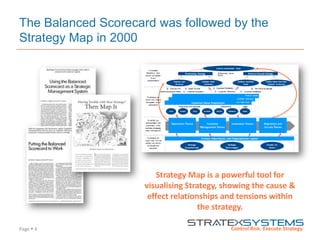
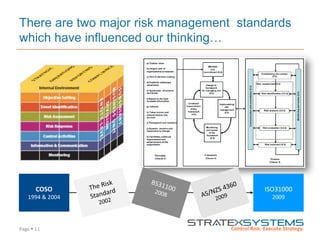
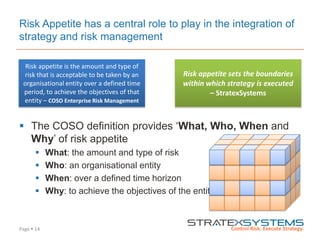
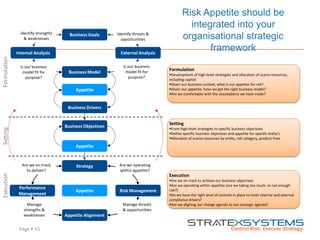
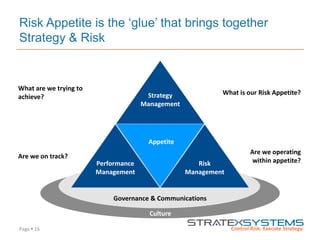
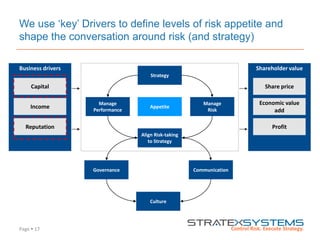
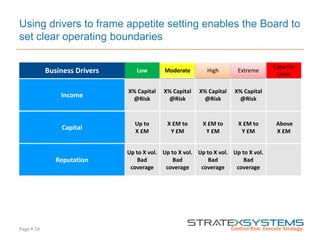
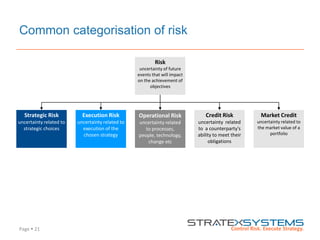
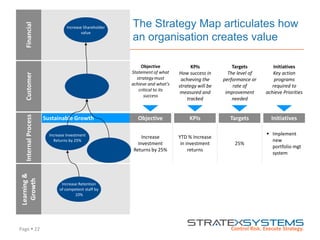
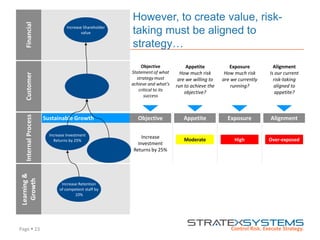
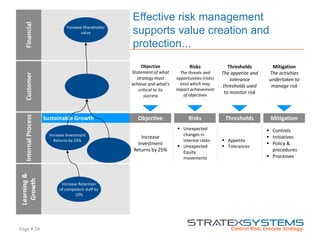
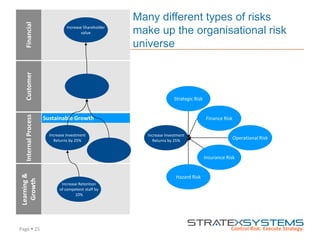
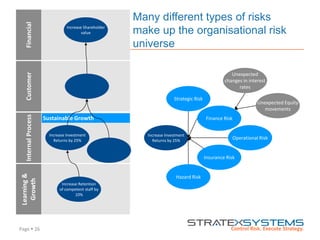
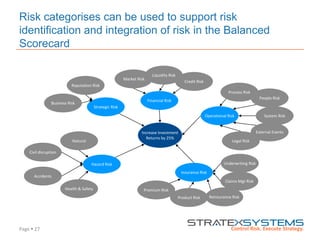
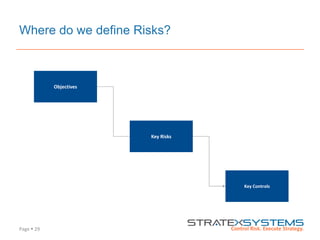
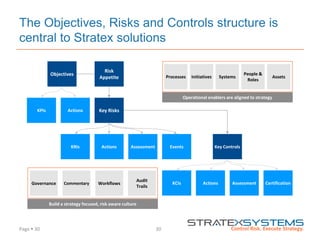
The document discusses the integration of risk management into the balanced scorecard framework, emphasizing the importance of aligning risk appetite with strategic objectives. It outlines the evolution of the balanced scorecard and presents strategies for defining risk levels using business drivers and risk taxonomies. Ultimately, it asserts that effective risk management enhances strategy execution and supports value creation.