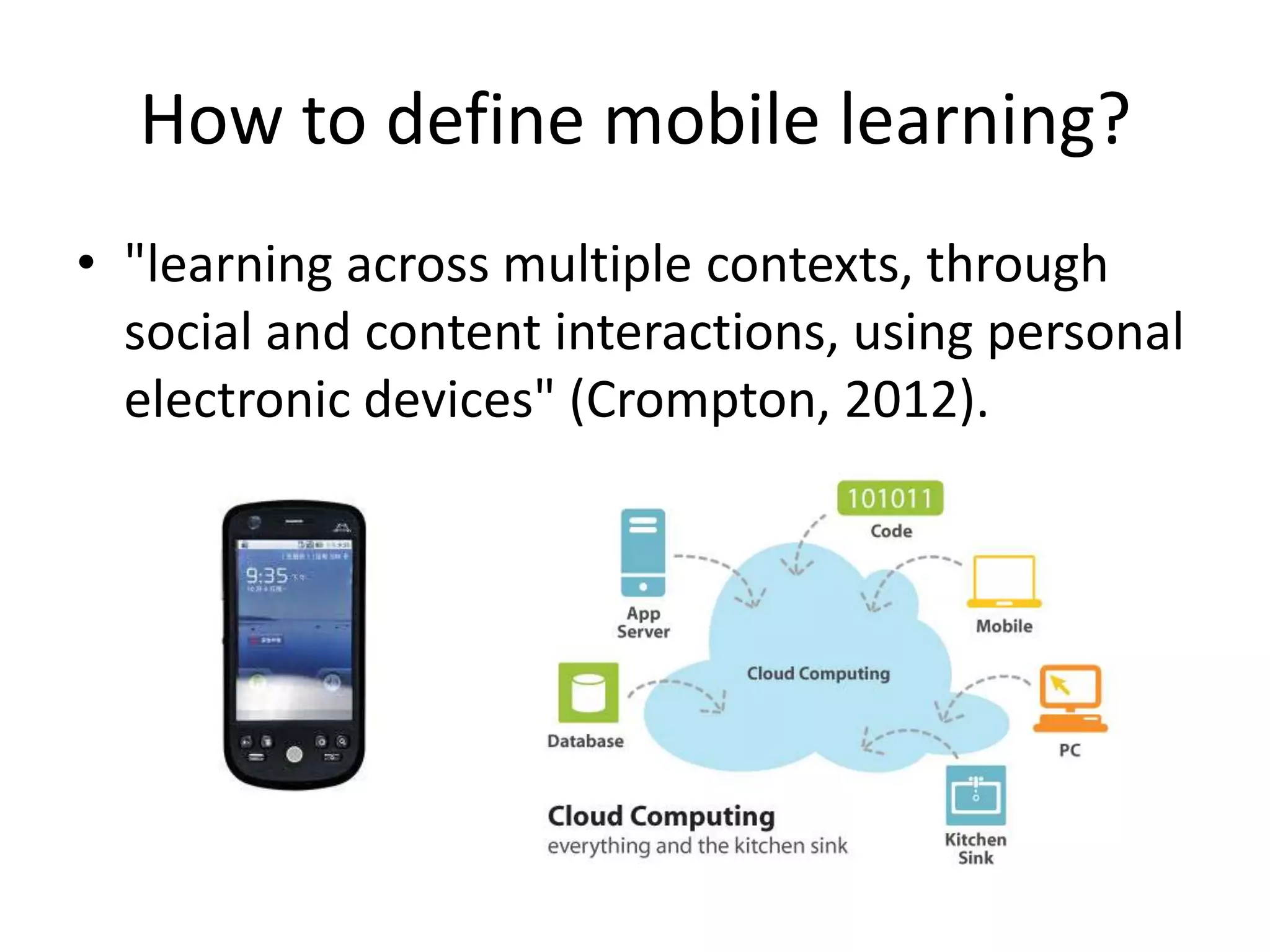
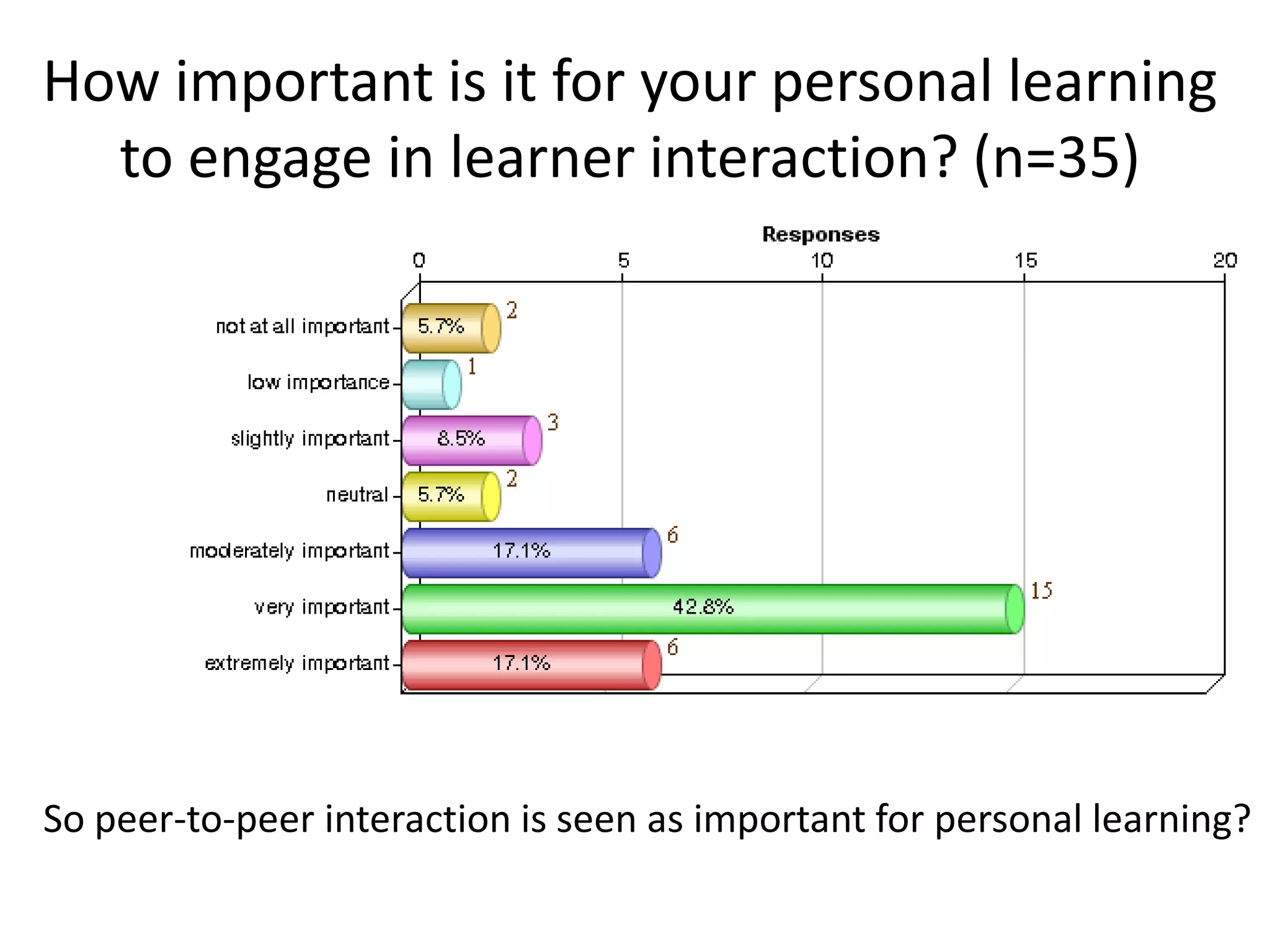
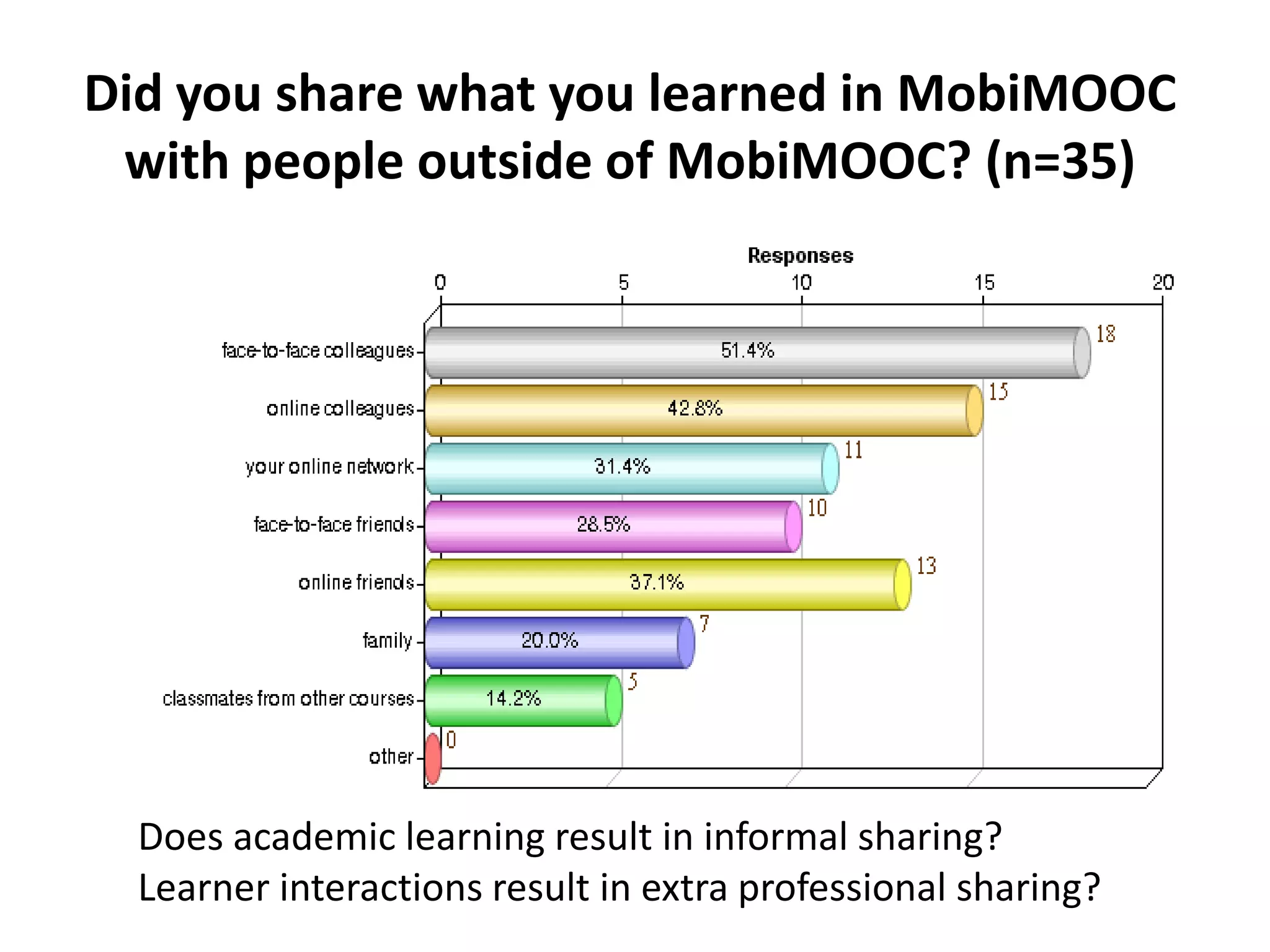
