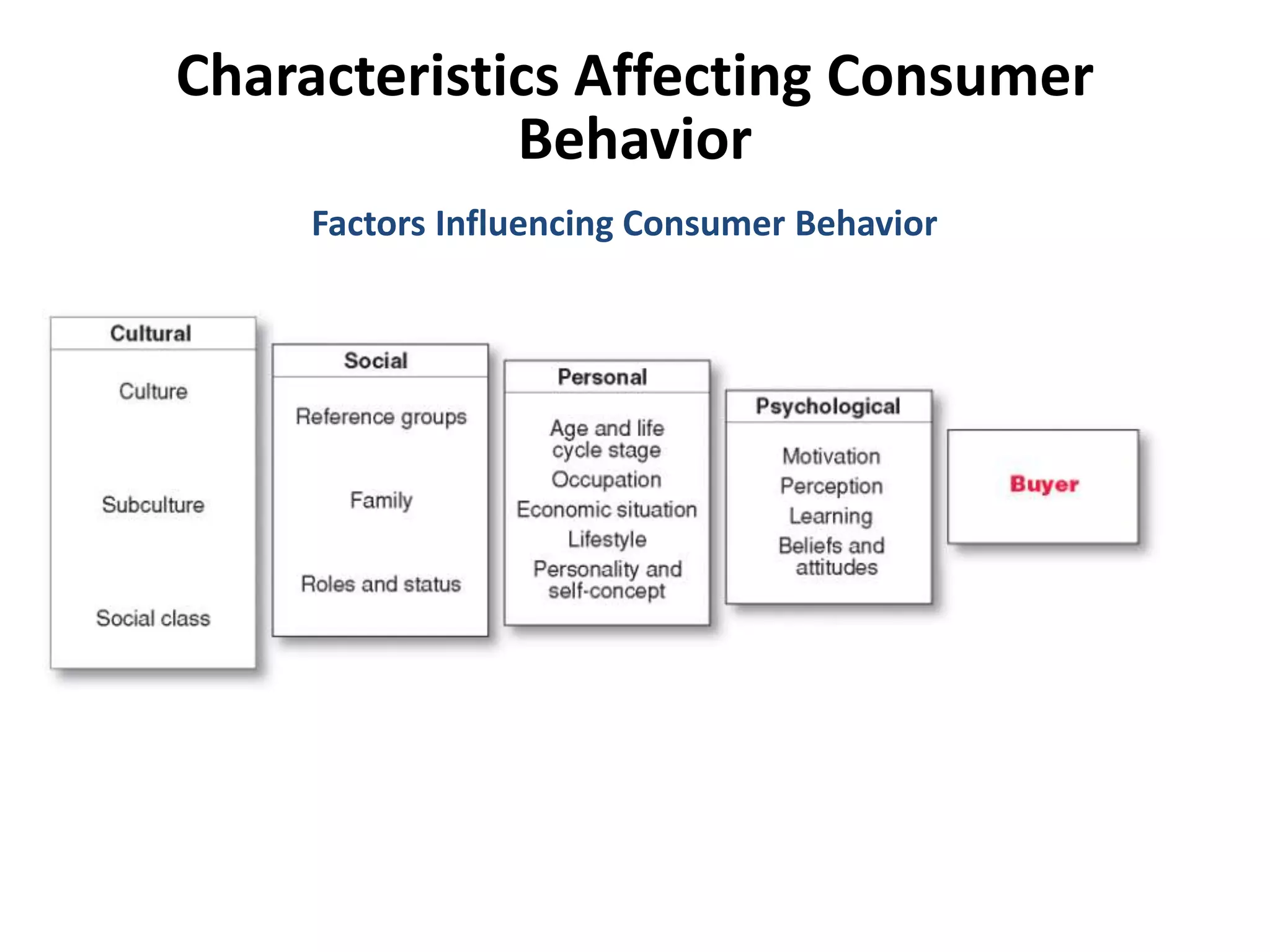
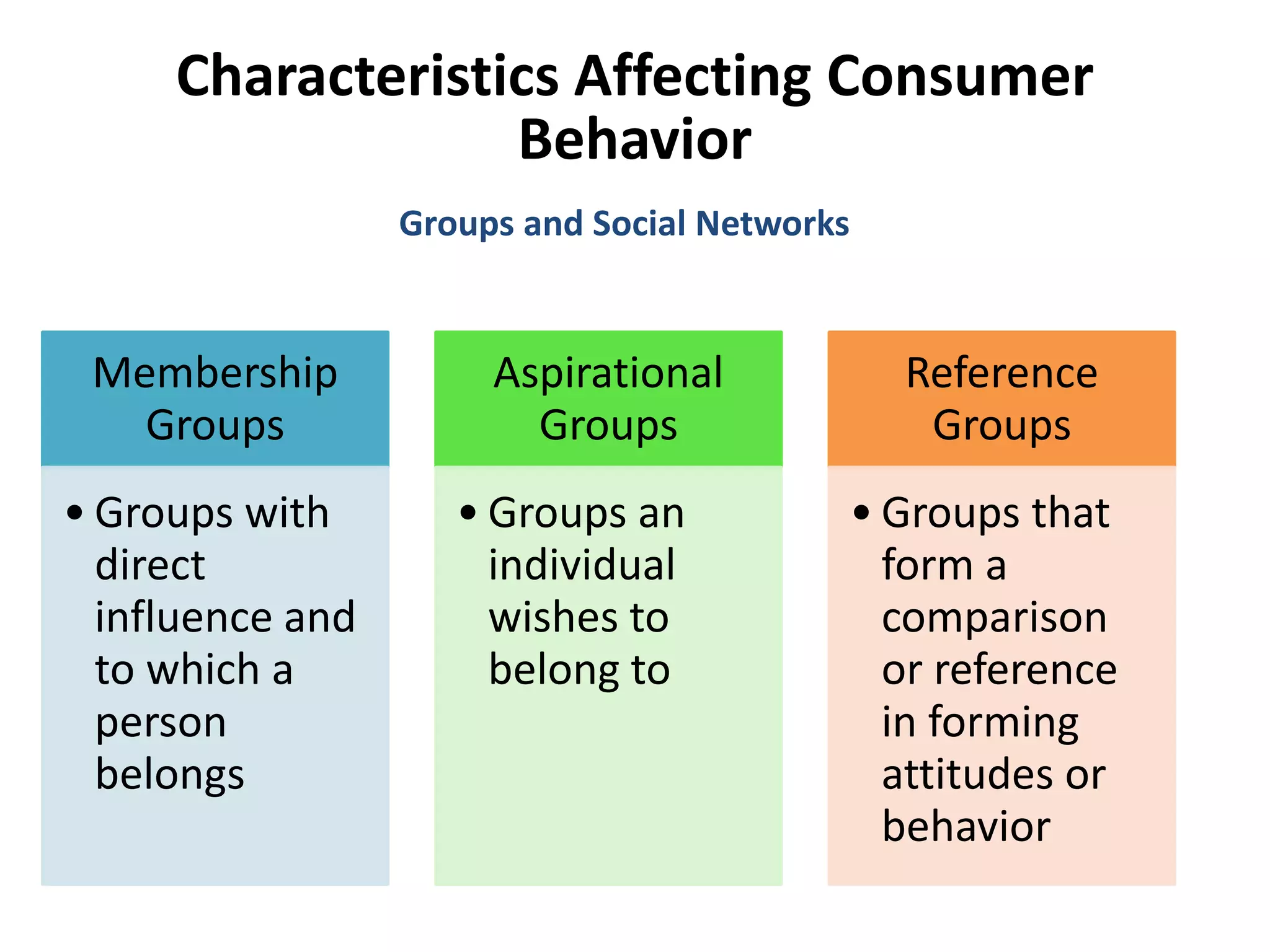
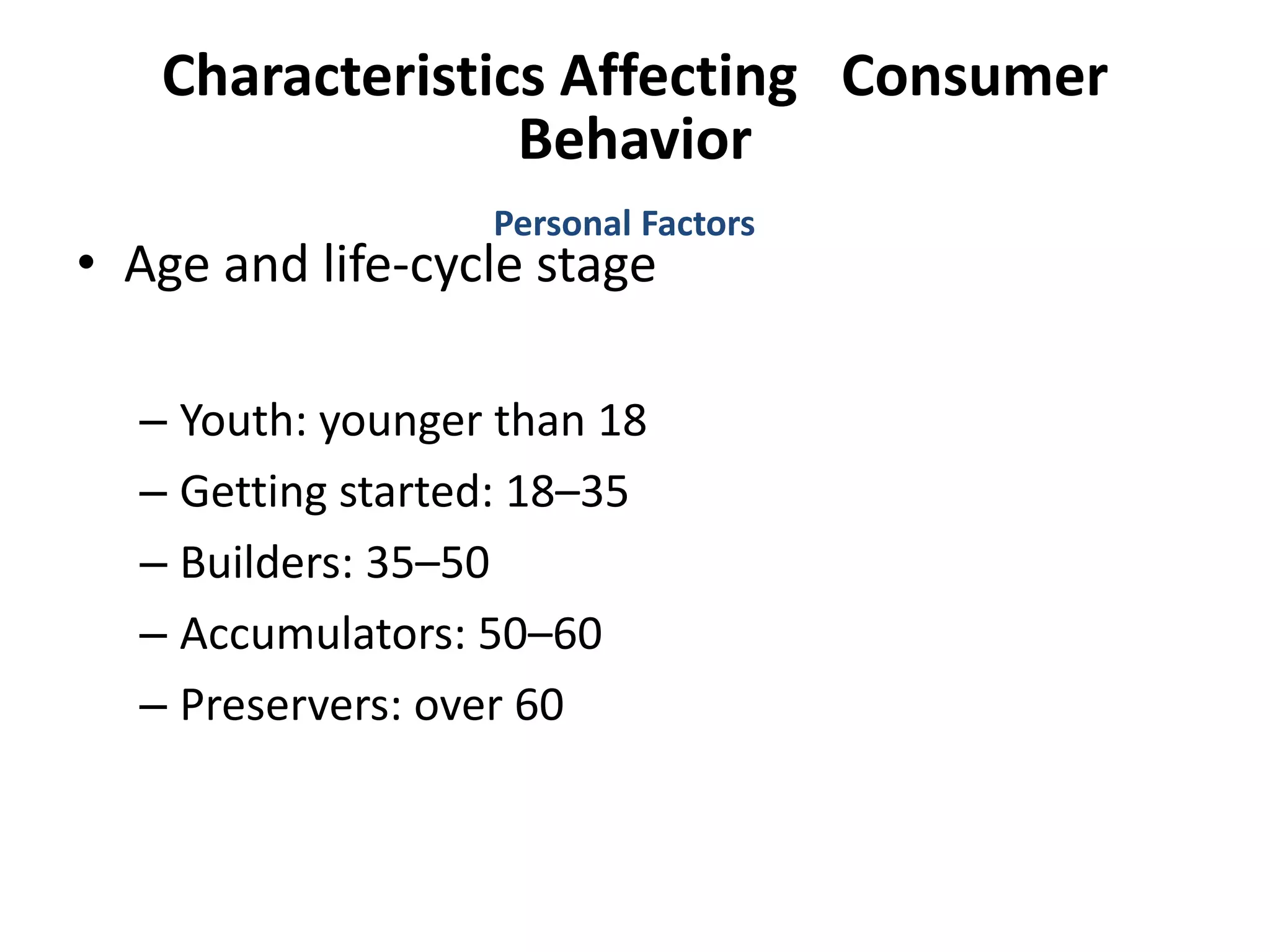
