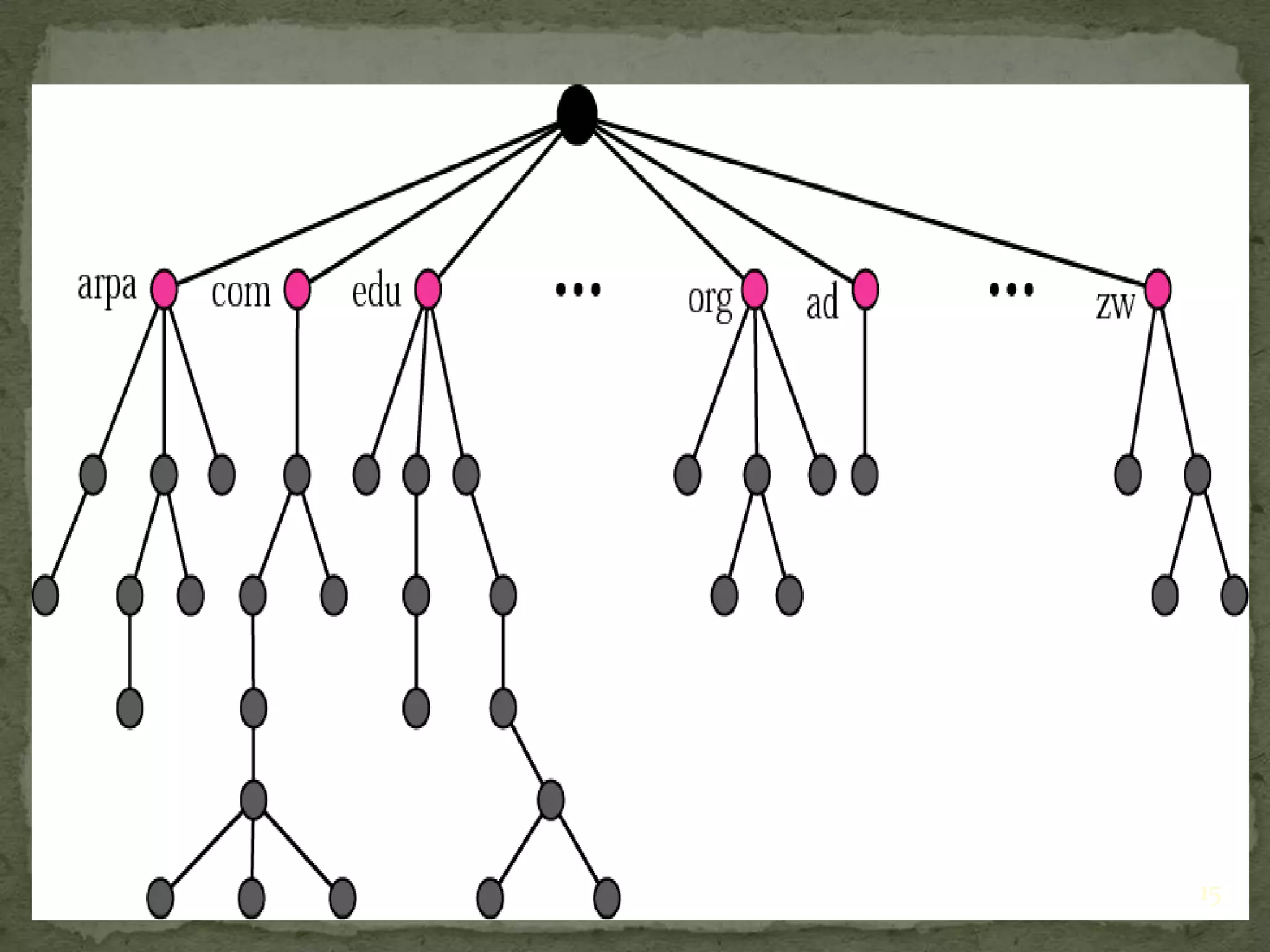
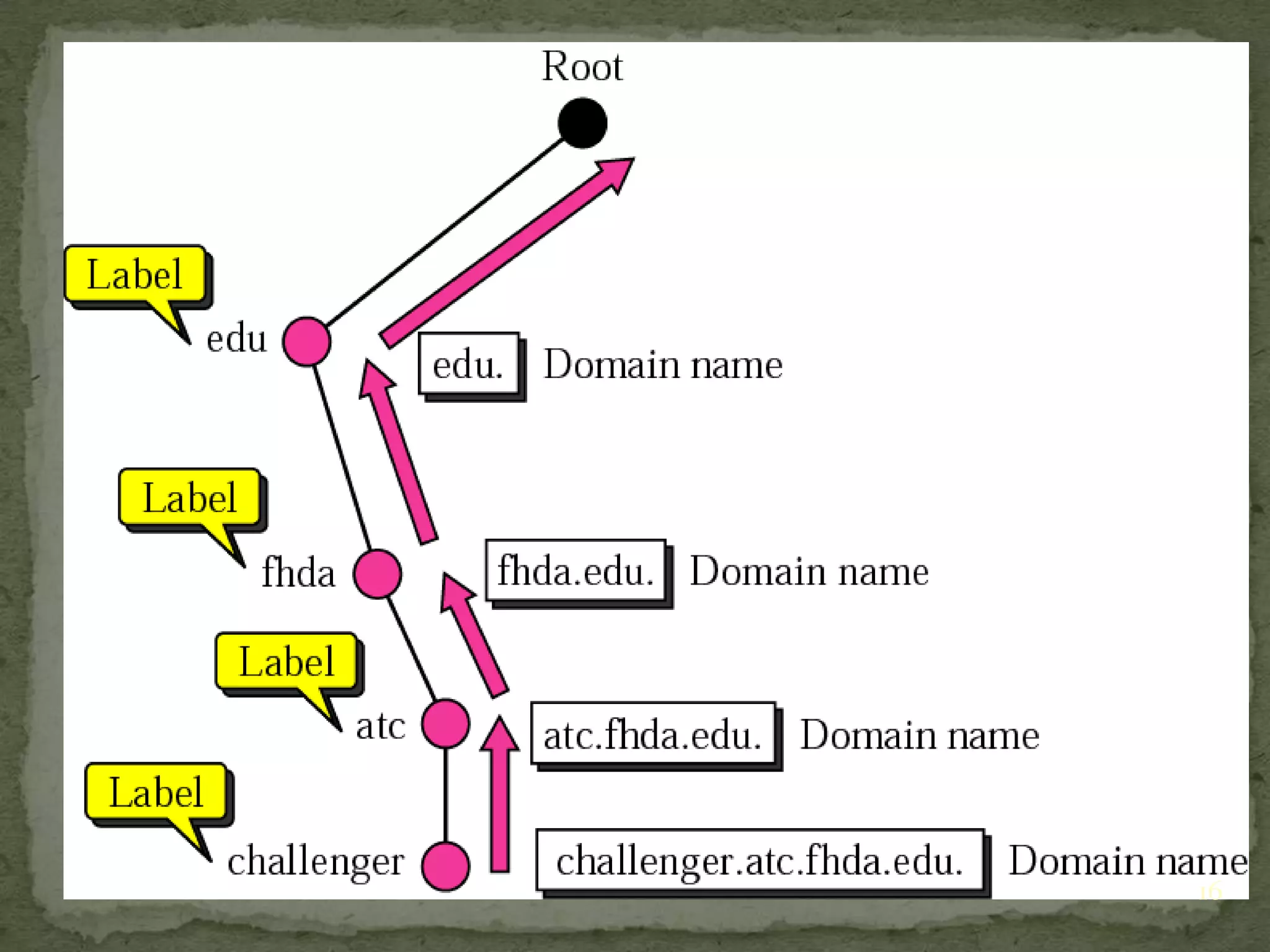
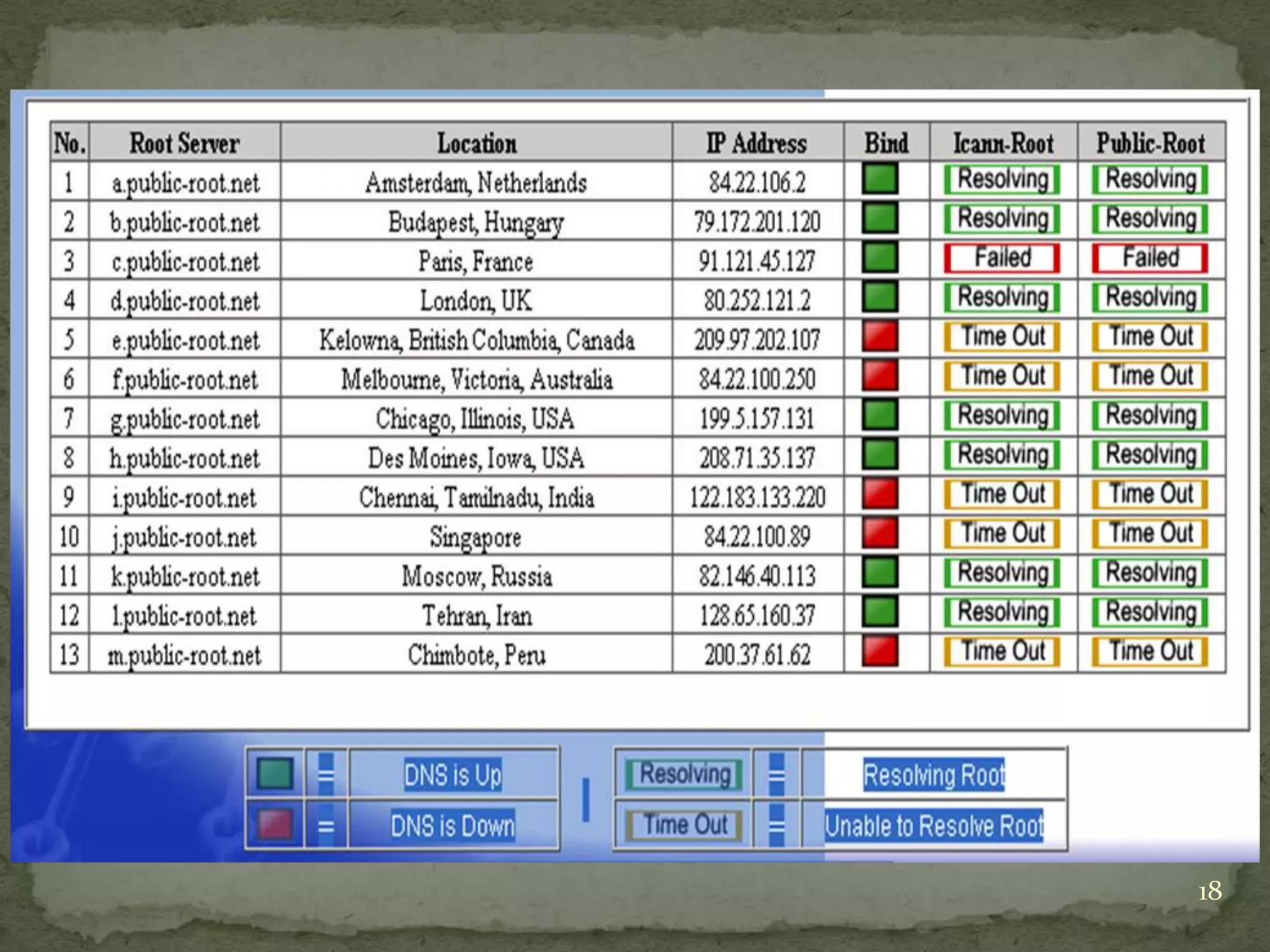
