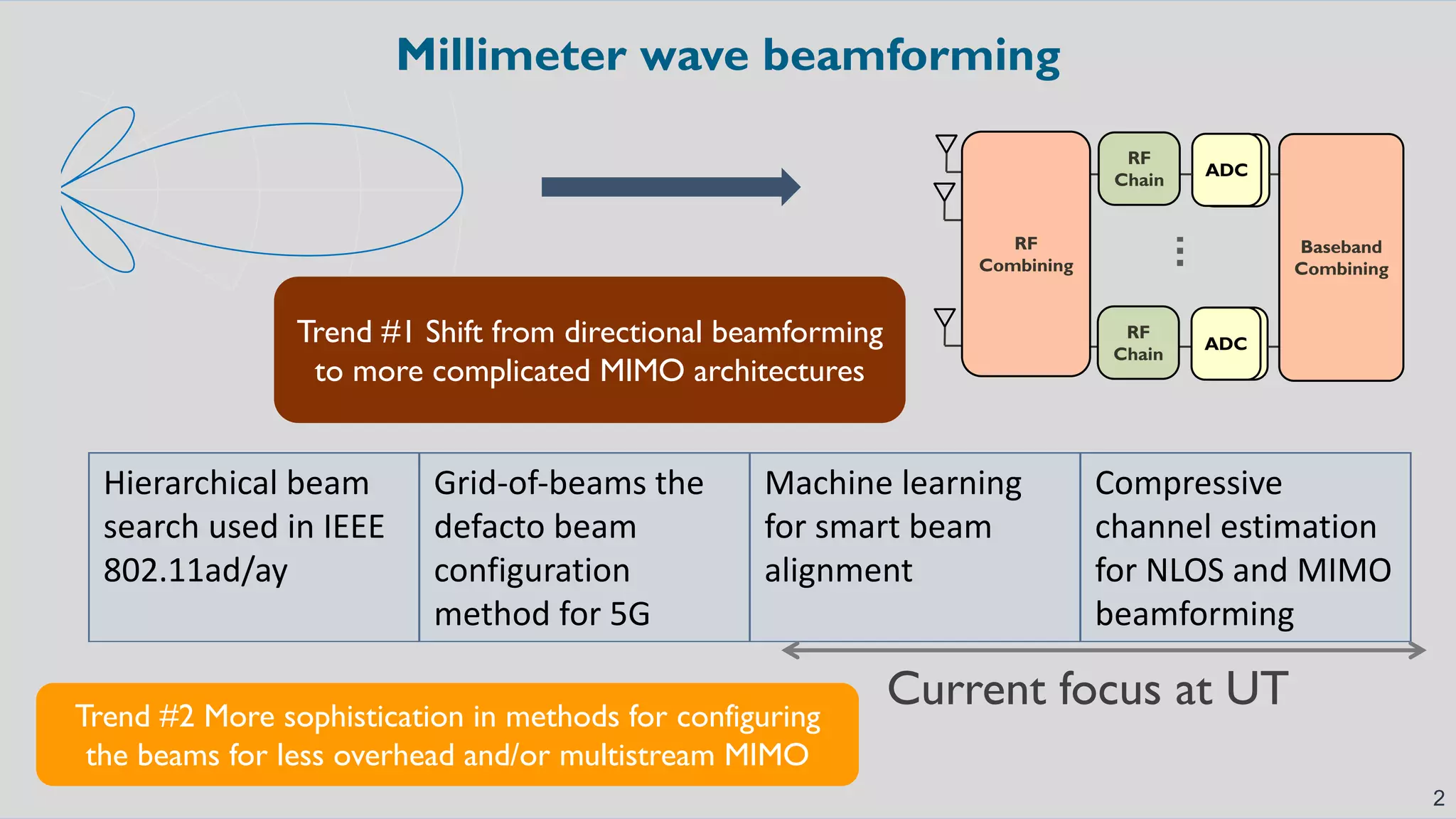
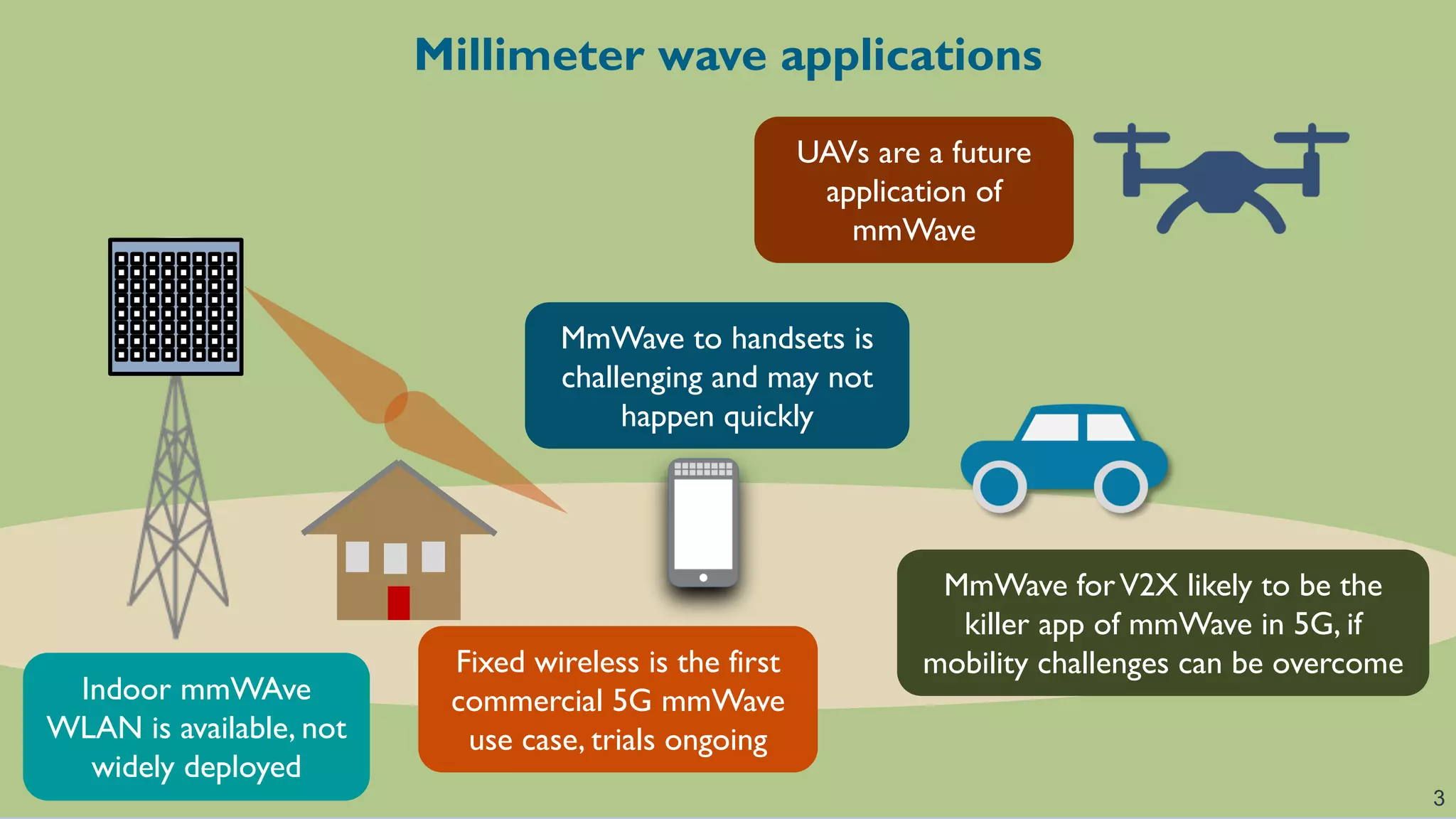
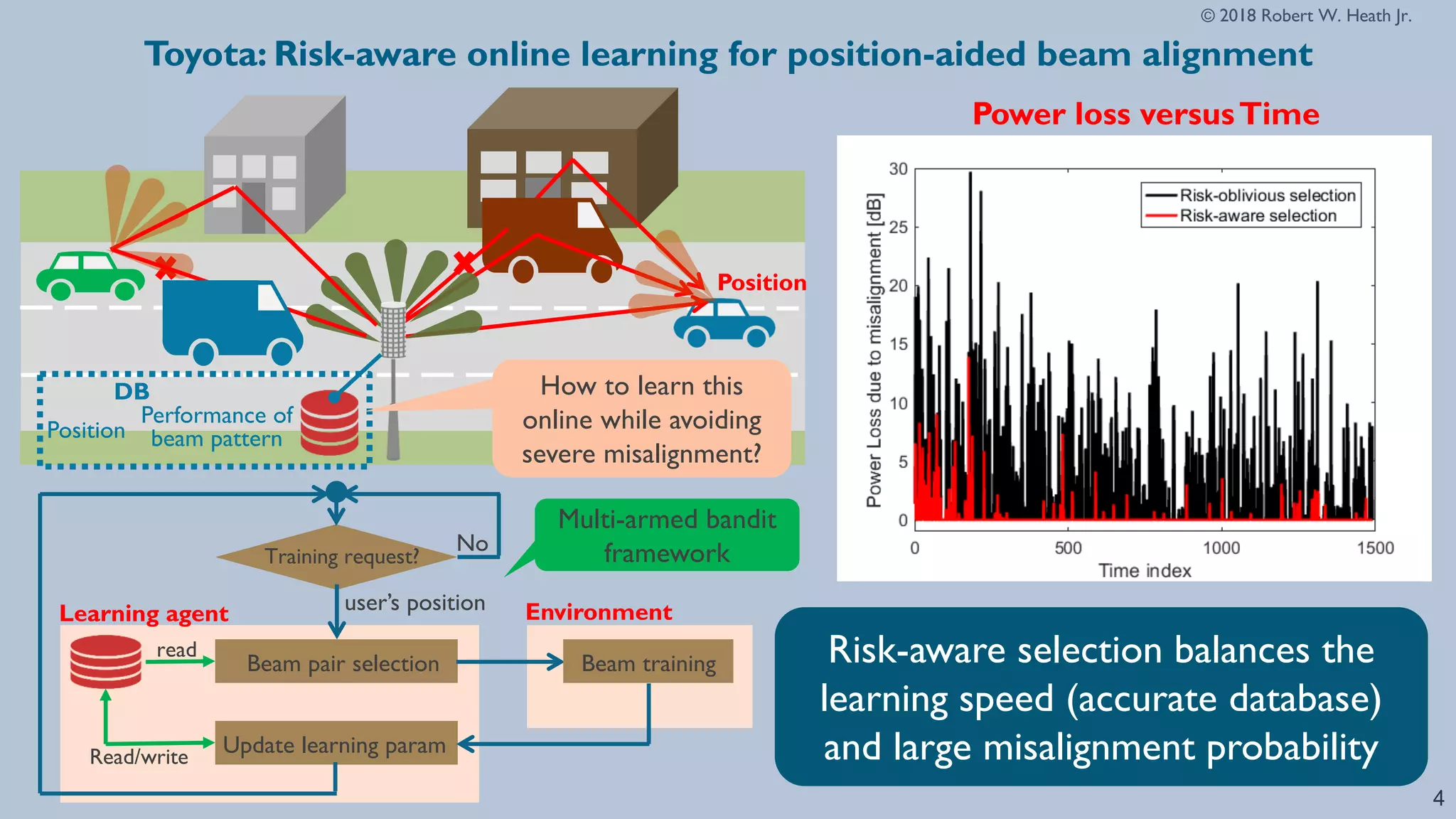
