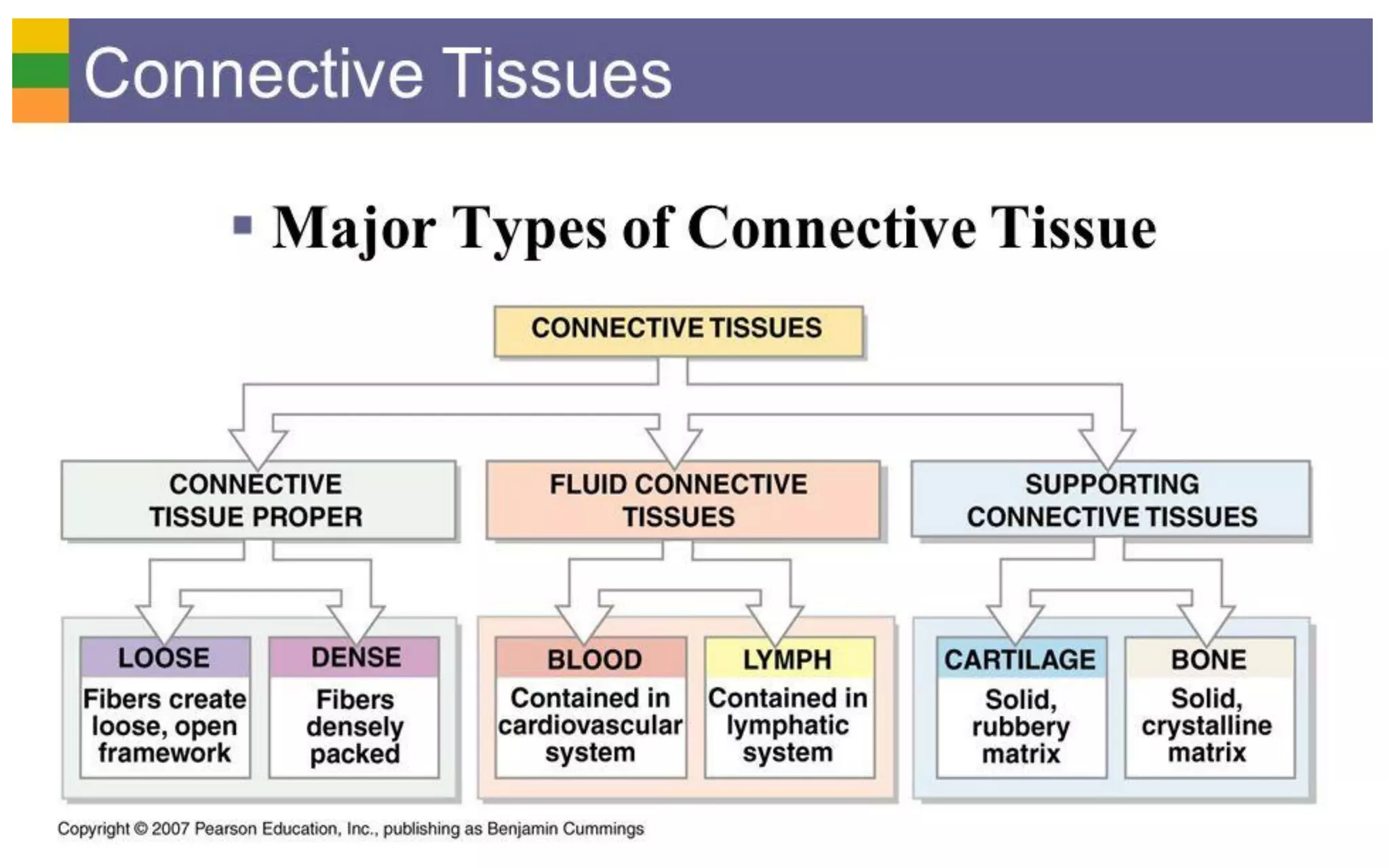
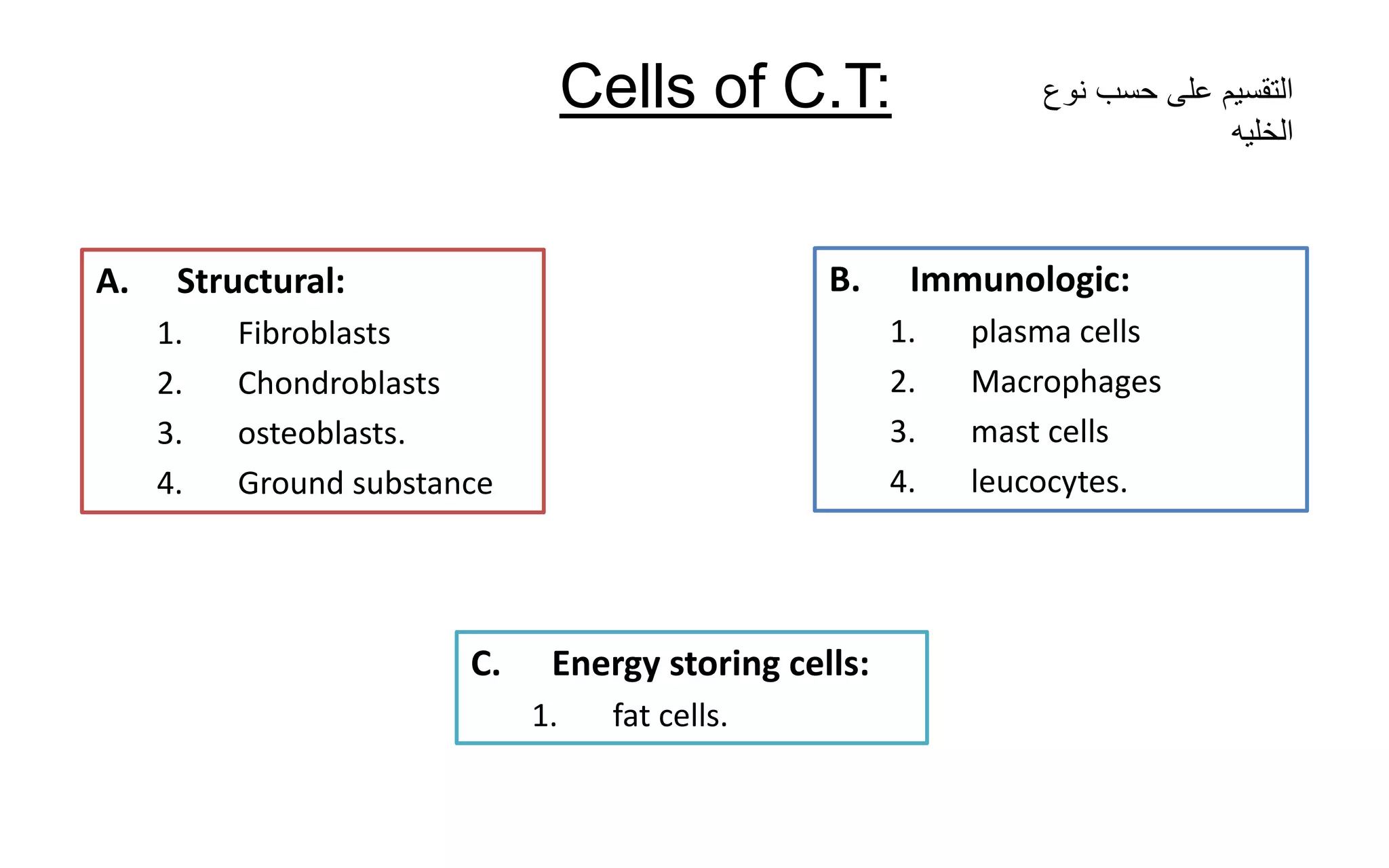