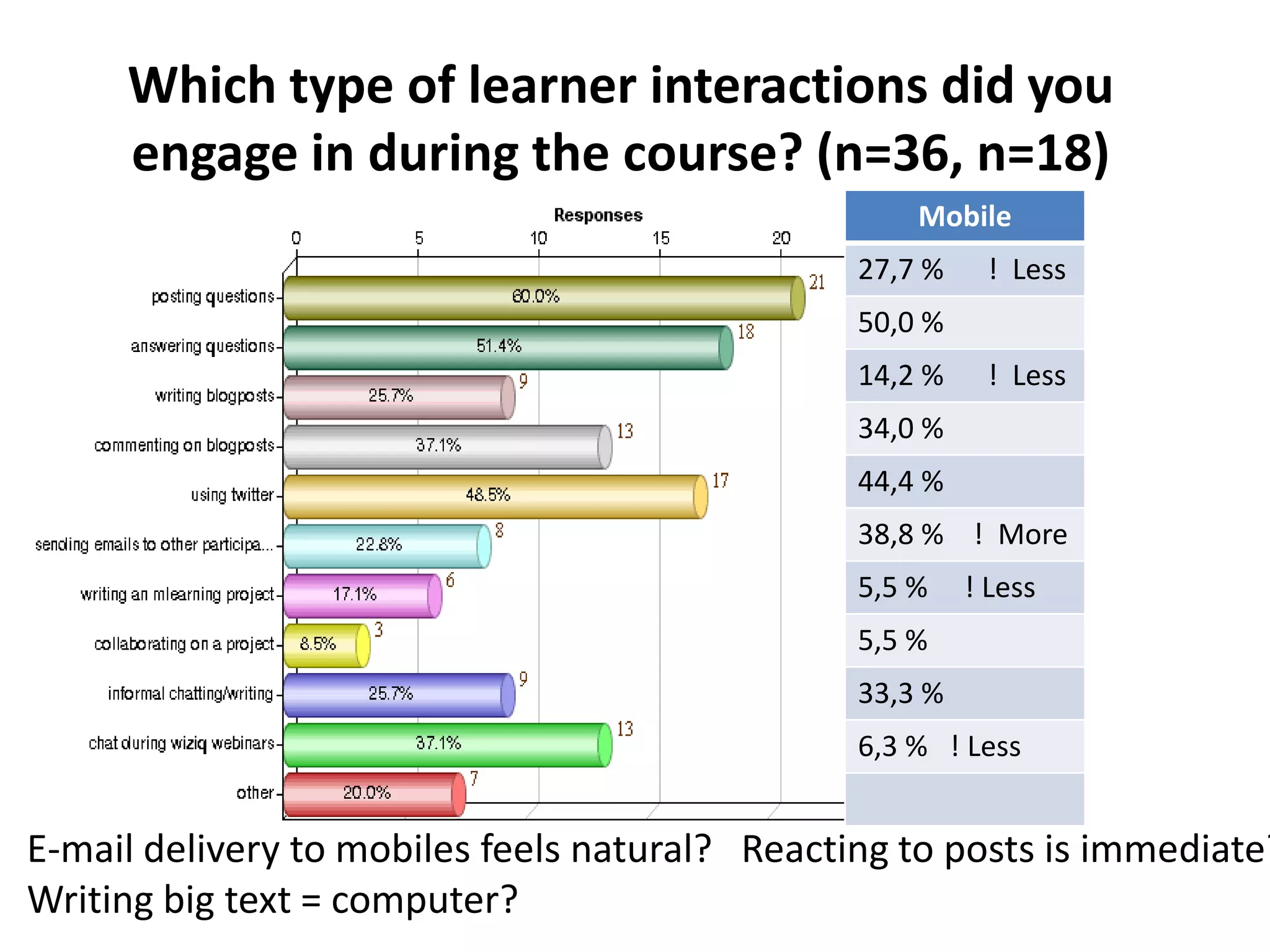
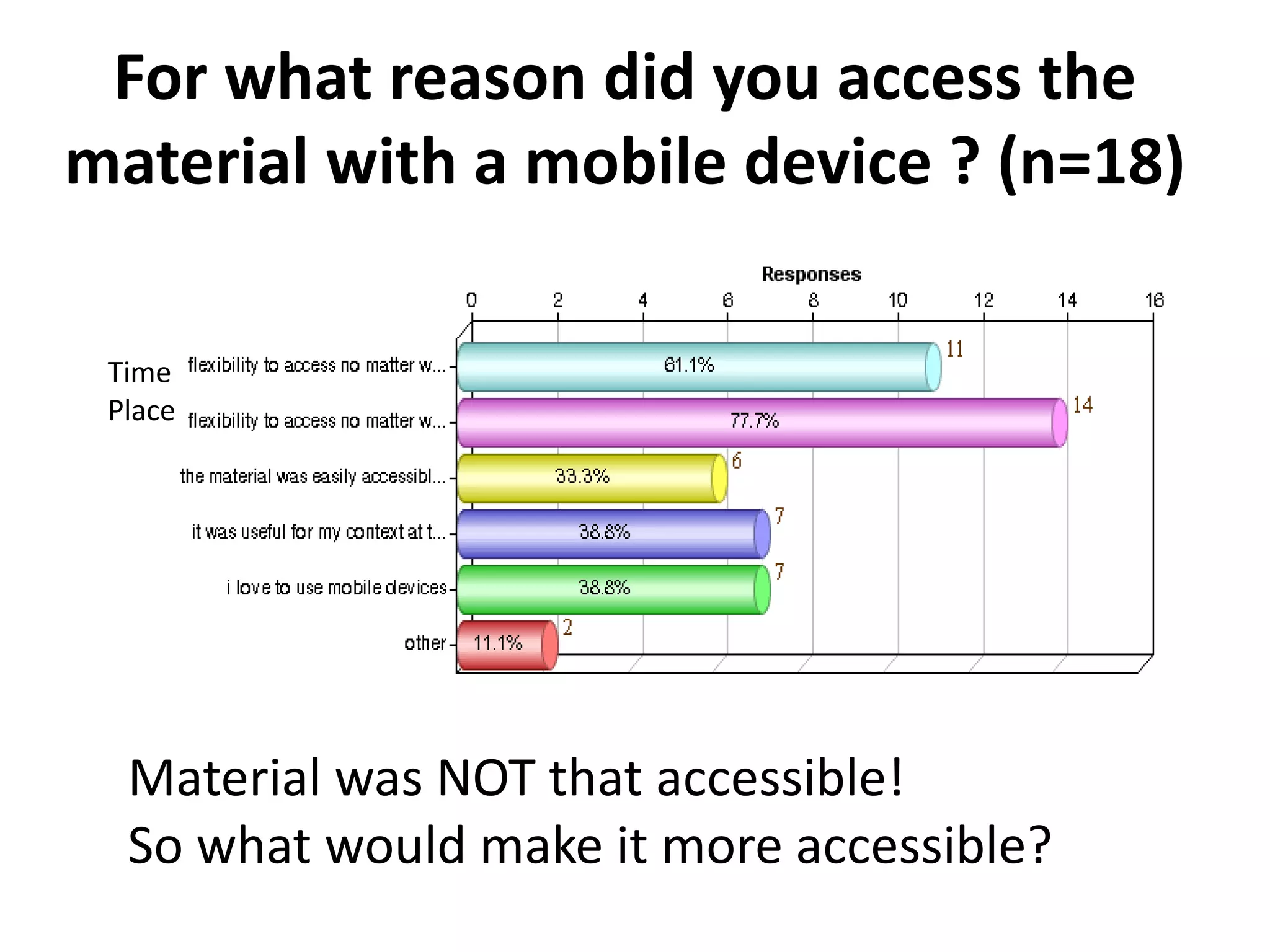
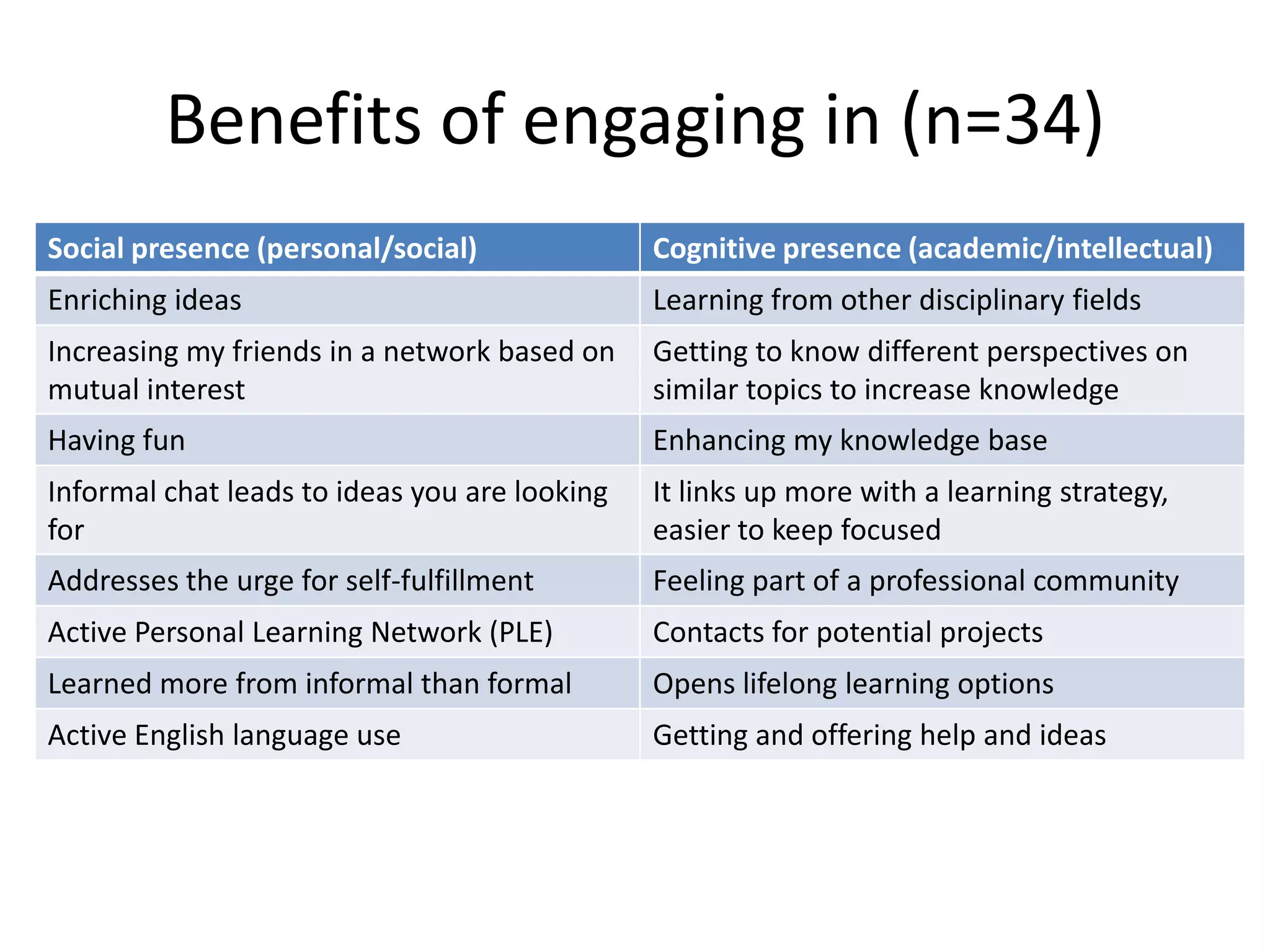
The document discusses the Mobimooc, a massive open online course focused on mobile learning, featuring diverse facilitator approaches and course architectures. It highlights participant interactions, the impact of mobile accessibility on social learning, and the evolution of MOOCs into two main formats: cMOOCs and xMOOCs. The research aims to analyze learner interactions in MOOCs, emphasizing the need for improved analytics and understanding of mobile learning dynamics.