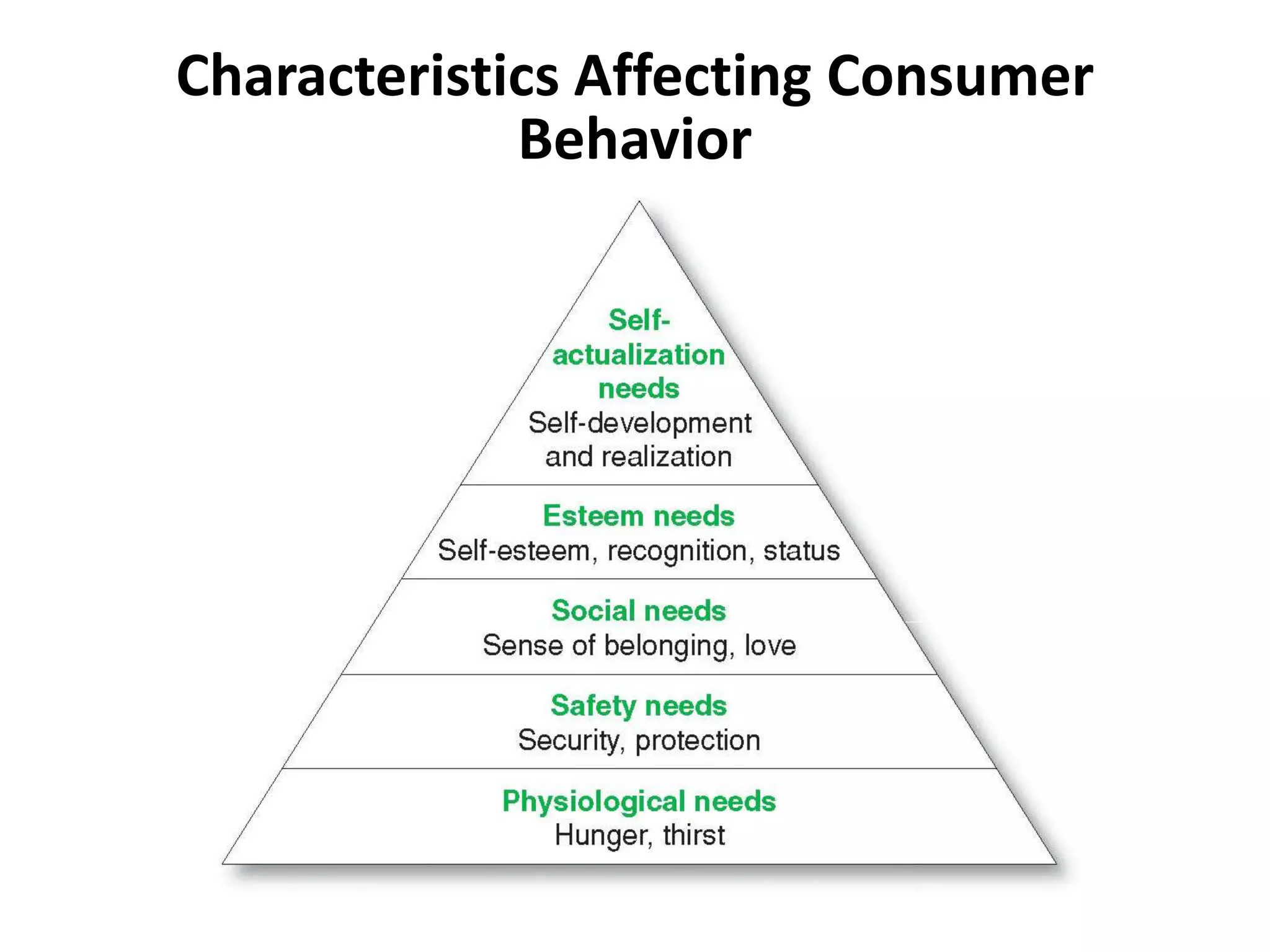
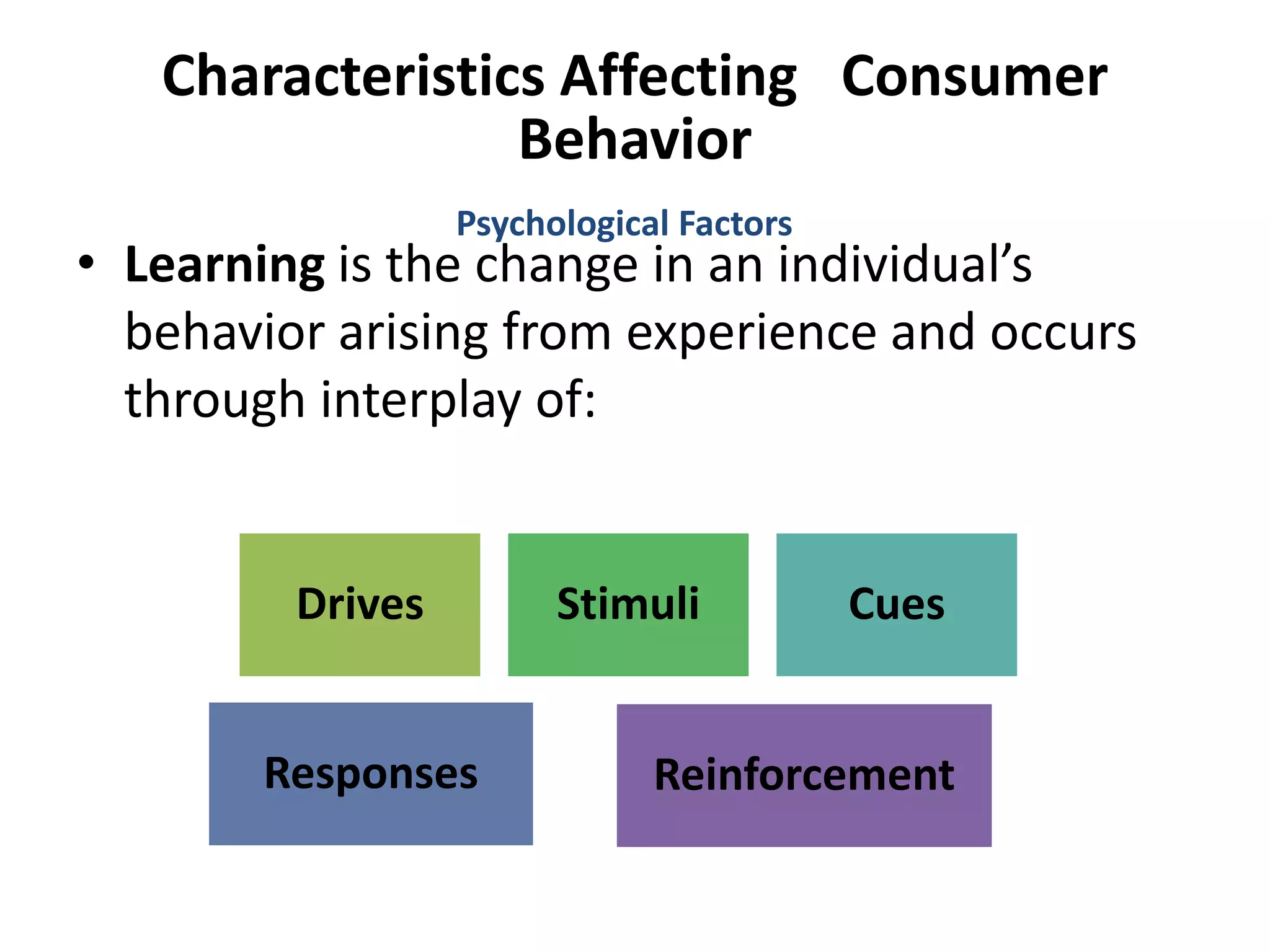
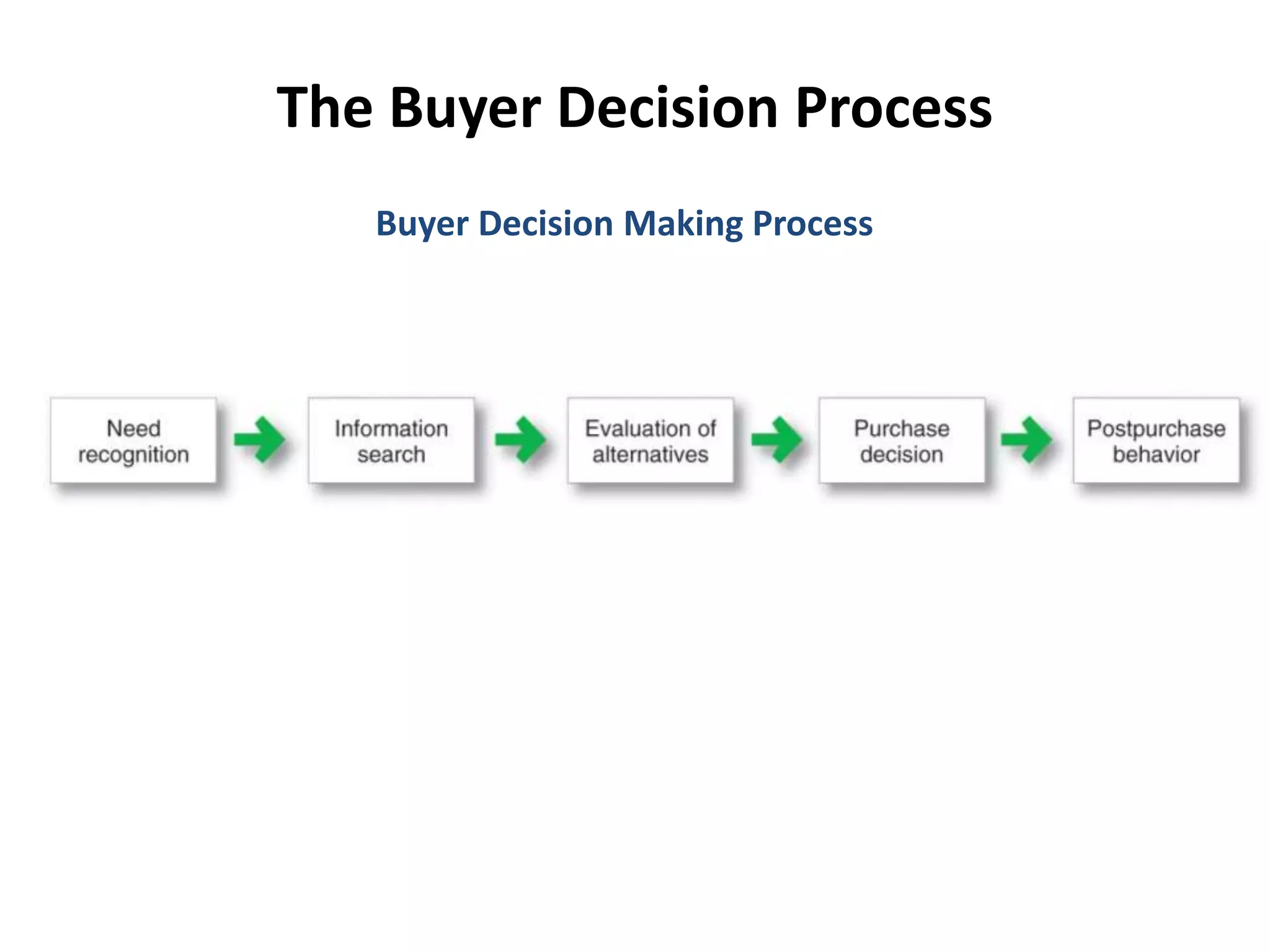
