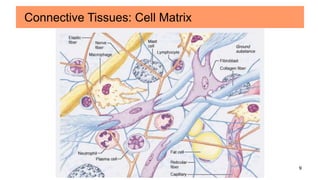
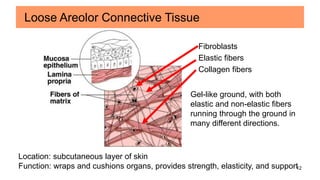
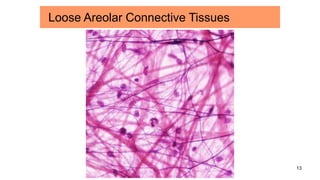
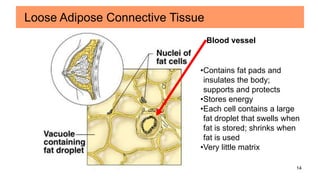
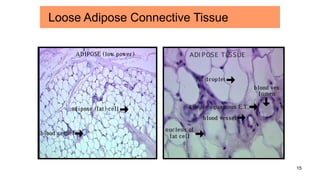
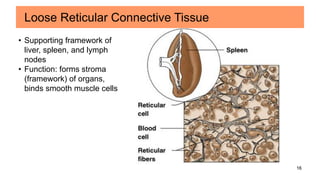
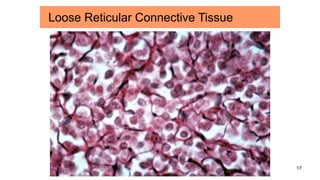
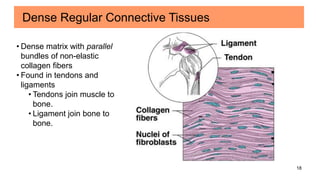
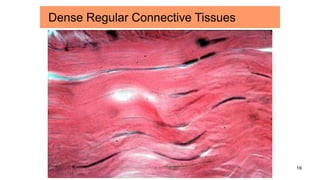
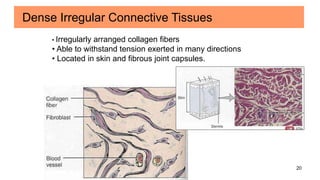
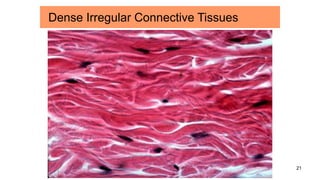
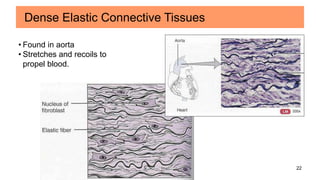
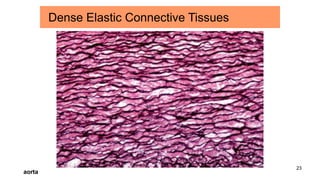
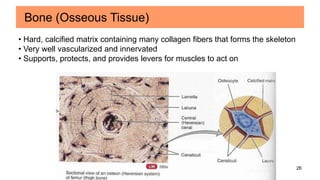
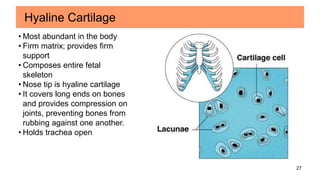
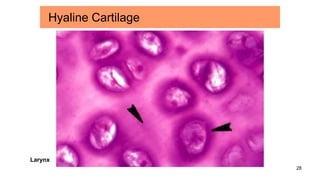
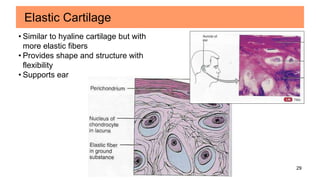
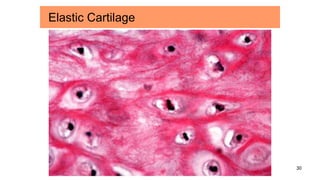
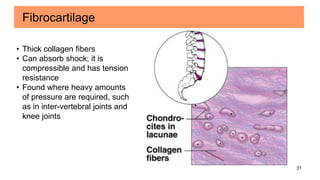
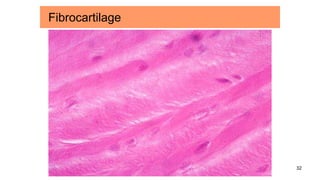
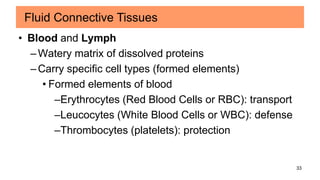
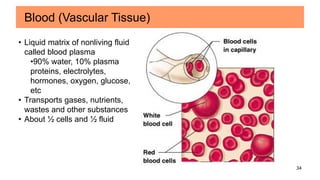
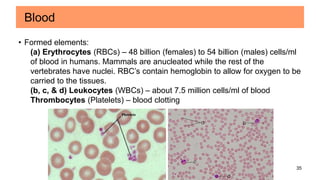
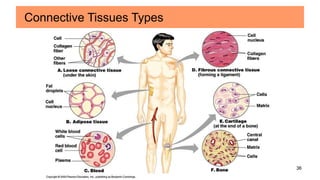
Connective tissues are the most abundant and diverse tissues in the body. They have three basic components: specialized cells, fibers made of proteins, and a ground substance. Connective tissues perform many important functions, including mechanical support, metabolic exchange, energy storage, thermal regulation, and defense. There are several major types of connective tissues classified based on their matrix, including connective tissue proper, fluid connective tissues, and supporting connective tissues. The main cells in connective tissues are fibroblasts, macrophages, adipocytes, mast cells, and stem cells.