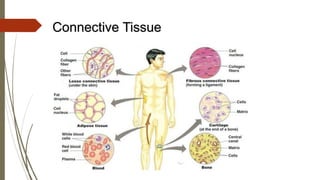
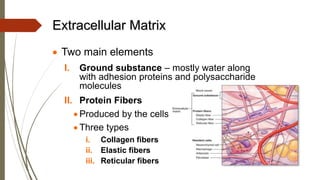
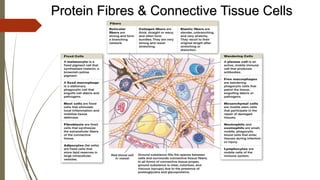
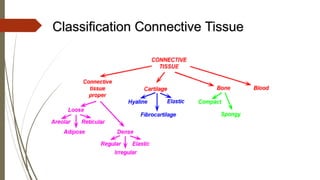
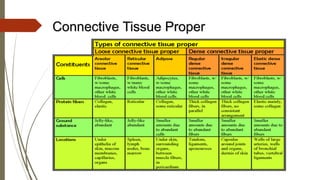
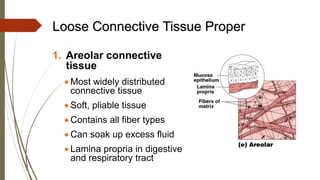
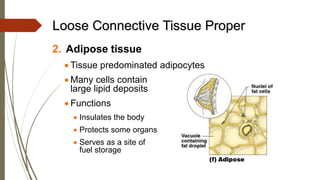
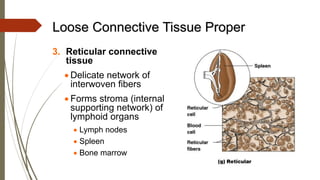
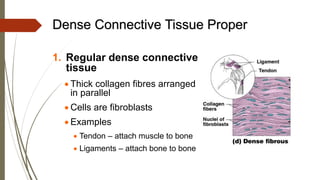
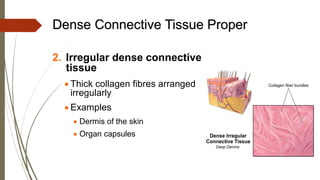
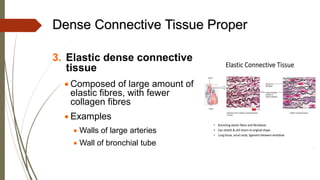
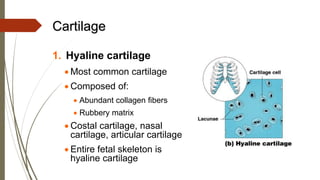
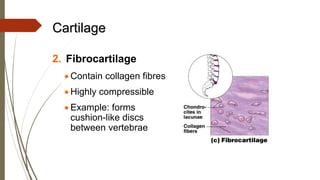
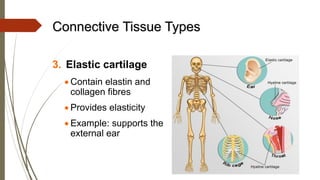
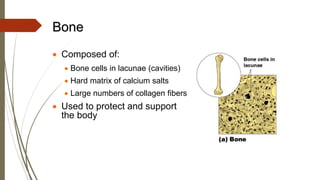
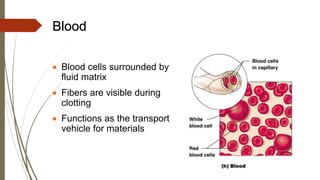
Connective tissue is found throughout the body and includes the most abundant and widely distributed tissues. It functions to bind tissues together, support the body, and provide protection. Connective tissue consists of an extracellular matrix and cells. The matrix contains ground substance and protein fibers like collagen, elastic, and reticular fibers. Connective tissue is classified into connective tissue proper, cartilage, bone, and blood. The main types of connective tissue proper are loose connective tissue (areolar, adipose, reticular) and dense connective tissue (regular, irregular, elastic).