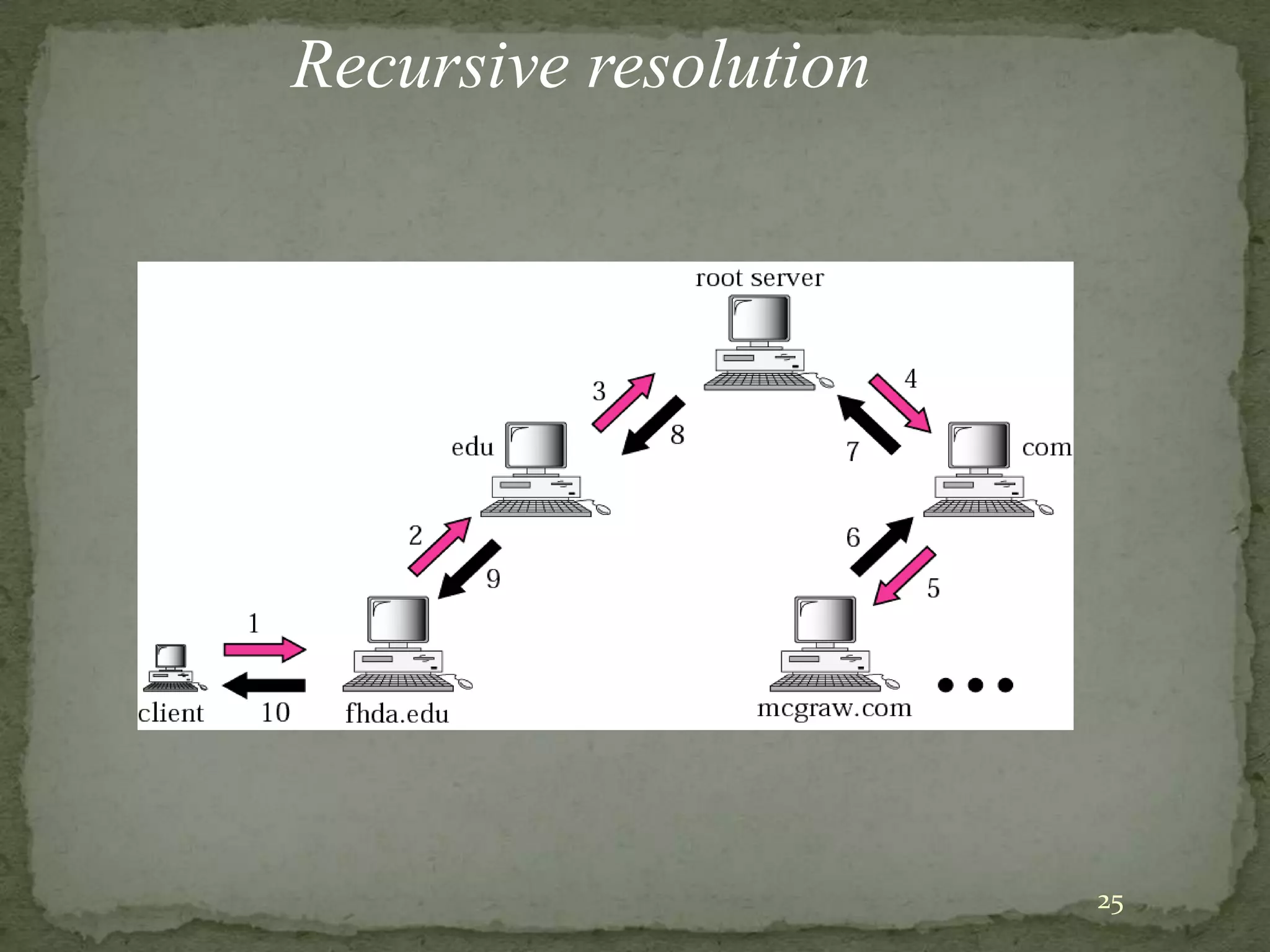
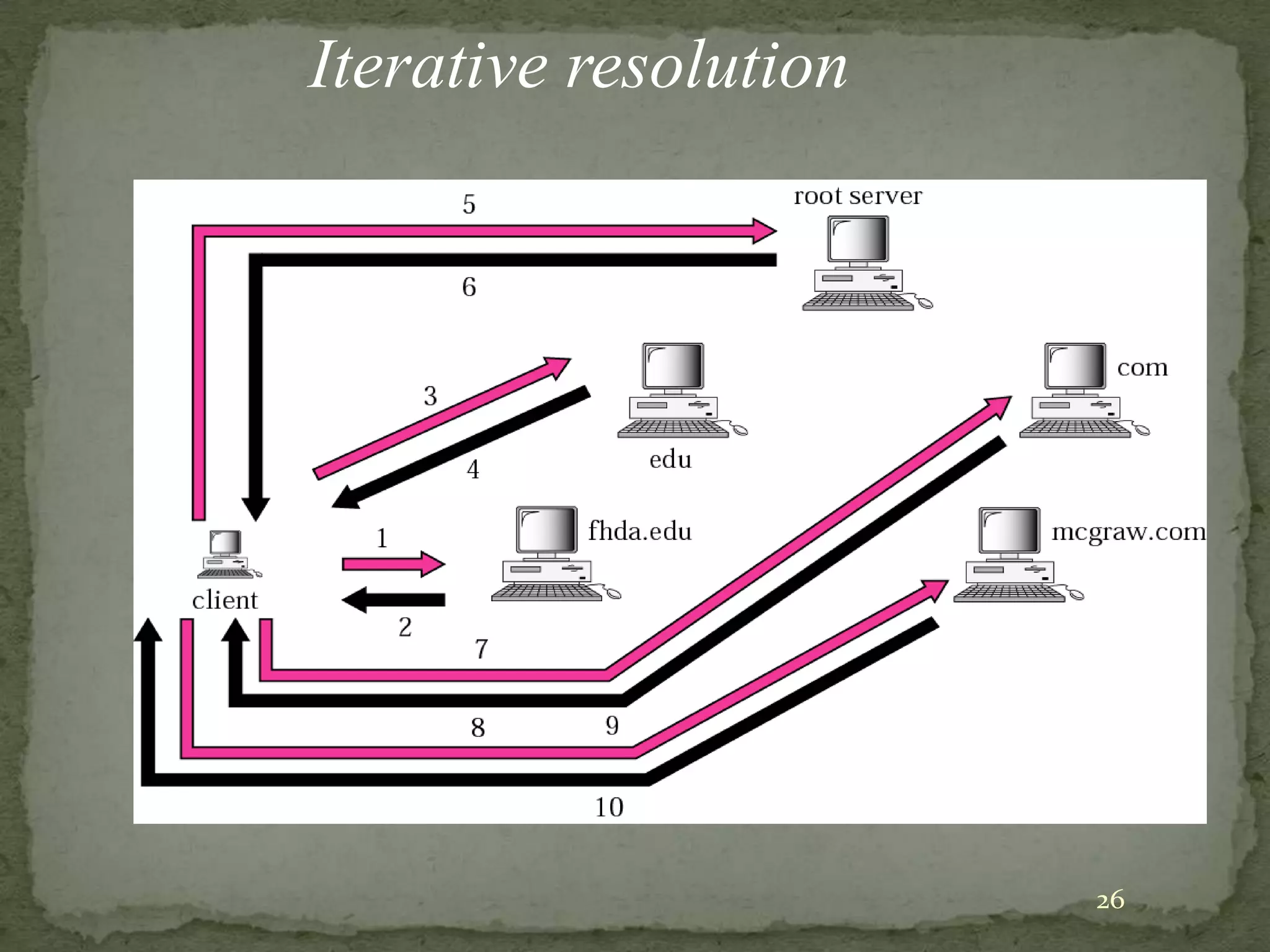
