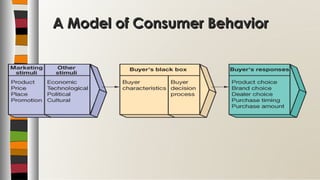
This document provides an overview of consumer buying behavior and the consumer decision-making process. It discusses factors that influence consumer behavior such as cultural, social, personal and psychological characteristics. A model of consumer behavior is presented showing how marketing stimuli interact with a consumer's characteristics to drive responses. The consumer decision process is also summarized, outlining the typical steps of need recognition, information search, evaluation of alternatives, purchase decision and post-purchase behavior. Key concepts in consumer behavior and motivation theories are defined.