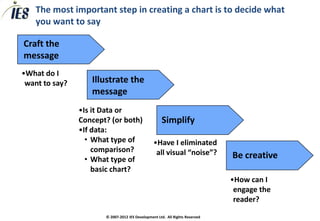
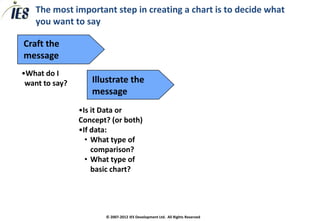
The document provides guidance on effectively communicating recommendations through charts. It discusses crafting clear messages, illustrating the message, simplifying charts by eliminating visual noise, and making charts engaging. Charts are seen as a key medium for professional business communication.