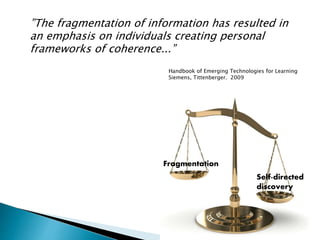
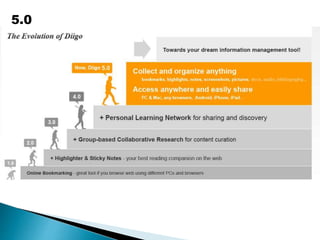
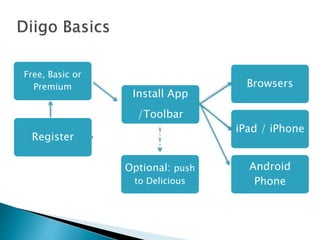
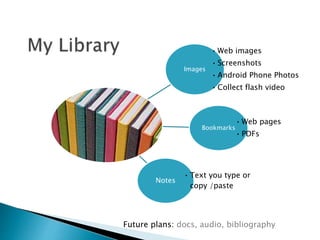
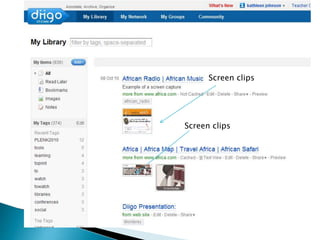
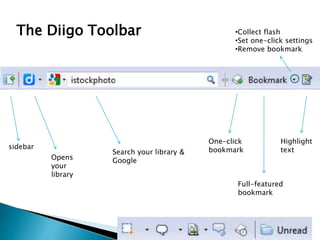
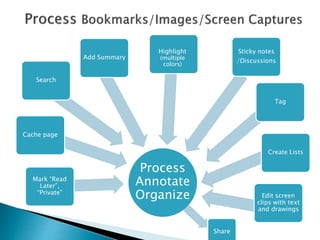
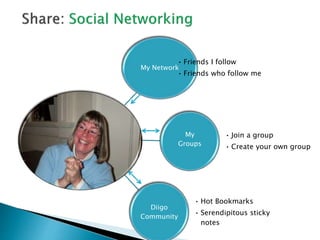
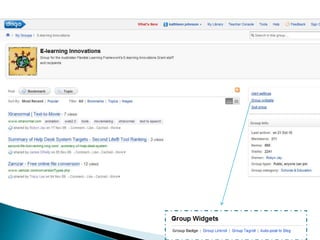
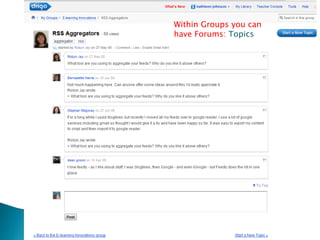
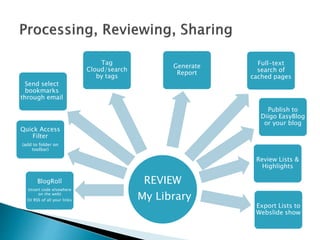
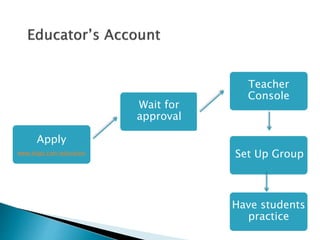
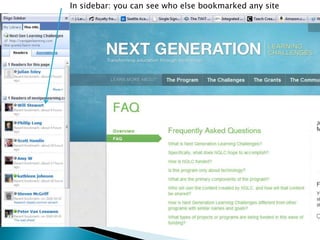
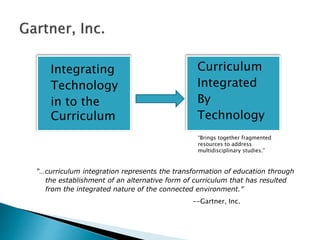
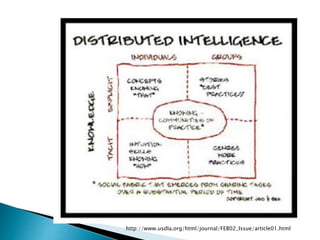
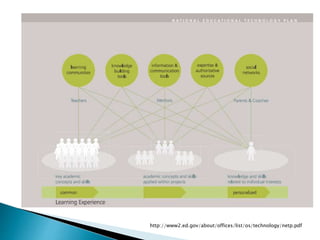
The document discusses the evolving role of technology in education, emphasizing the need for self-directed learning and the creation of personal learning networks. It highlights tools like Diigo that facilitate collaborative knowledge building, manage information overload, and allow for interaction among users. The shift towards integrating curriculum with technology reflects a need for more interactive and engaged educational practices in the digital age.