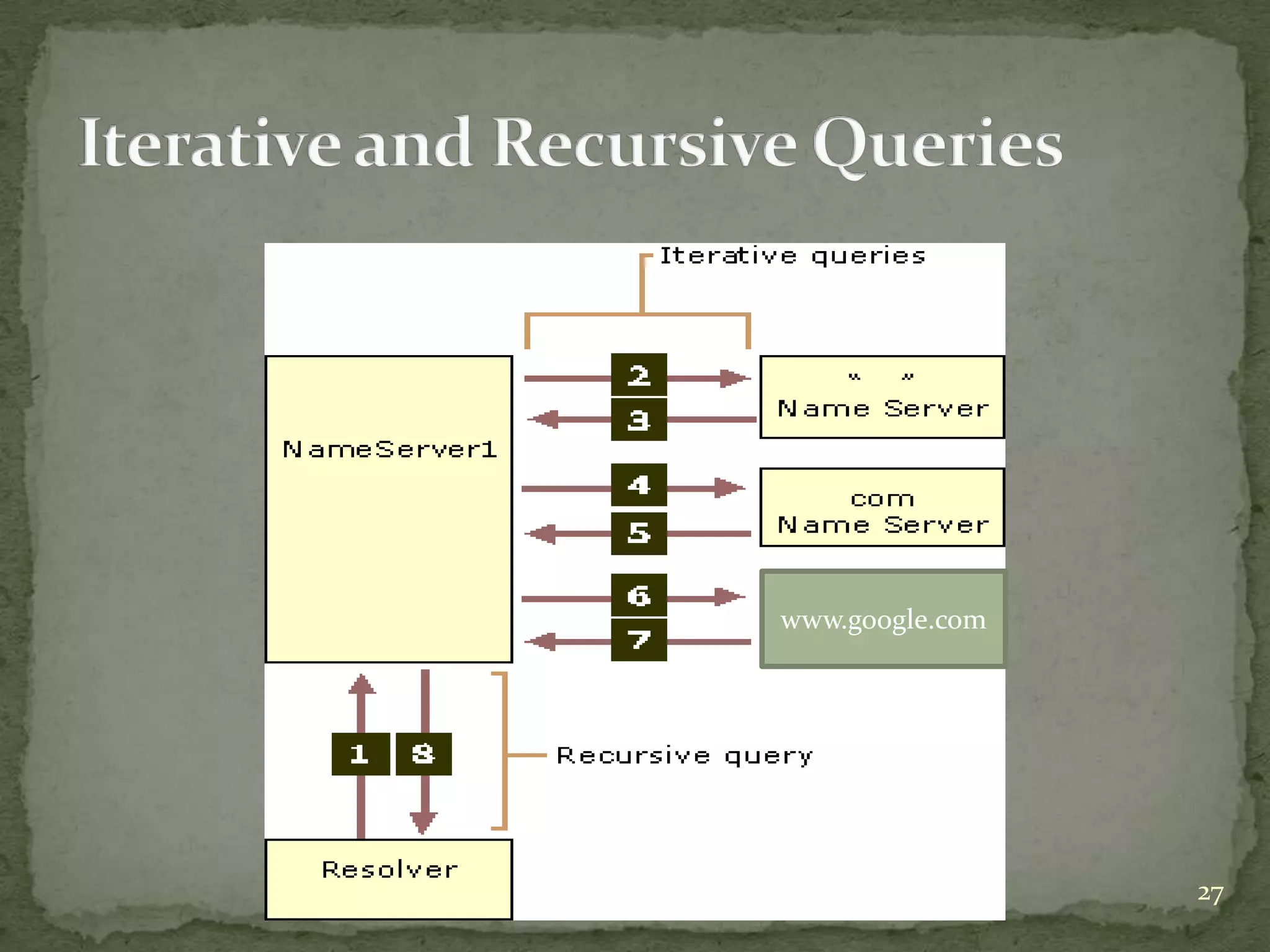
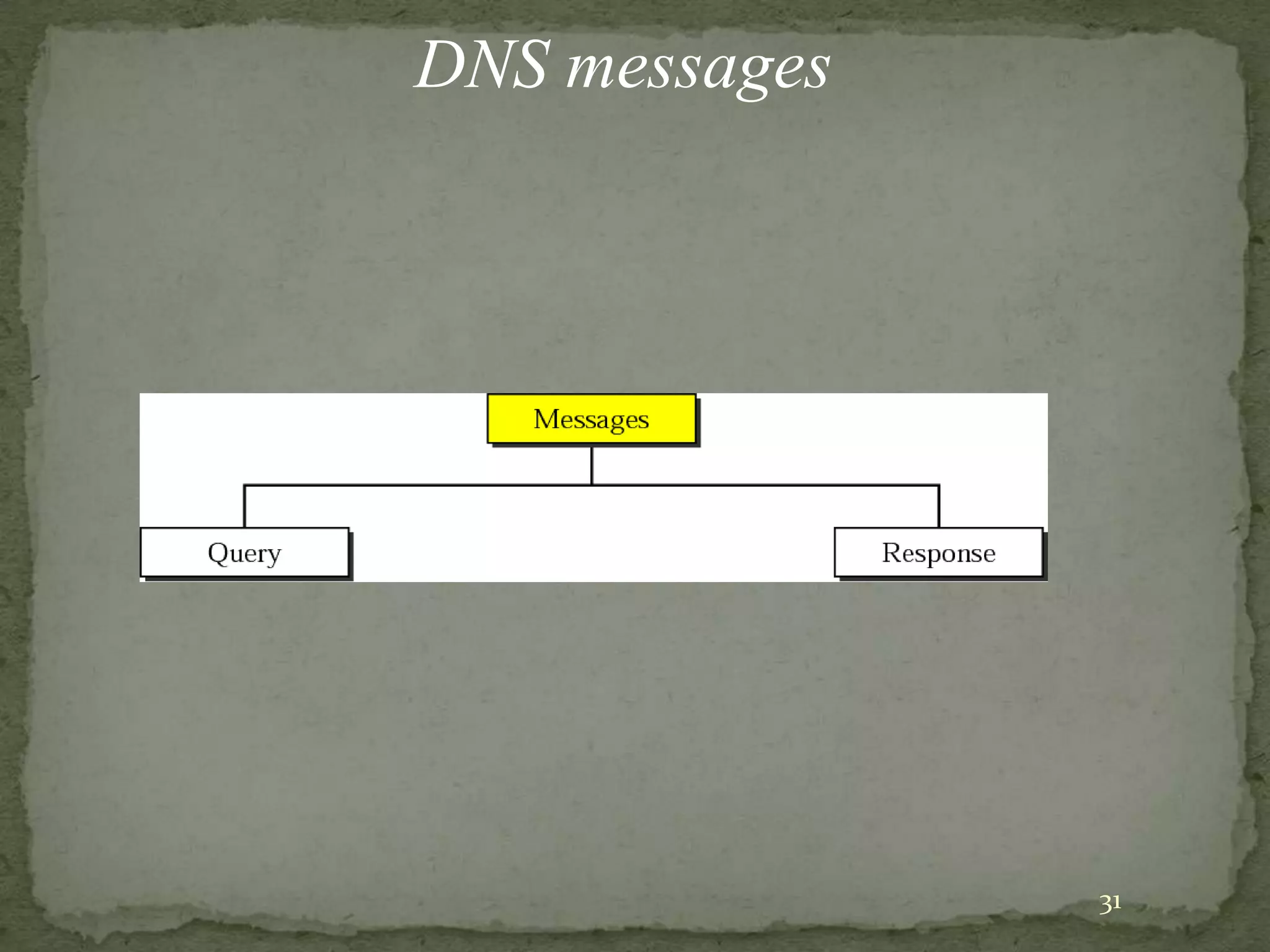
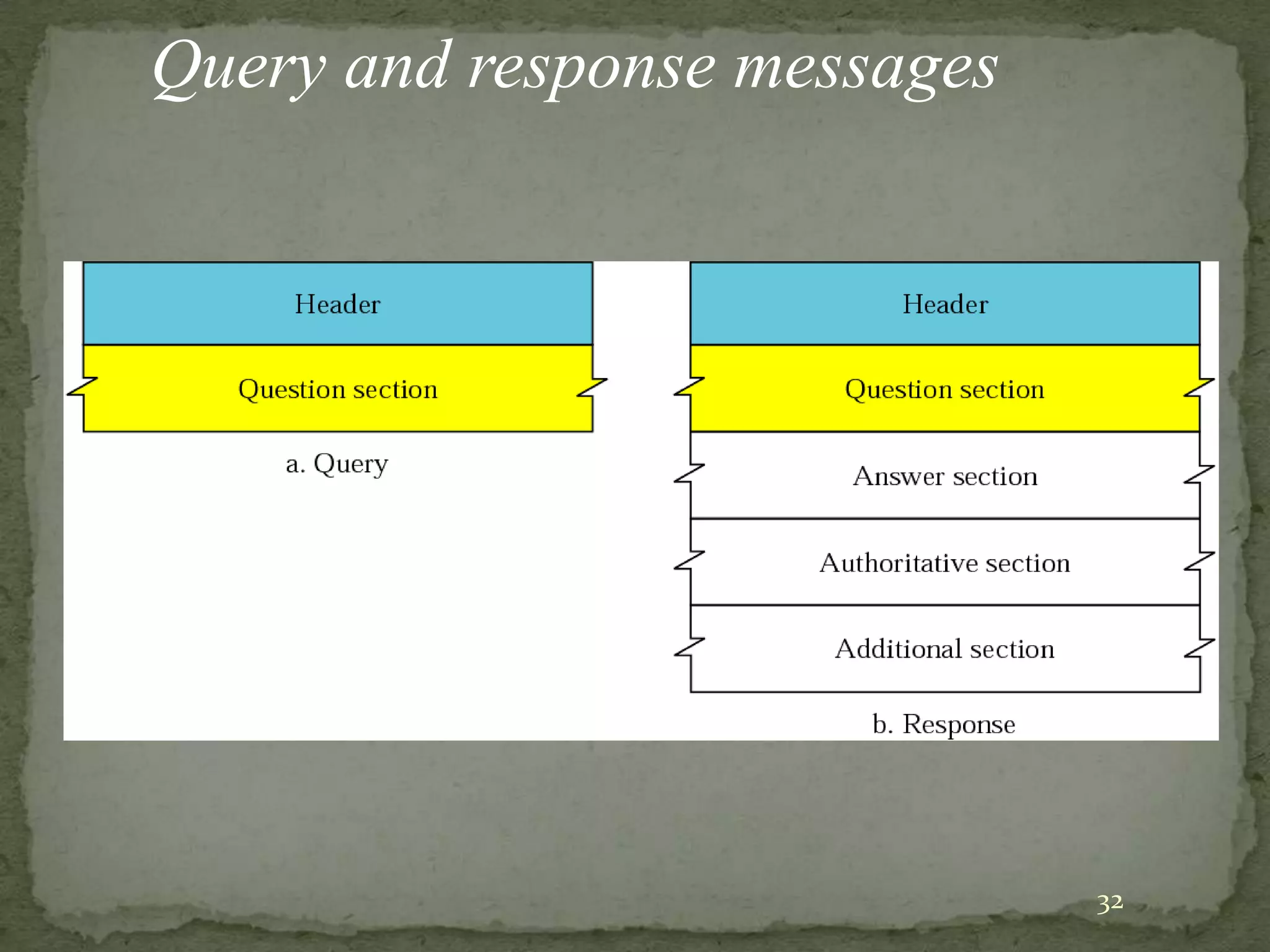