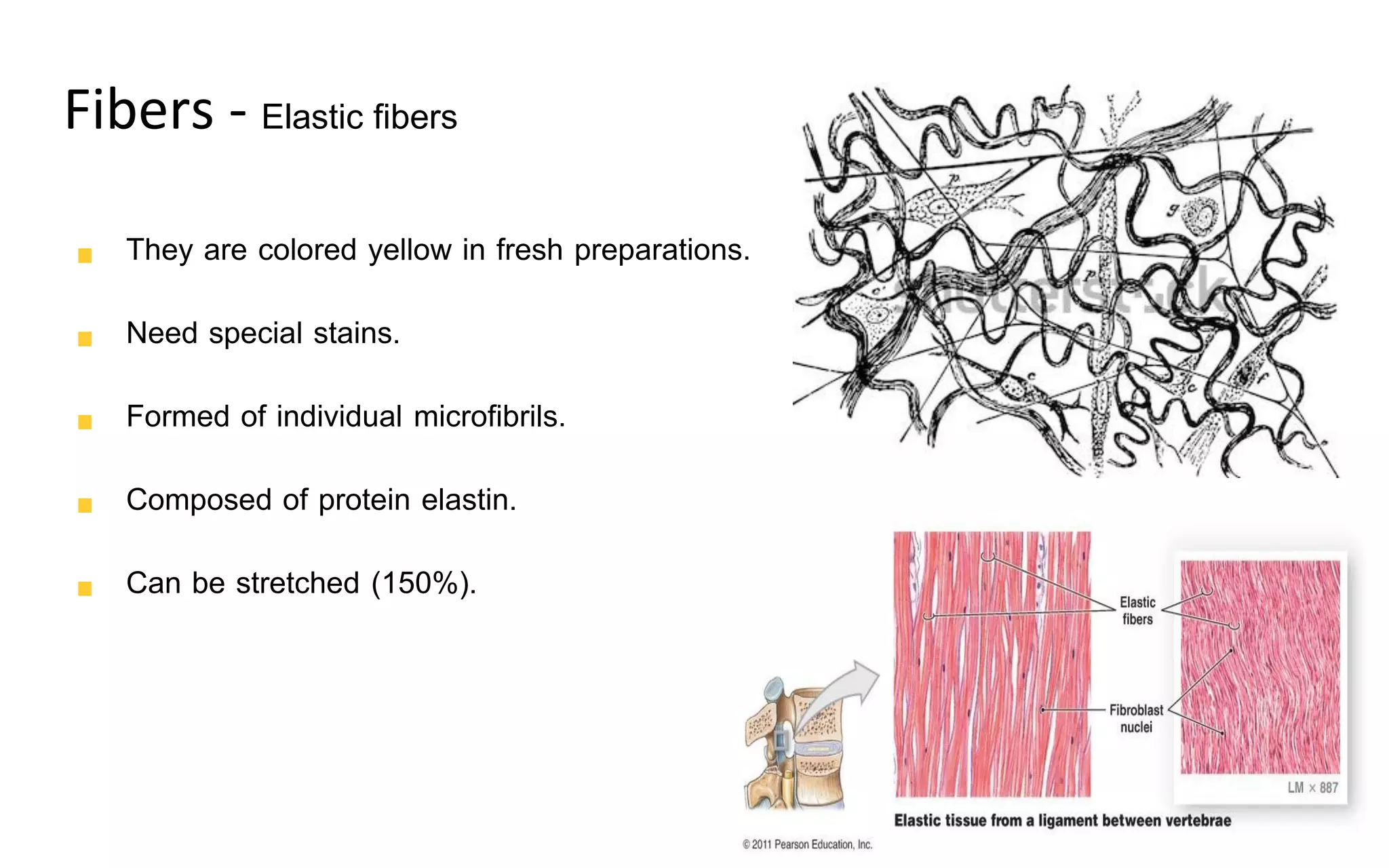
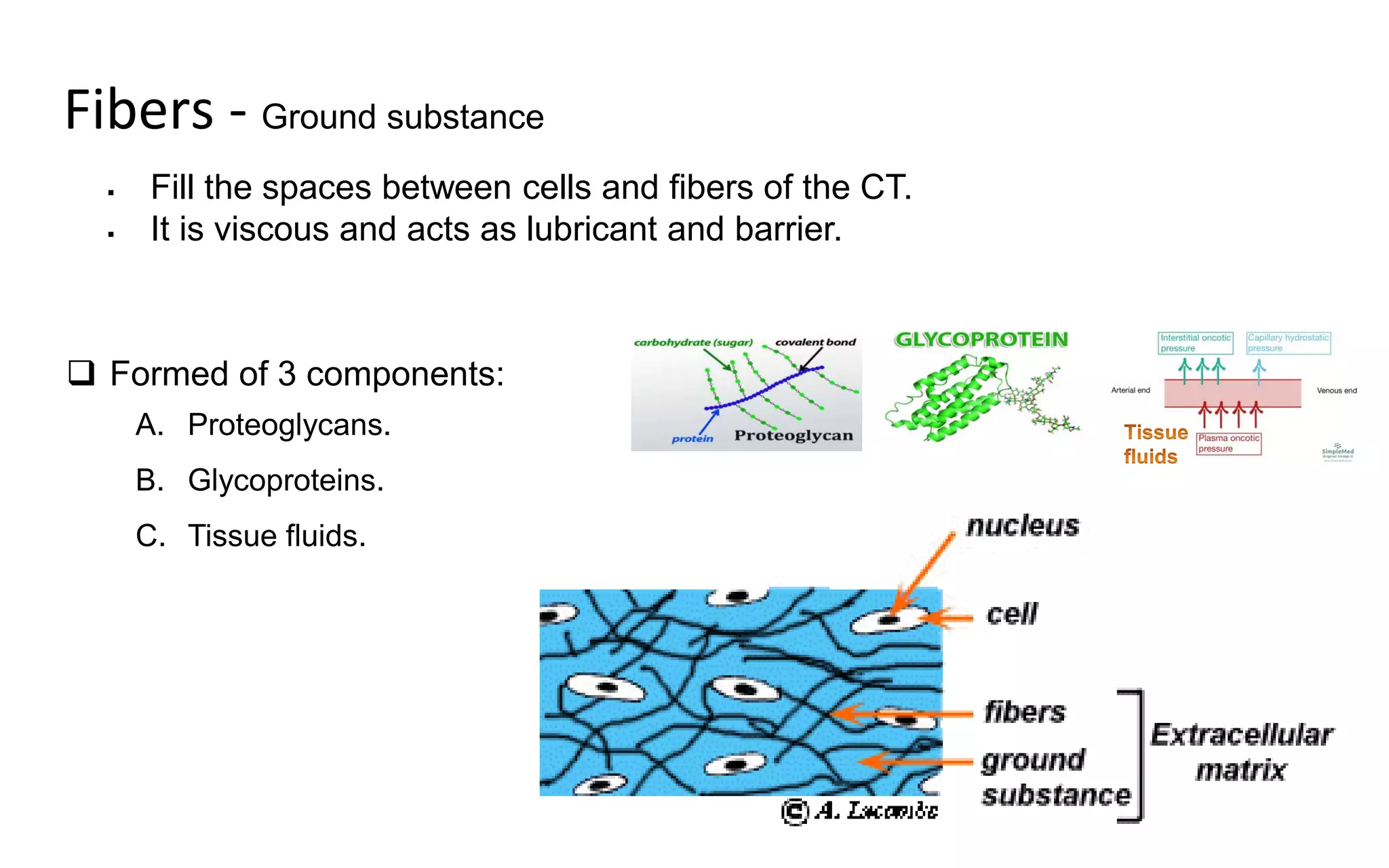
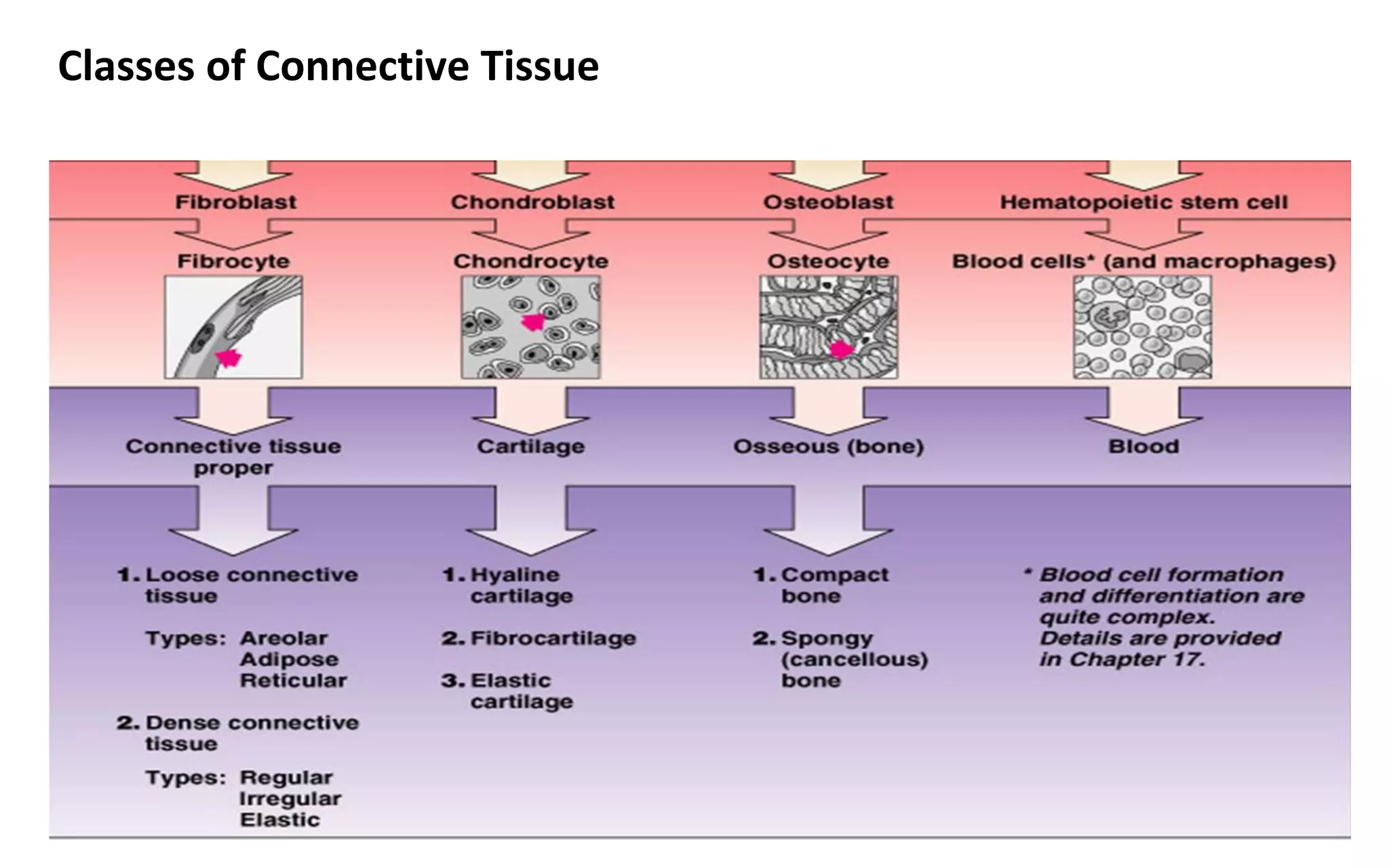
