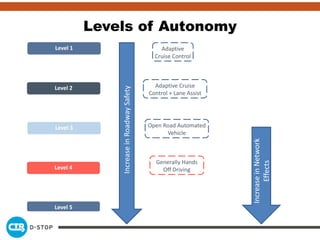
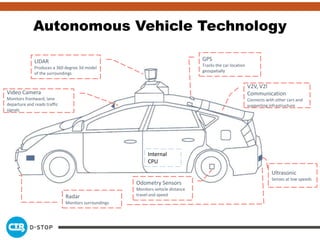
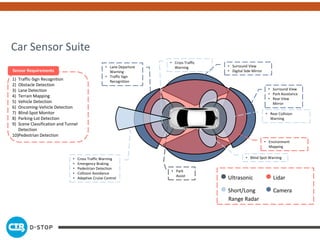
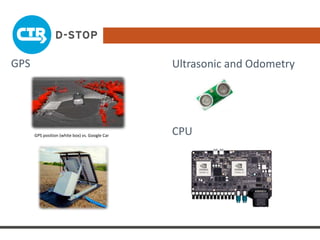
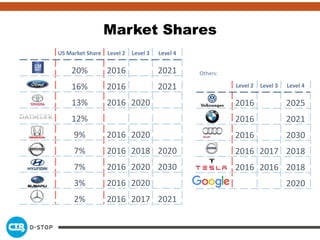
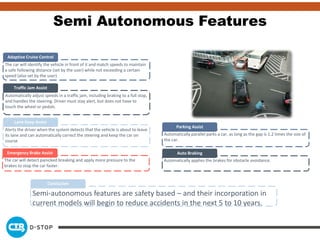
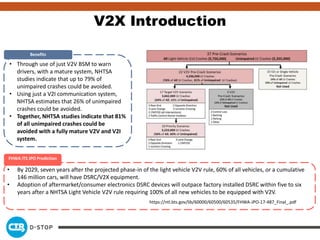
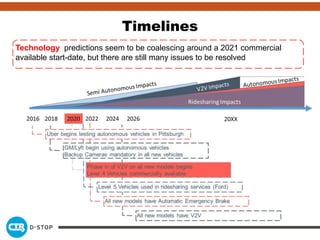
The document discusses connected and autonomous vehicles, detailing their definitions, levels of autonomy, and the necessary sensor technologies for their operation. It outlines semi-autonomous features that enhance safety and reduce accident rates, projecting significant crash avoidance percentages with mature vehicle-to-vehicle (V2V) and vehicle-to-infrastructure (V2I) systems. The timeline suggests that by 2029, a substantial portion of vehicles will be equipped with dedicated short-range communication (DSRC) for V2V capabilities.