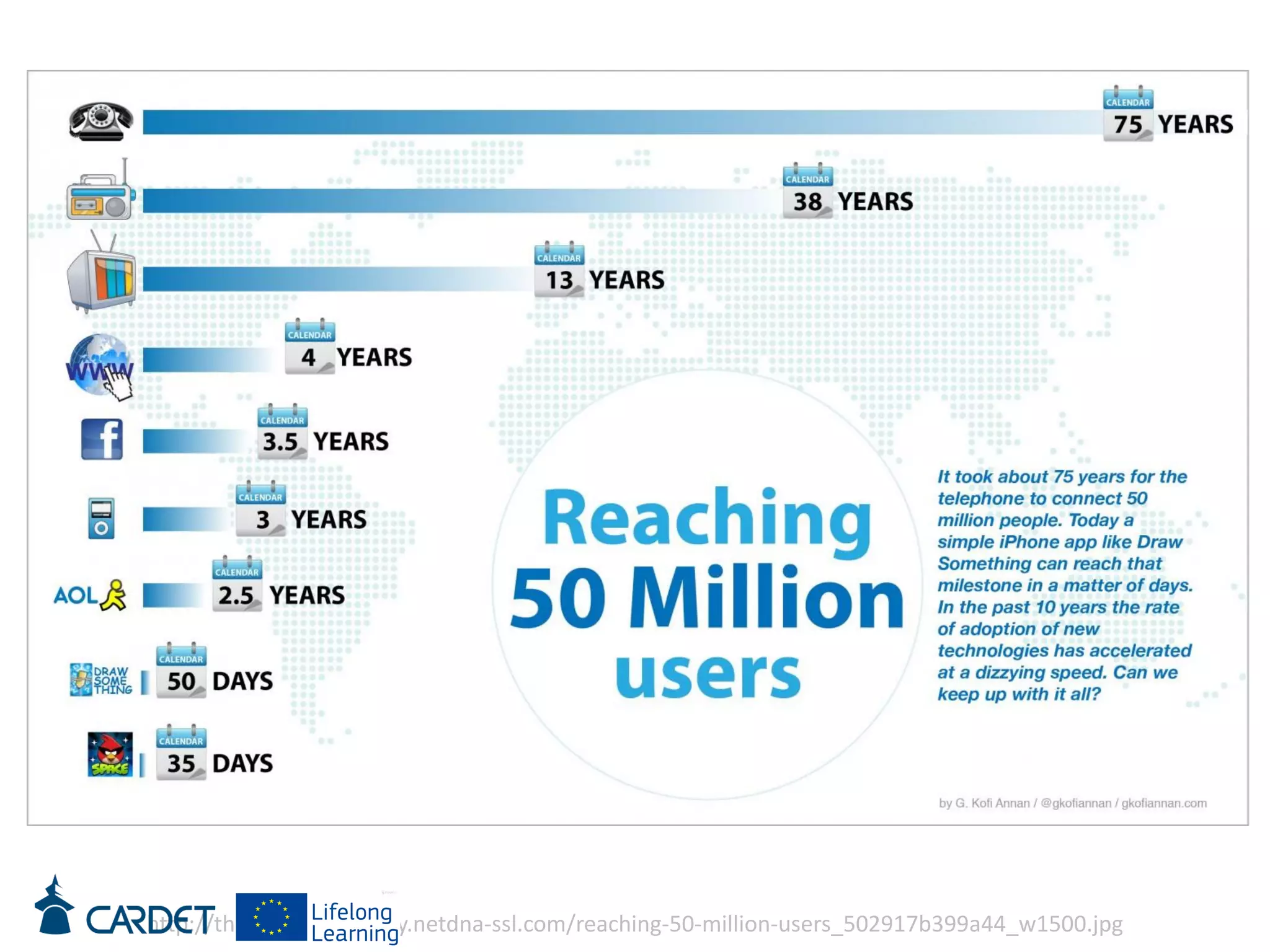
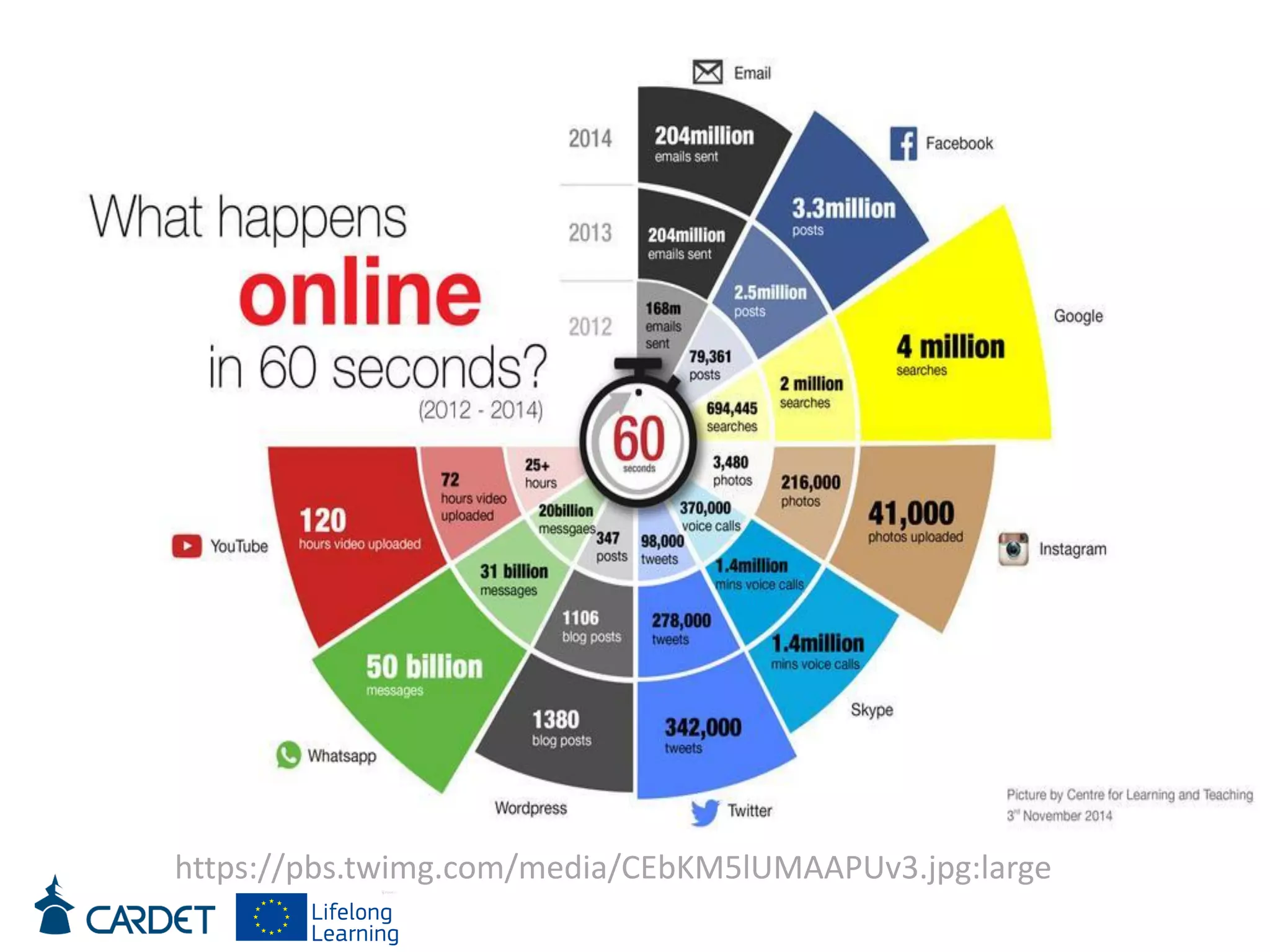
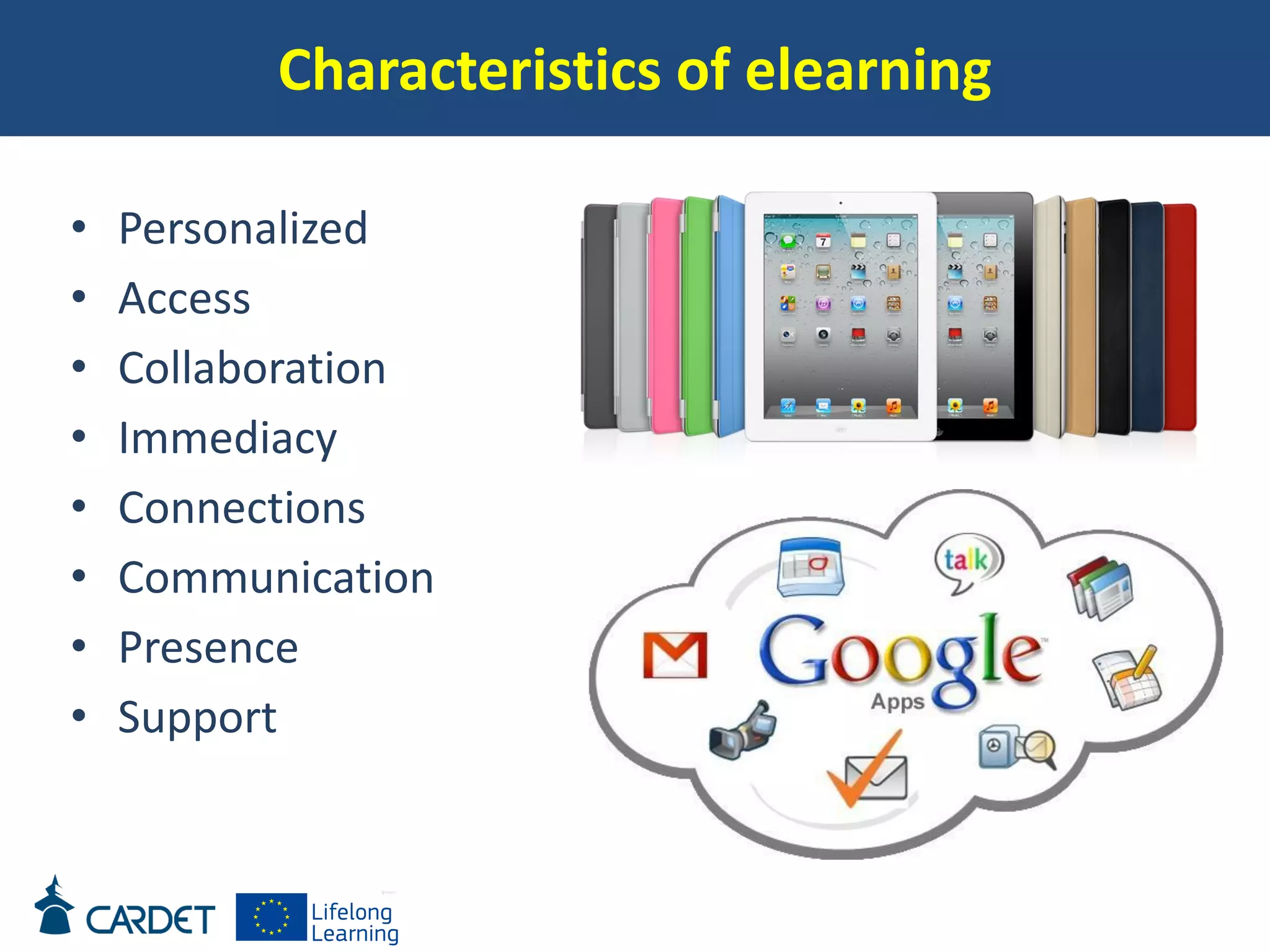