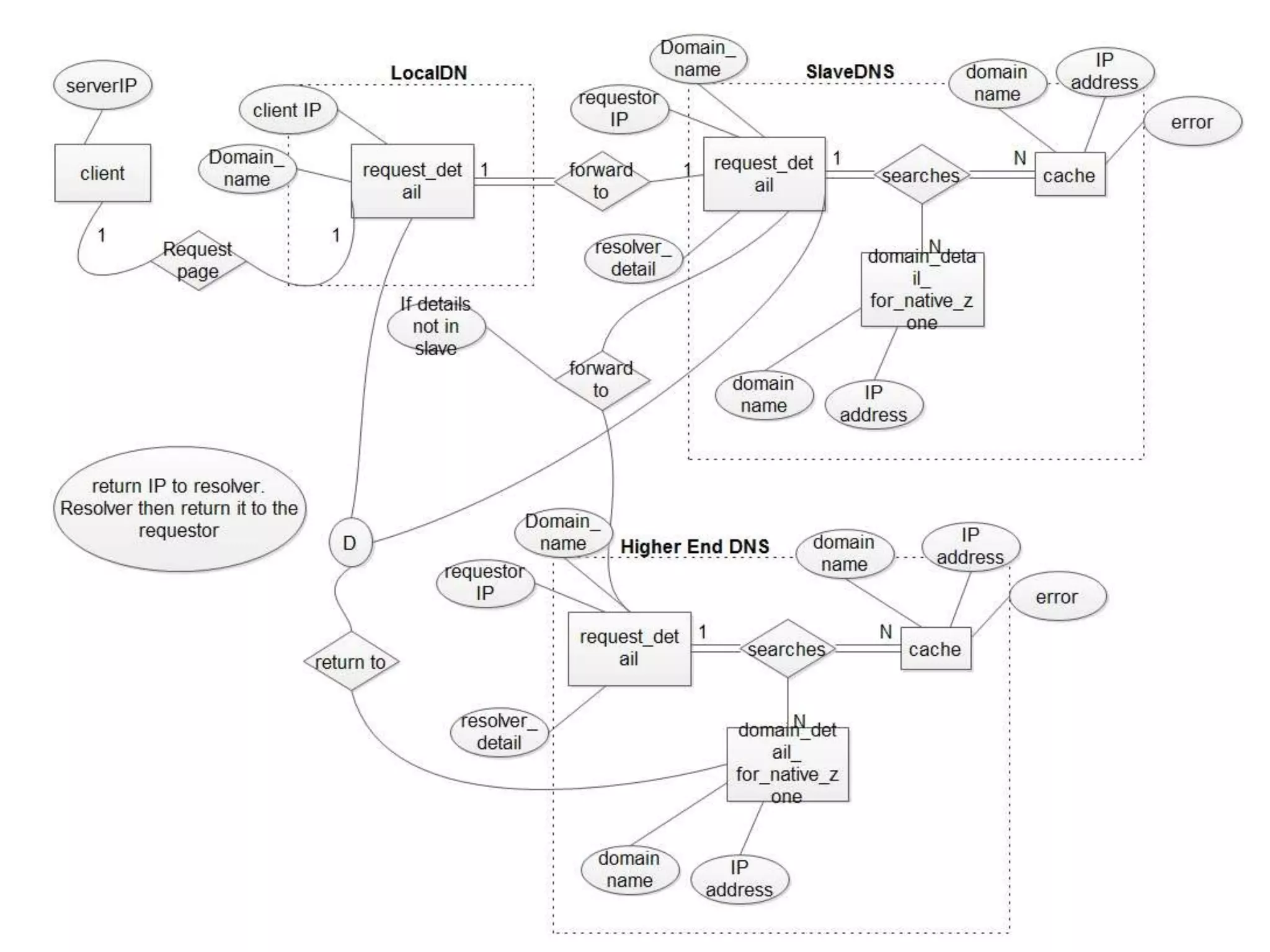
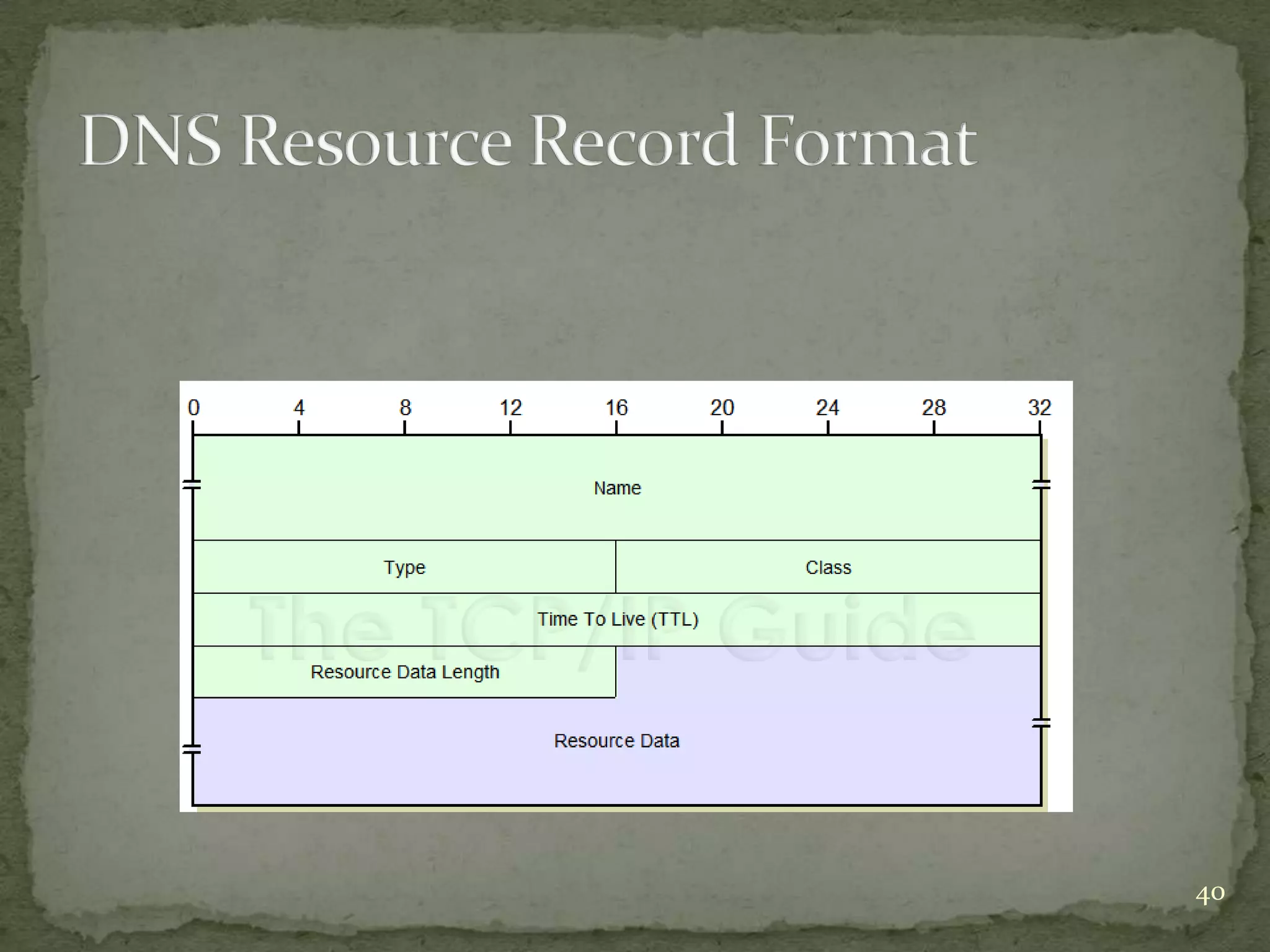
The document discusses the Domain Name System (DNS), explaining that it is a globally distributed database that translates human-friendly website addresses into computer-friendly IP addresses and vice versa. DNS uses a hierarchical system to organize domain names and resolve queries through recursive or iterative processes, with DNS messages containing header, question, answer, and additional record sections to facilitate name-address mapping.