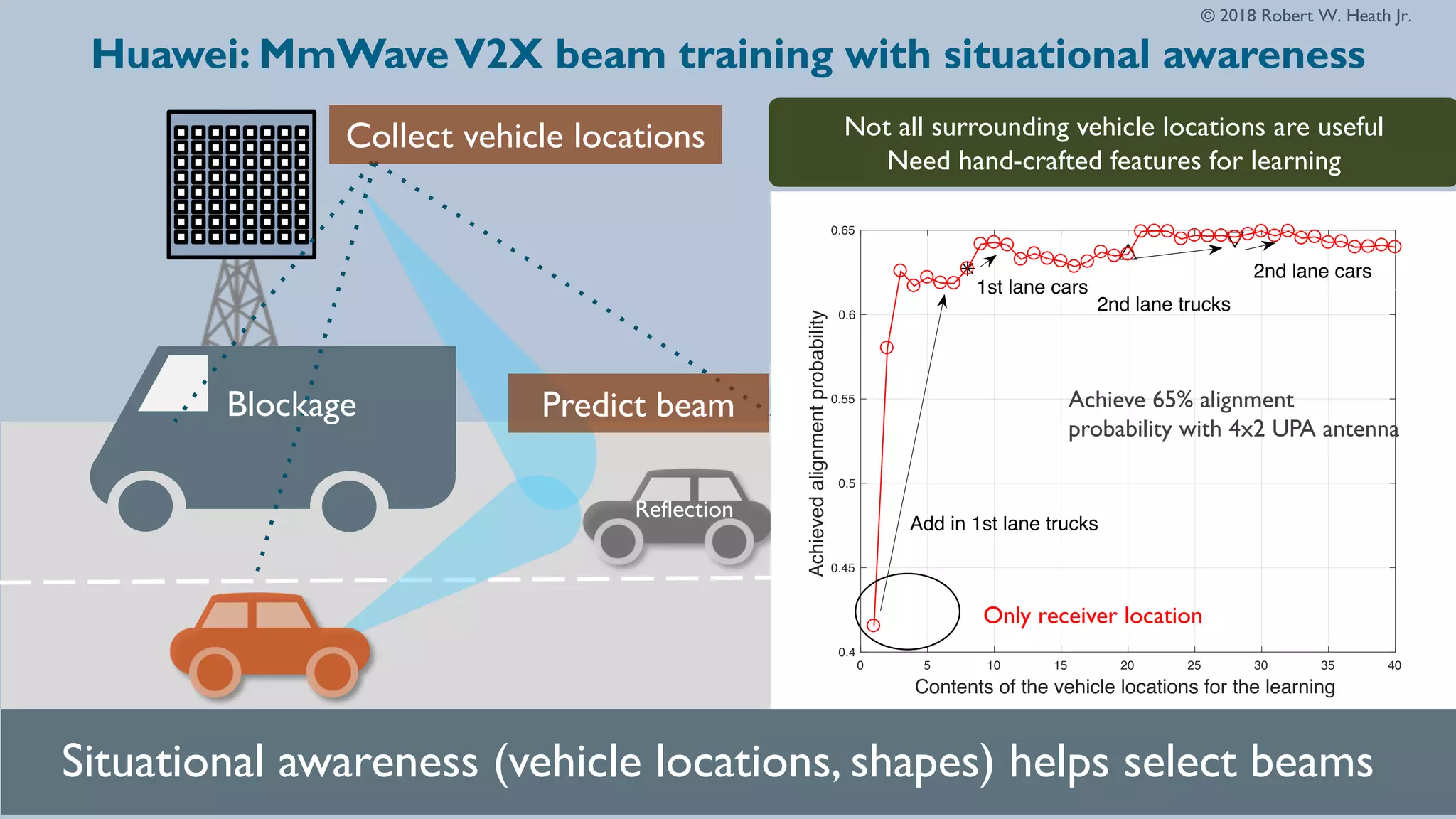
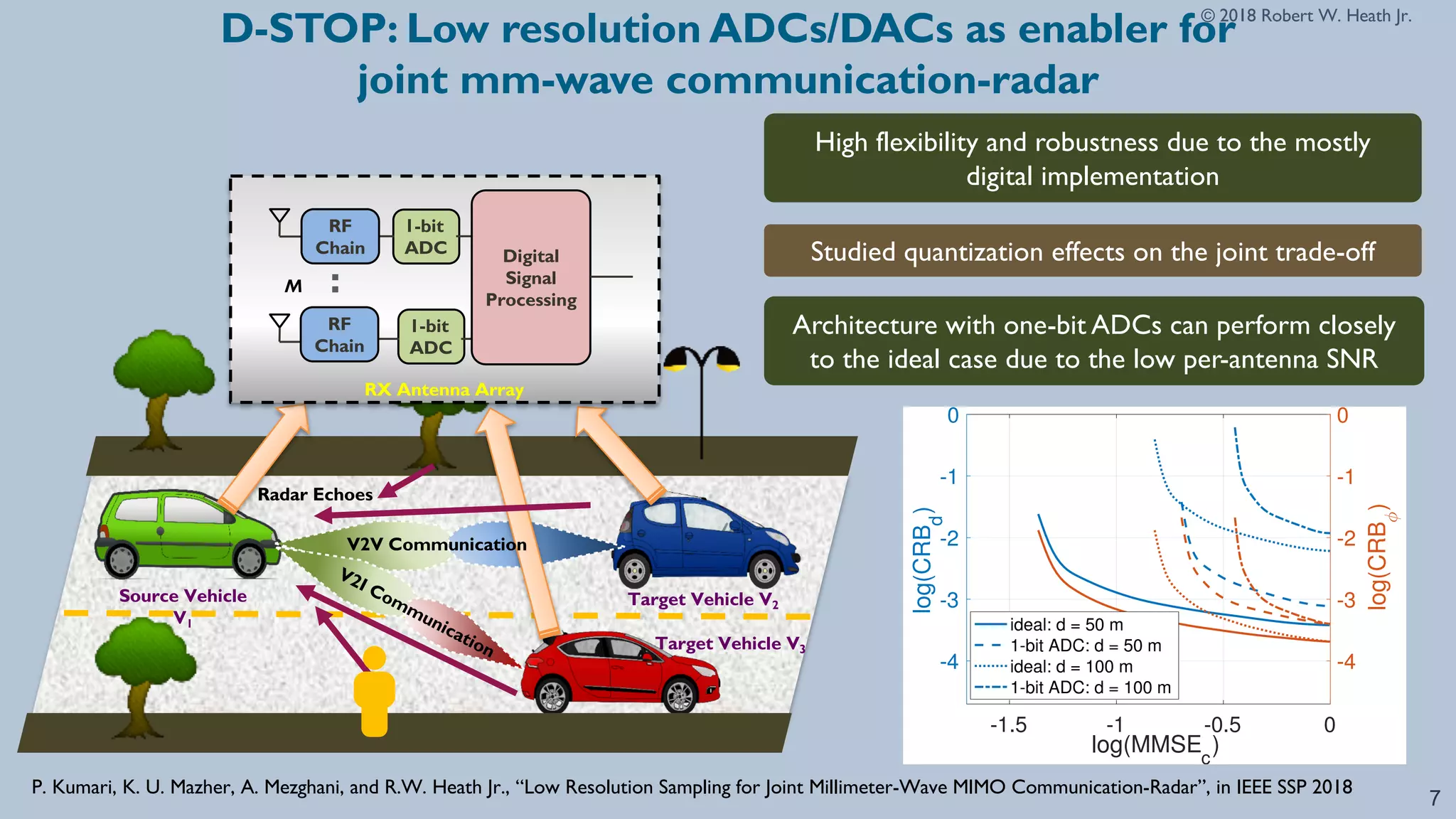
The document discusses advancements in millimeter wave (mmWave) technology for vehicle-to-everything (V2X) communications, highlighting significant research conducted at the University of Texas. It covers key applications such as fixed wireless, UAVs, and the challenges of beam alignment using machine learning methods. The research also explores using low-resolution ADCs for joint communication and radar applications, indicating potential for improved performance even with limited resources.