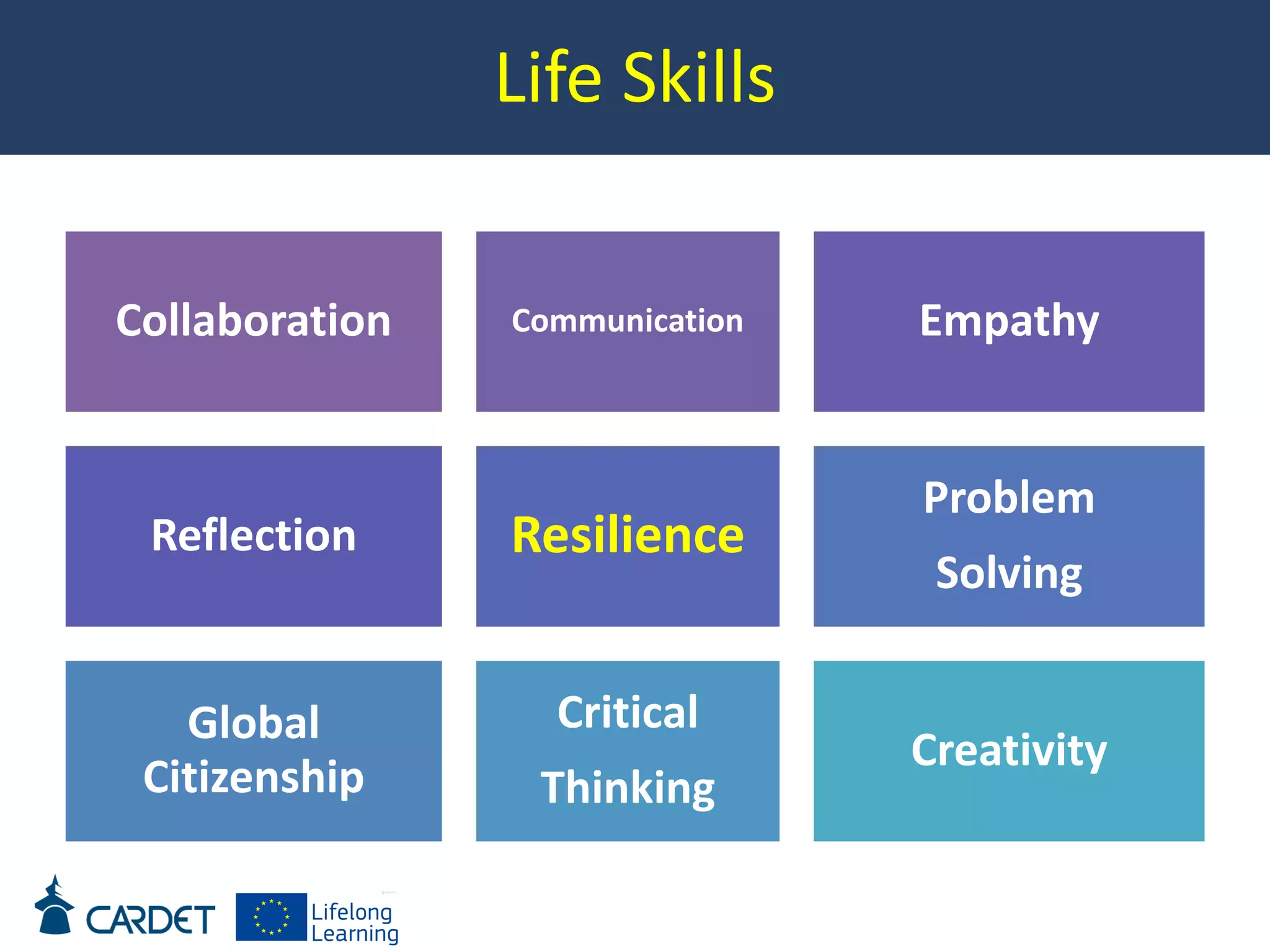
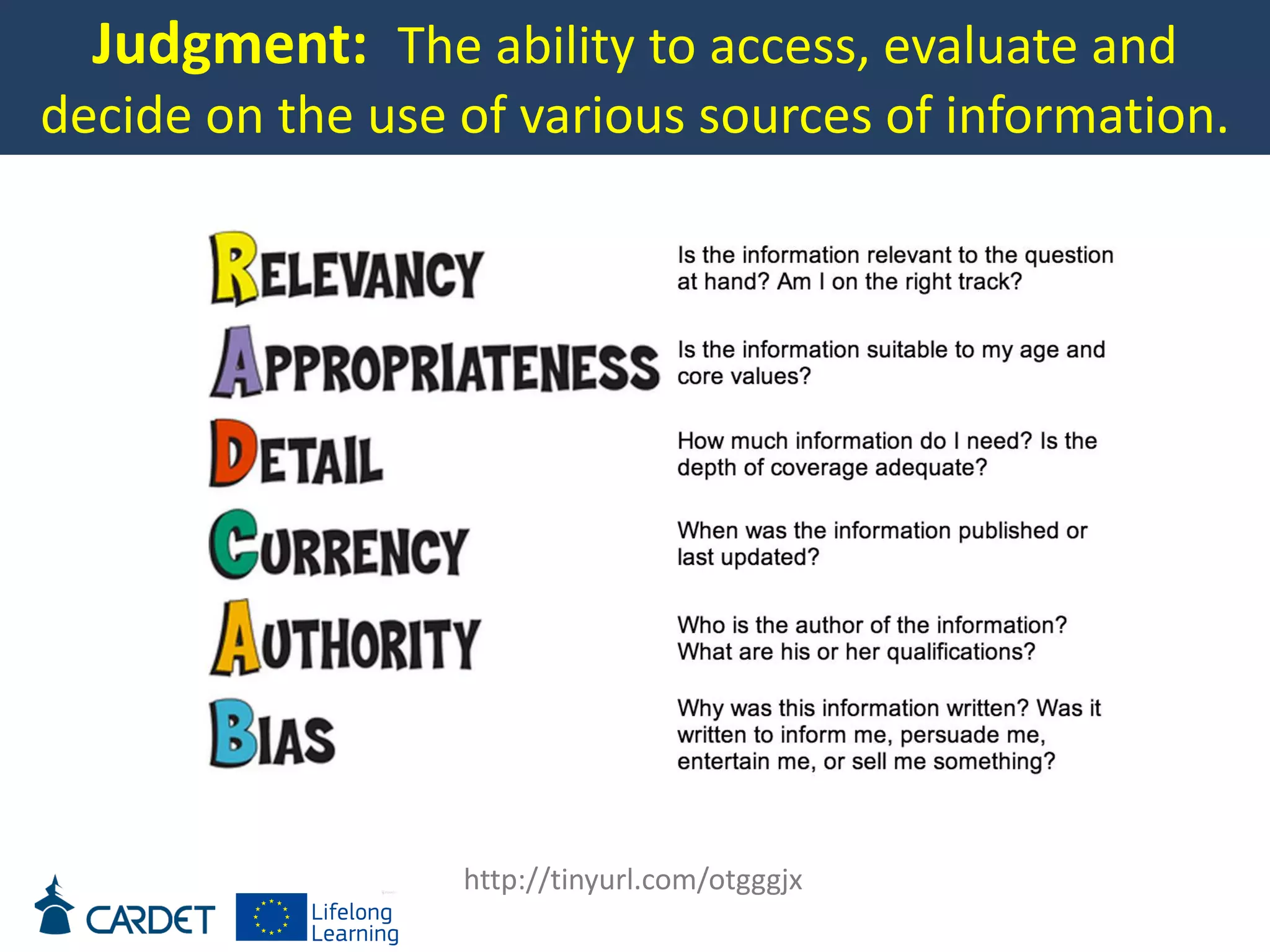
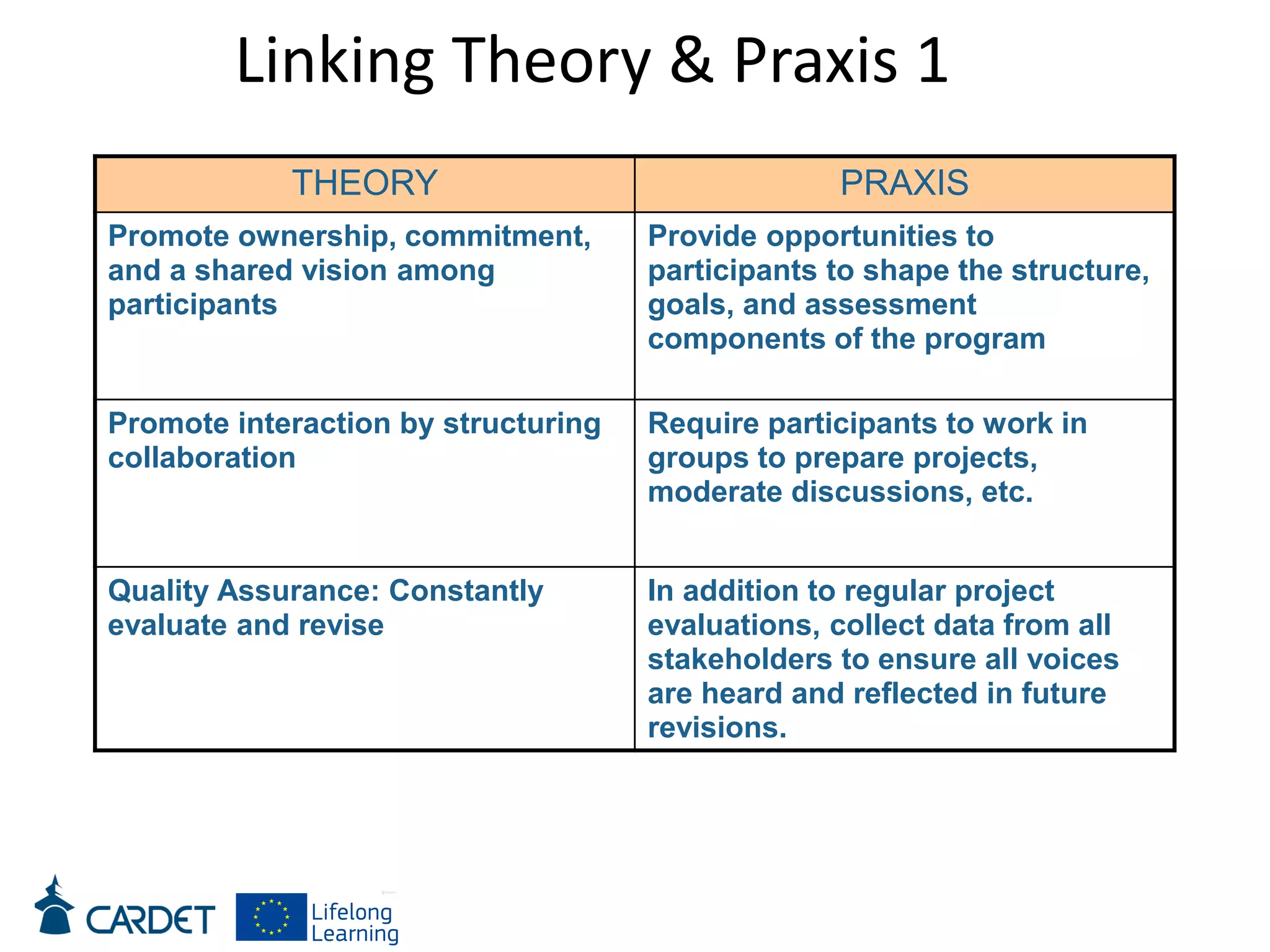