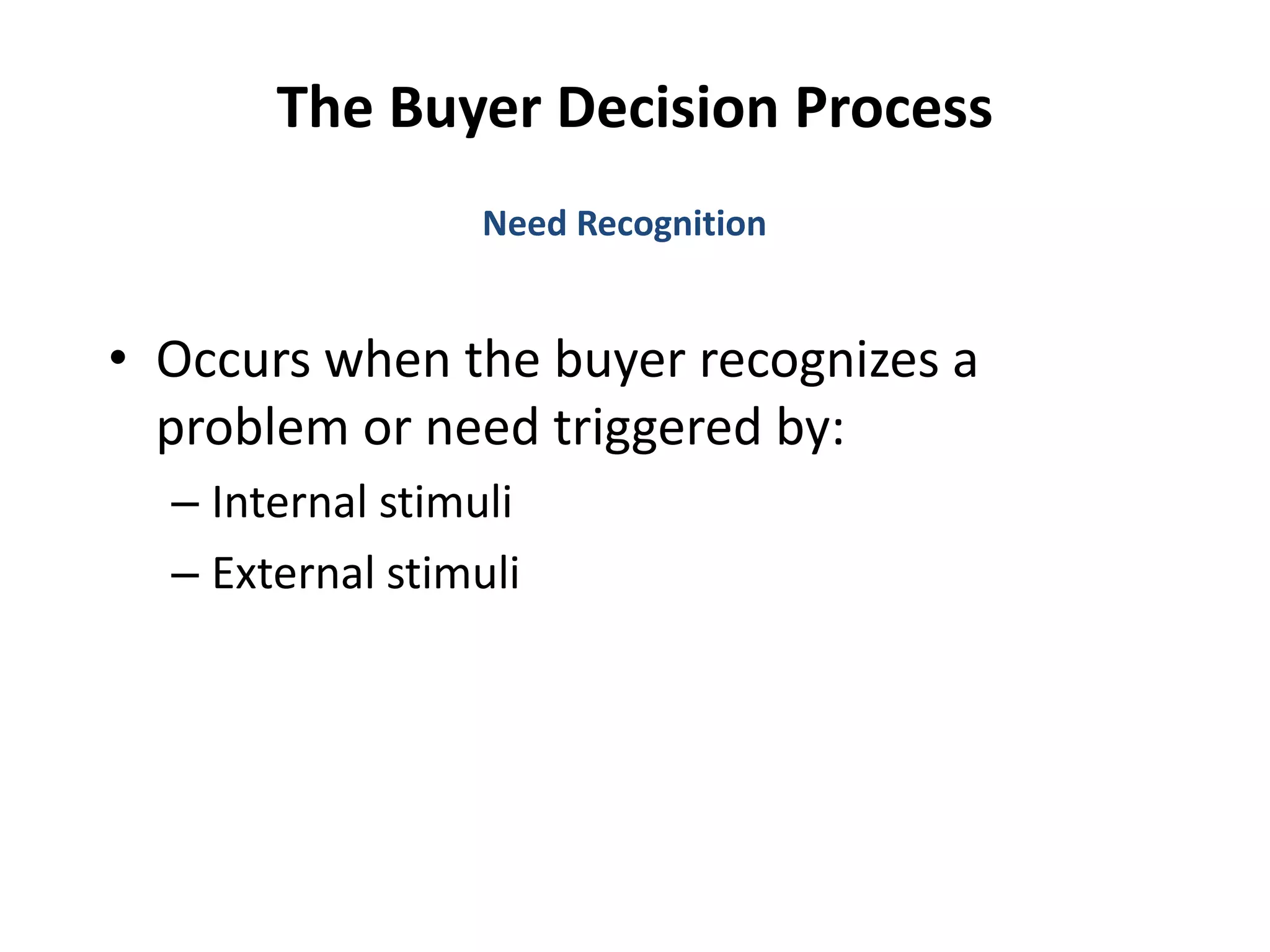
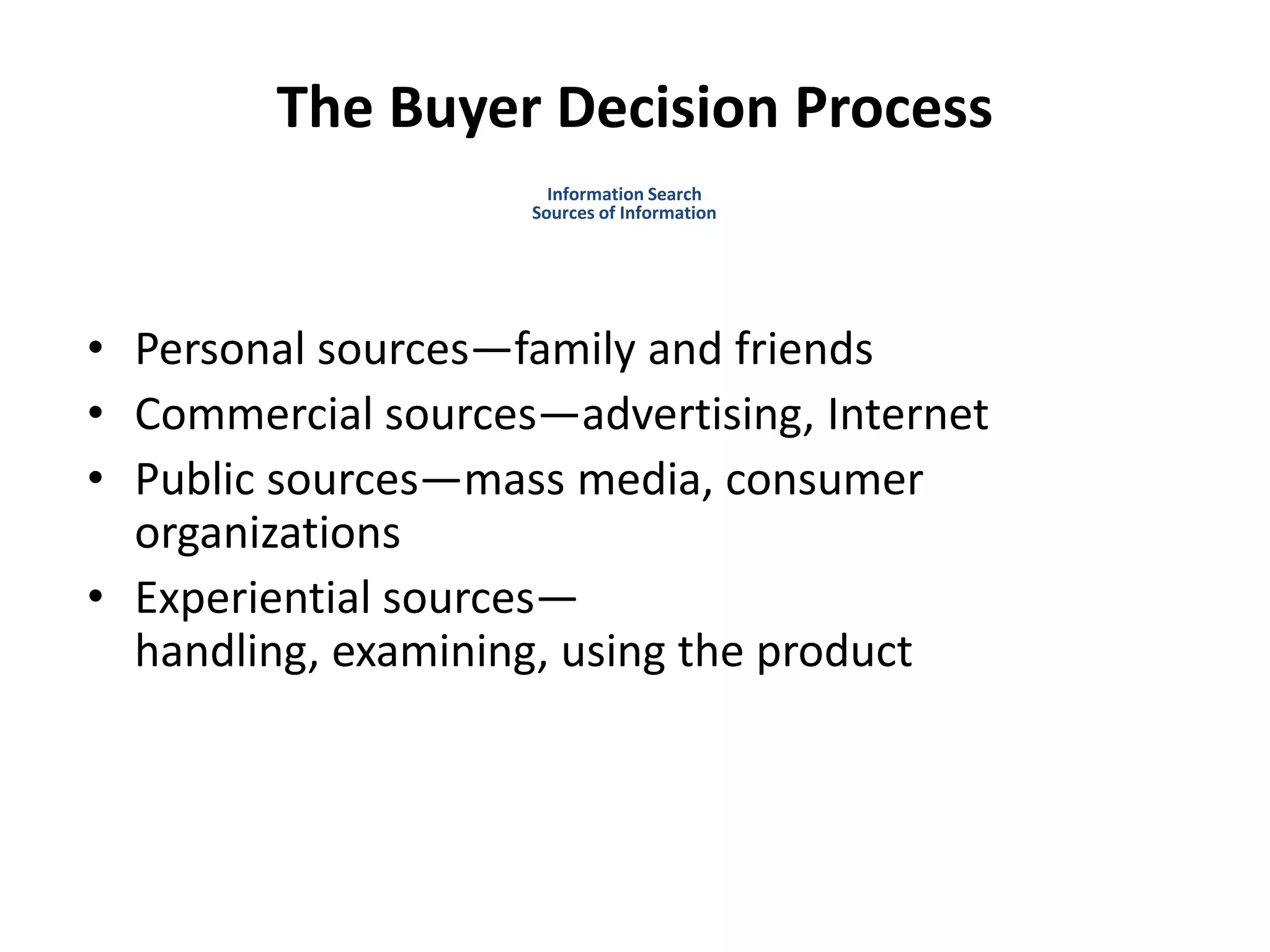
