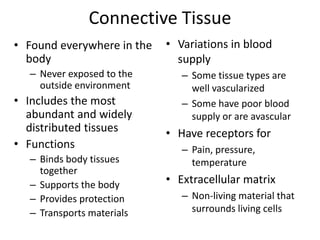
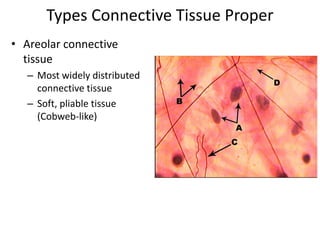
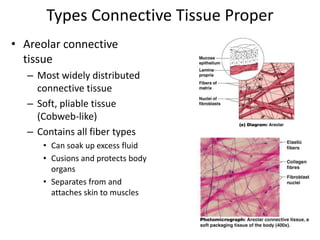
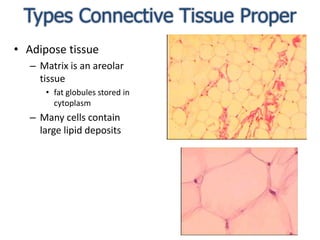
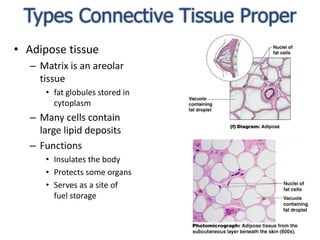
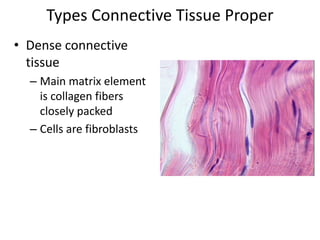
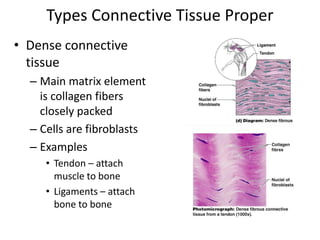
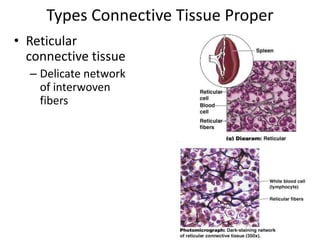
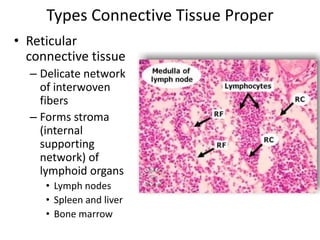
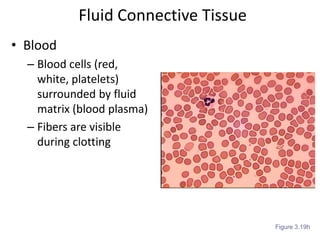
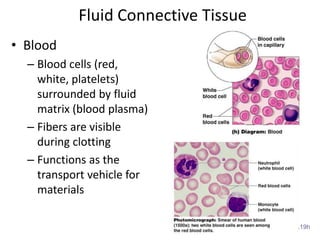
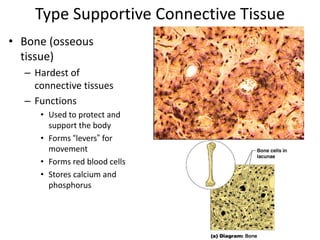
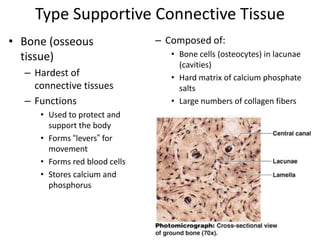
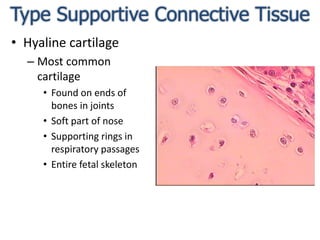
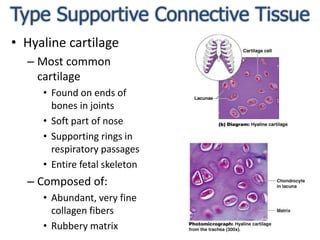
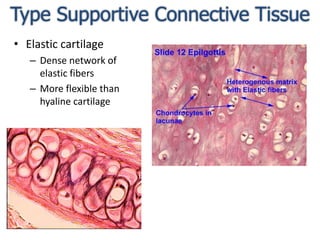
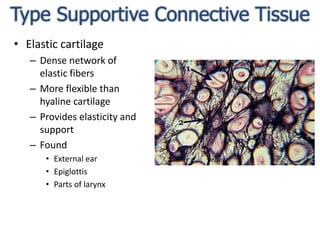
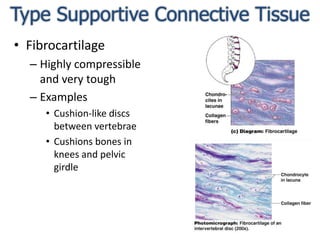
Connective tissue is found throughout the body and binds tissues together. It has various types including connective tissue proper, fluid connective tissue, and supportive connective tissue. Connective tissue proper contains fibroblasts, macrophages, mast cells, and an extracellular matrix with ground substance and fibers like collagen, elastic, and reticular fibers. It includes areolar, adipose, dense, and reticular connective tissues. Fluid connective tissue includes blood with its fluid plasma and blood cells. Supportive connective tissues are bone, hyaline cartilage, elastic cartilage, and fibrocartilage which provide structure and support.