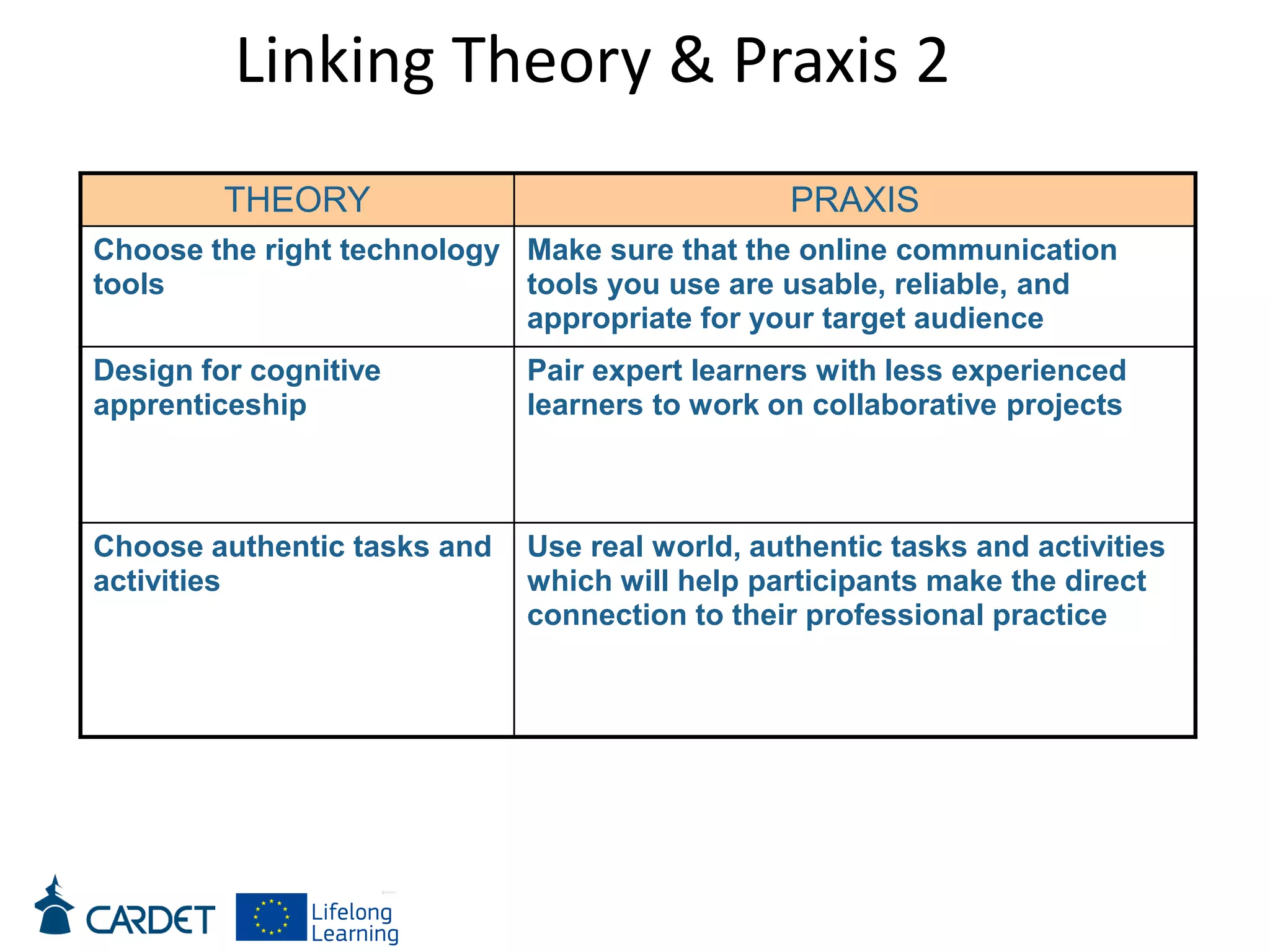
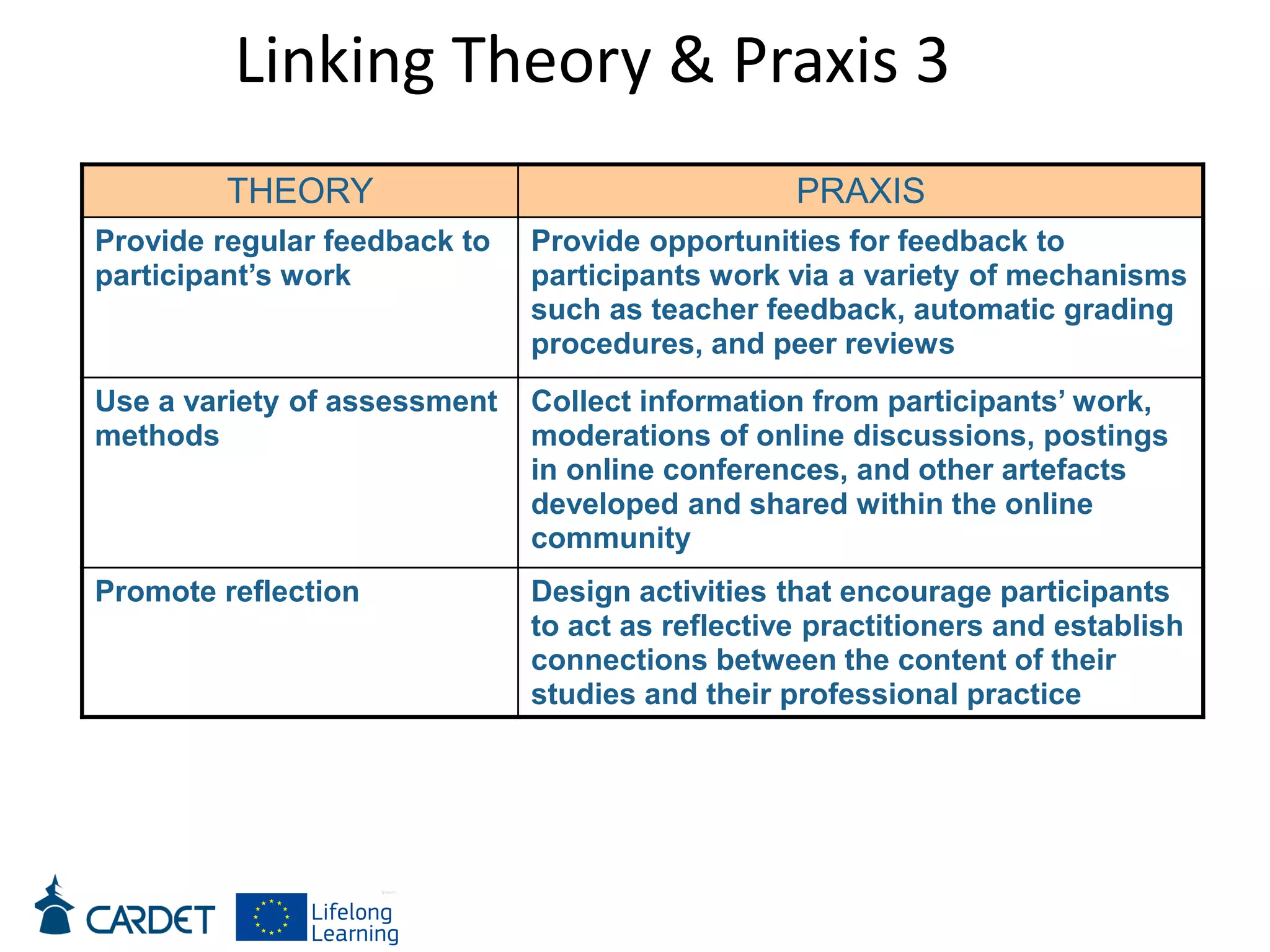
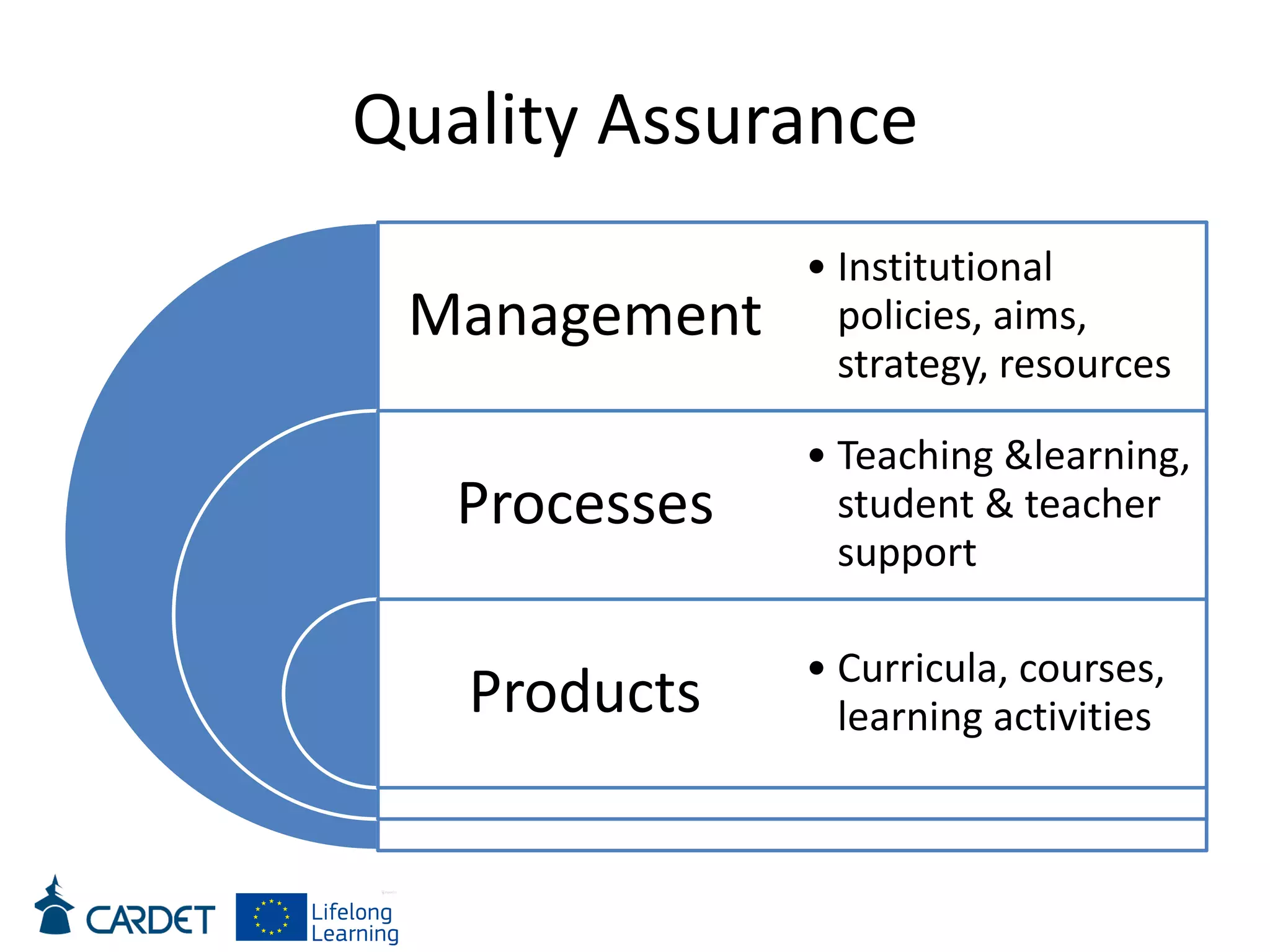