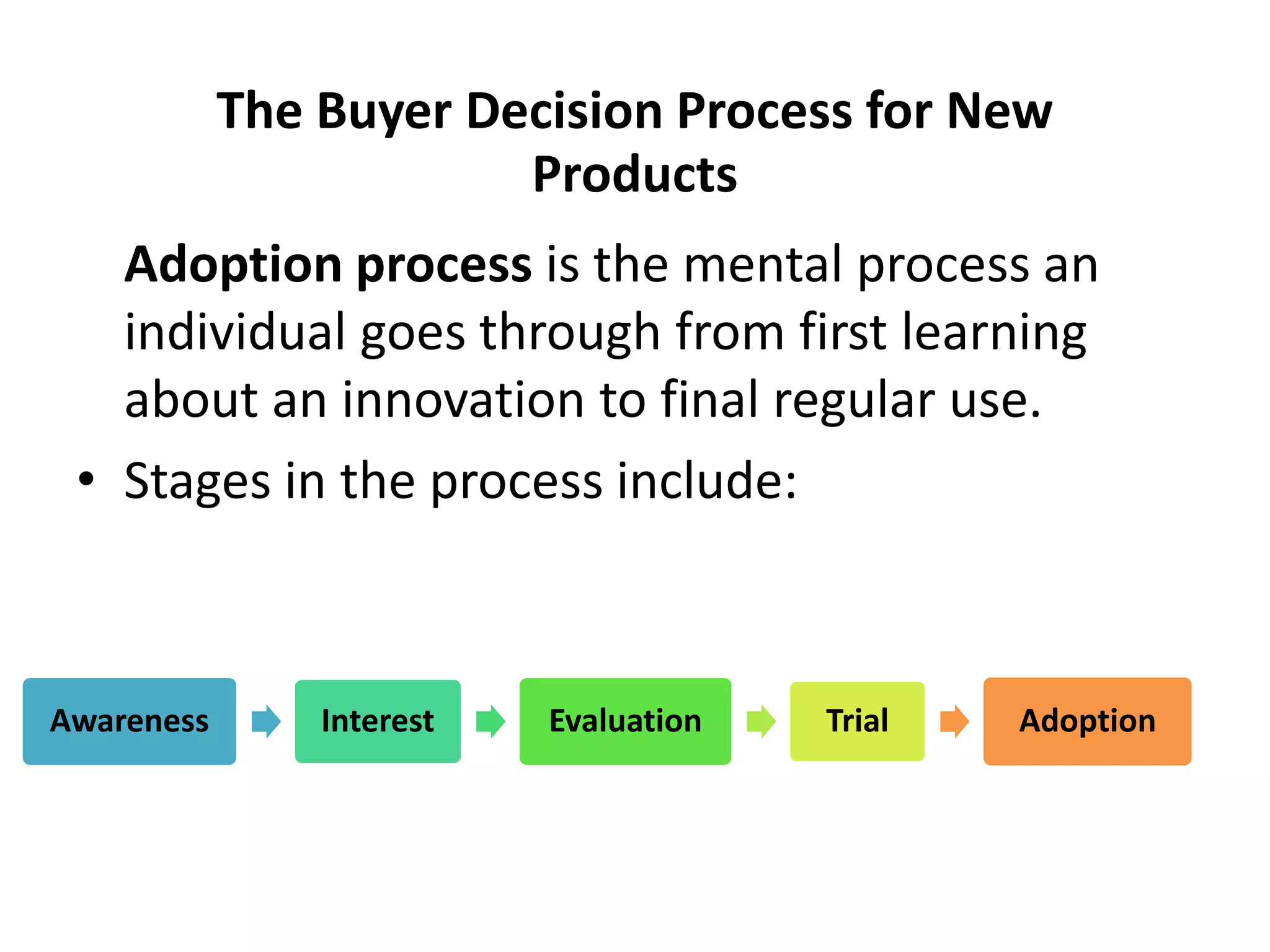
This document discusses consumer buyer behavior and the factors that influence purchasing decisions. It outlines the consumer decision process, which begins with need recognition and information search. The consumer then evaluates alternatives and makes a purchase decision. After purchasing, the consumer experiences post-purchase satisfaction or dissonance based on whether expectations match actual product performance. Key factors like culture, social class, personality, motivation, and perception shape how consumers move through the decision stages.