identify and meet individual learning needs. As pharmacy practice evolves, CPD is necessary to keep knowledge and skills updated. The key principles are that CPD is ongoing, self-directed, and covers the entire scope of a pharmacist's practice. Barriers to CPD include lack of time, resources, and motivation. Continuing education provides structured learning activities but CPD emphasizes a self-directed approach to lifelong learning.