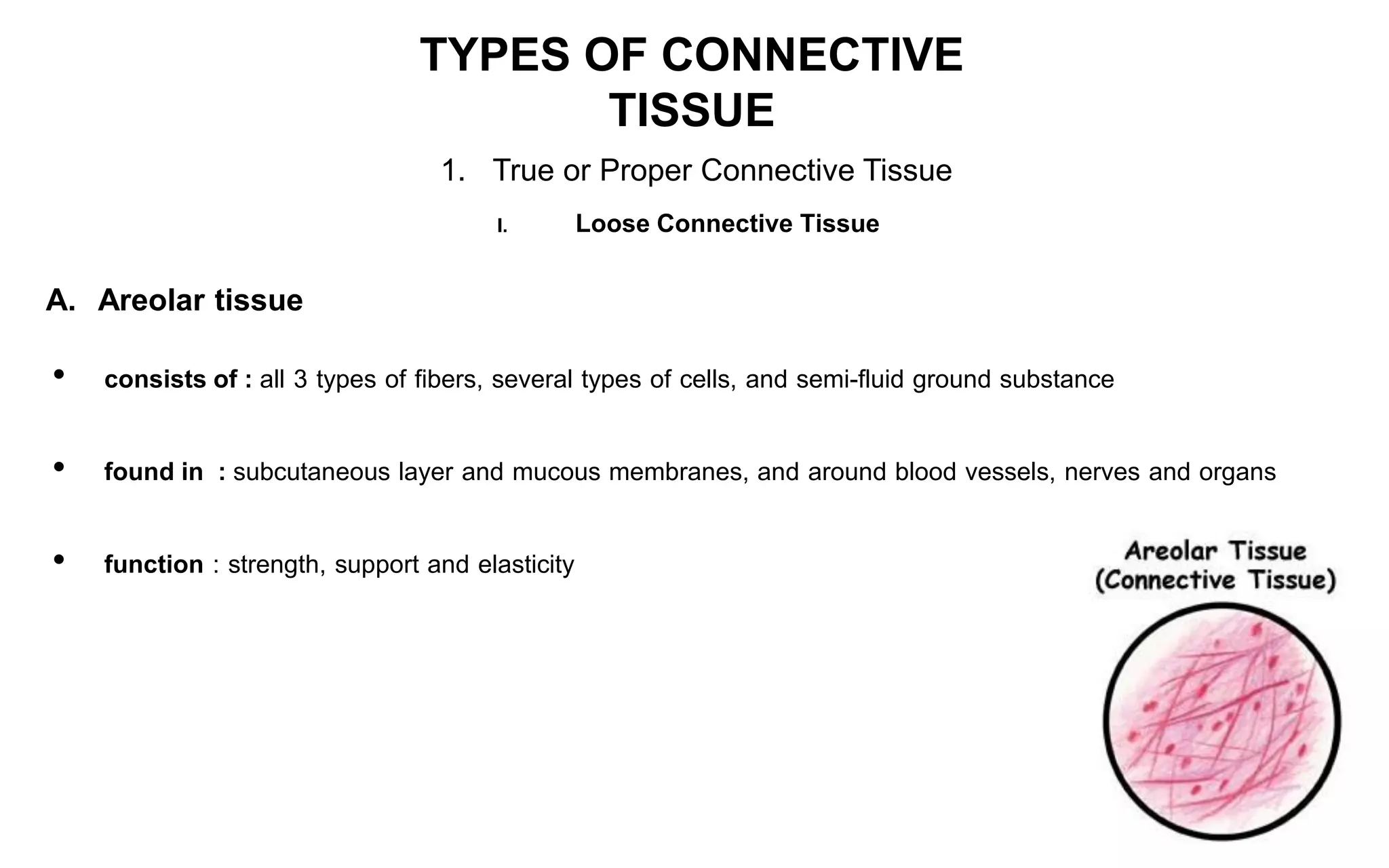
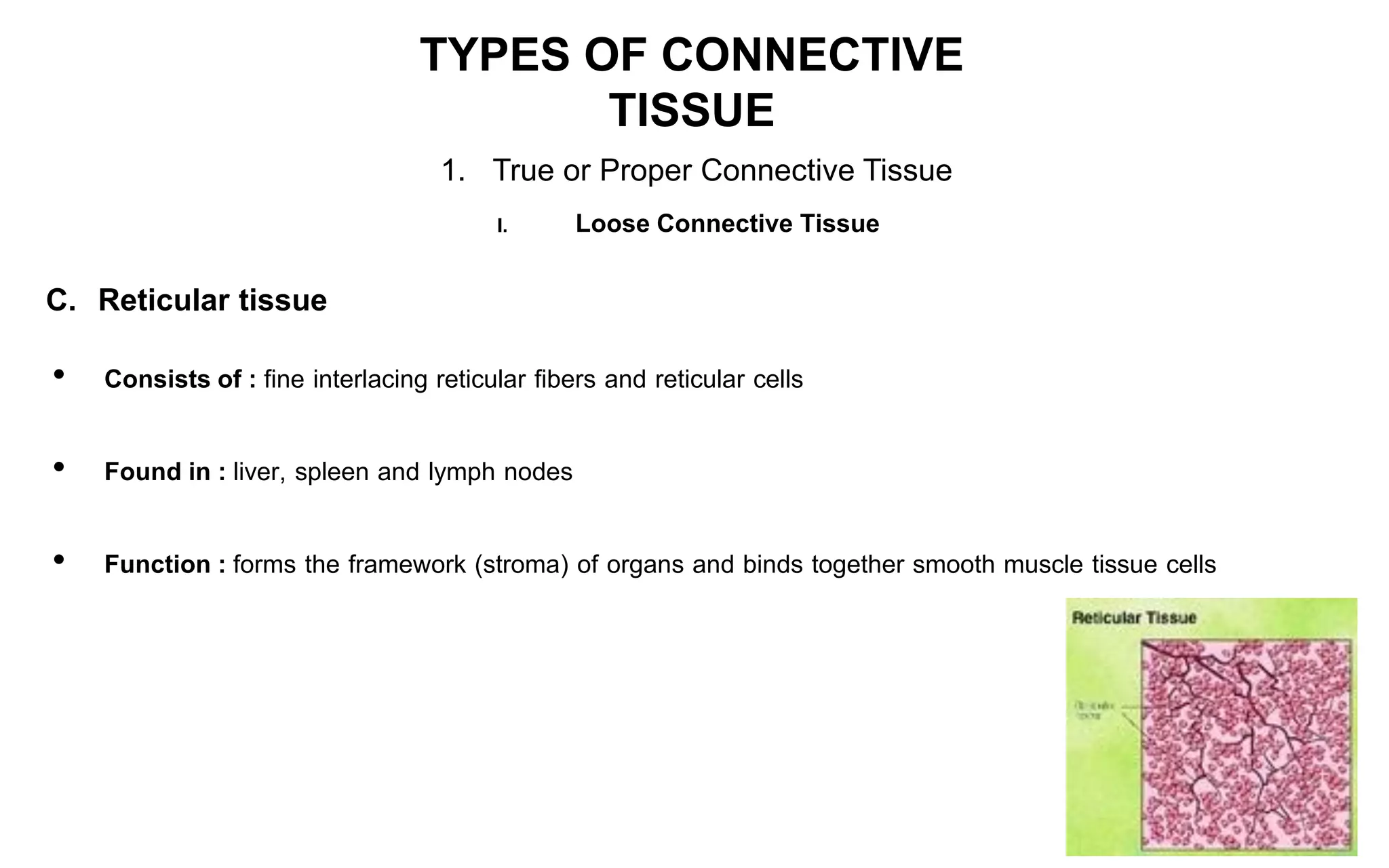