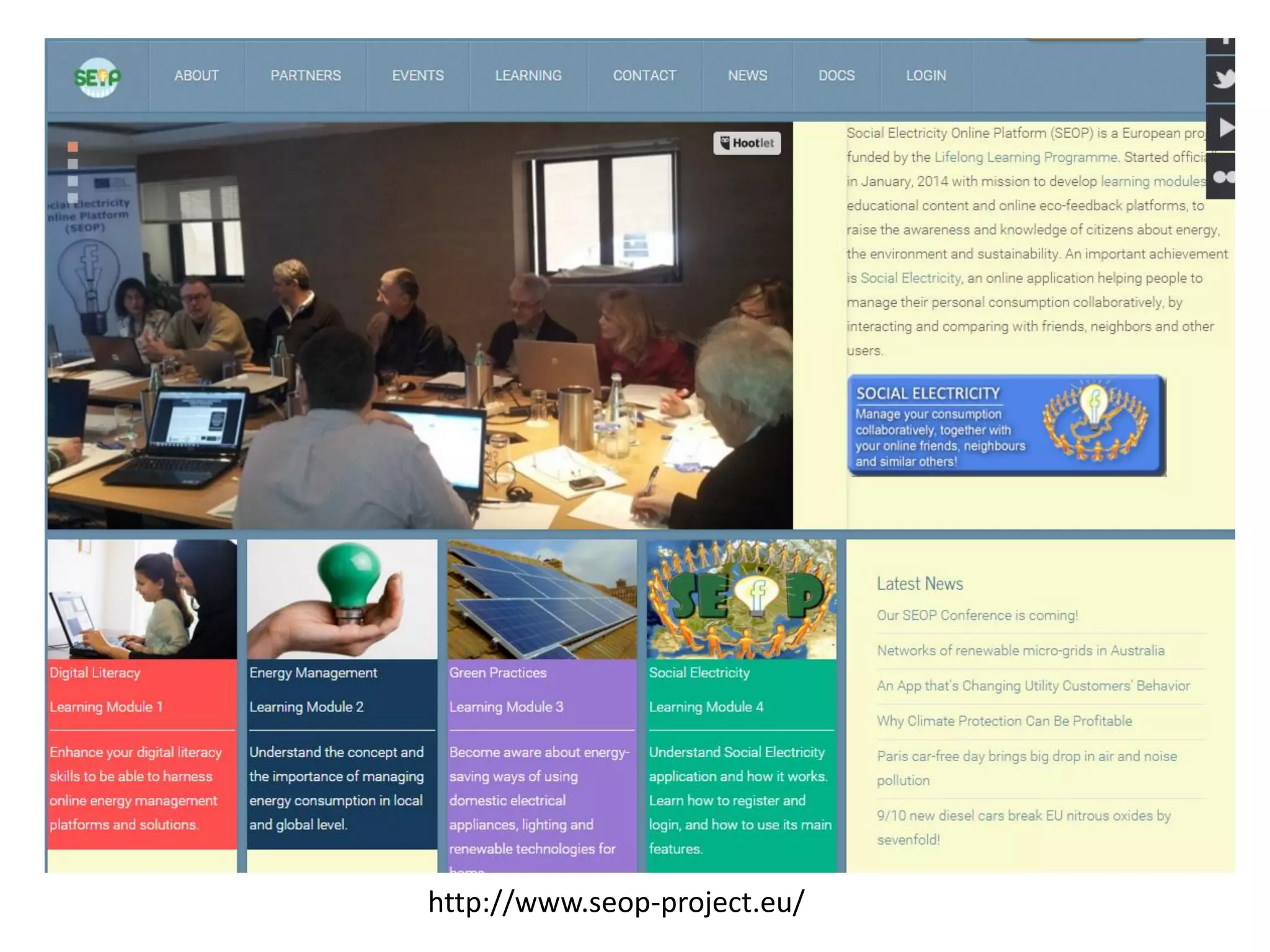
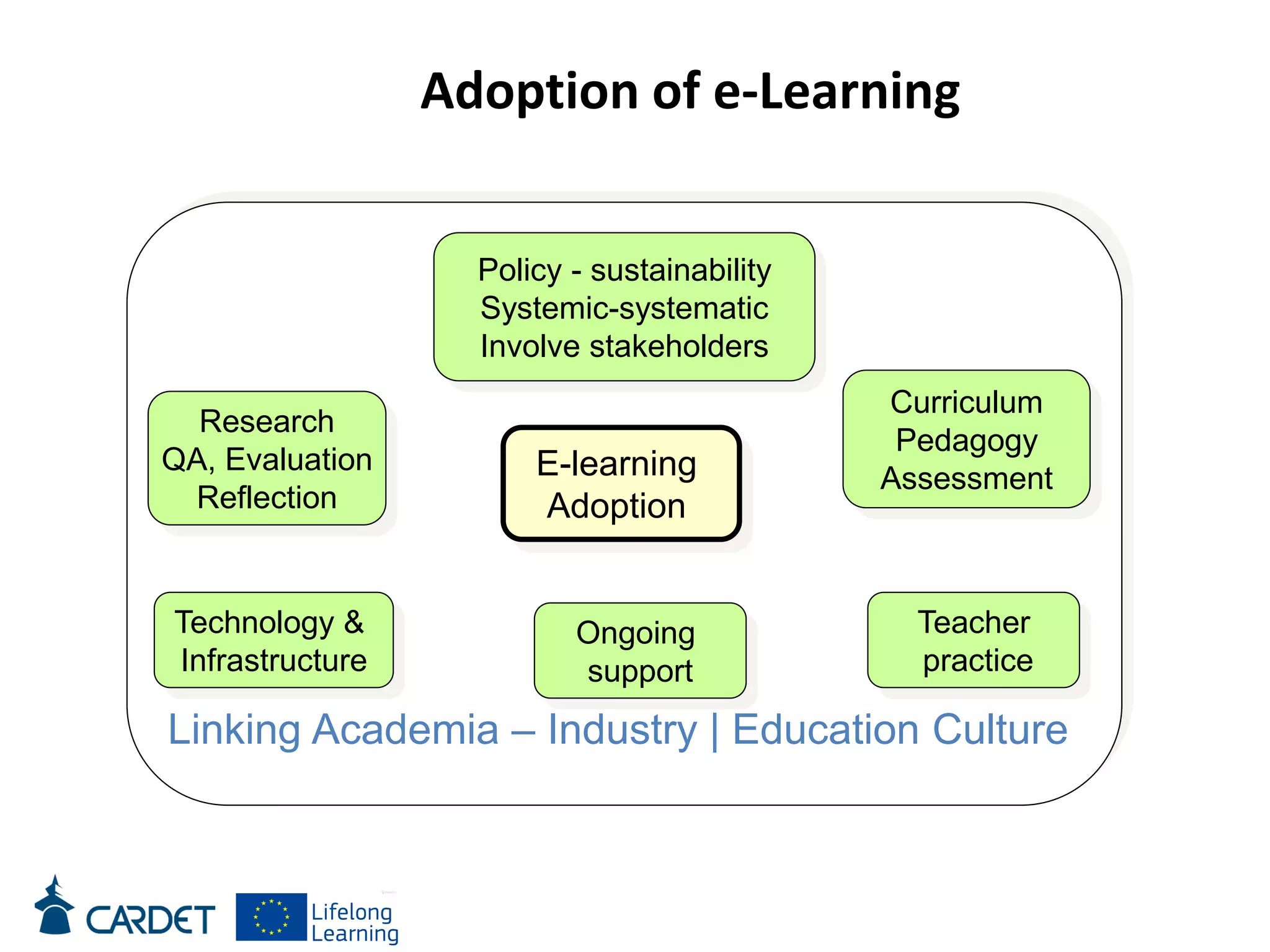
The document discusses evolving learning methods and the integration of technology in education, highlighting the significance of e-learning features such as personalization, collaboration, and engagement in curriculum design. It emphasizes the development of 21st-century skills, including critical thinking and global citizenship, as essential for students in a rapidly changing world. The paper also stresses the importance of continuous feedback, quality assurance, and active participation in both teaching and learning processes.