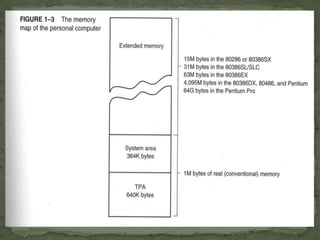
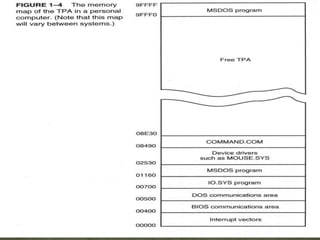
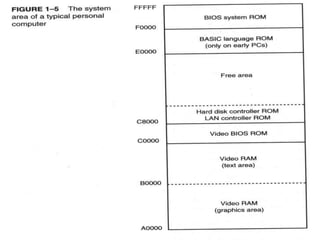
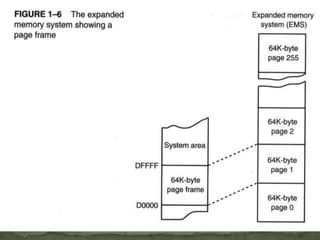
The memory system is divided into three main parts: TPA, system area, and XMS. The first 1MB of memory is called real or conventional memory. It is divided into TPA (640KB) and system area (384KB). TPA holds the operating system, active programs, and inactive programs. The system area is smaller and contains programs like video control programs in ROM/flash. Memory above 1MB is available for use by expanded memory systems.