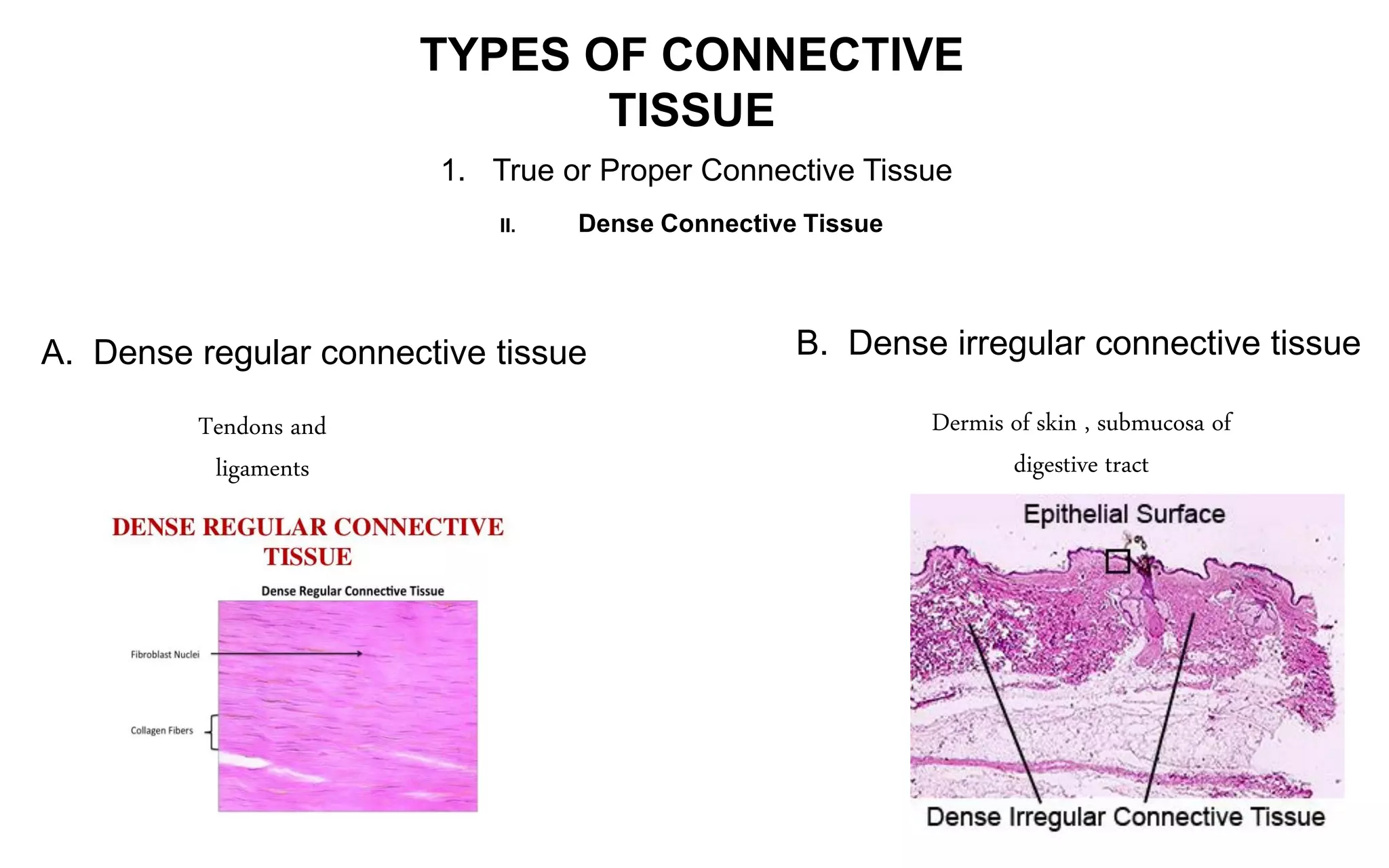
There are four main types of tissue: epithelial, connective, nervous, and muscular. Connective tissue forms a matrix beneath epithelial layers and supports organs. It is composed of cells and an extracellular matrix containing fibers and ground substance. There are several classes of connective tissue including true connective tissue which is divided into loose tissues like areolar and adipose tissue, and dense tissues like tendons.