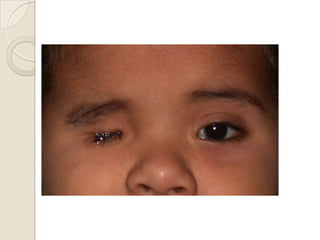
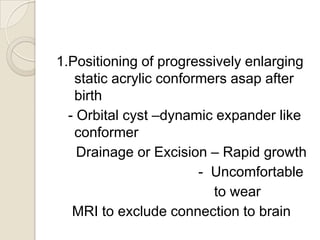
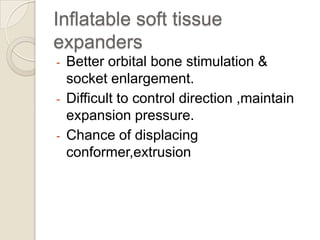
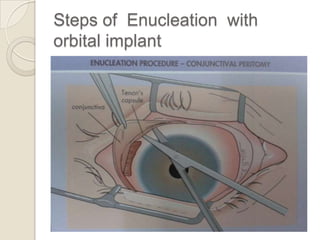
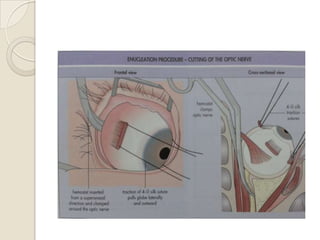
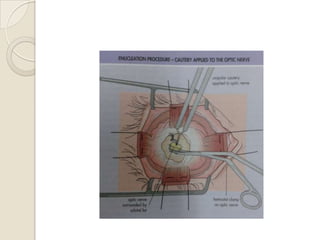
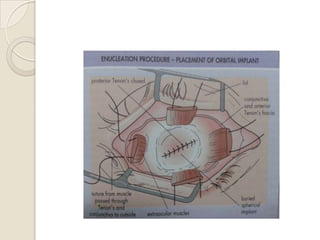
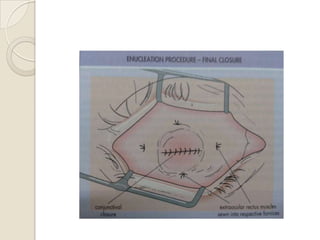
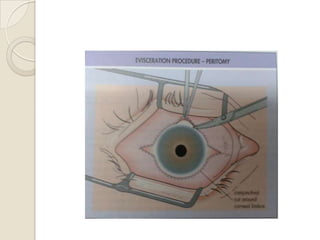
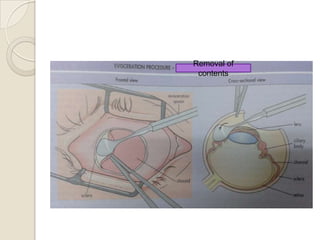
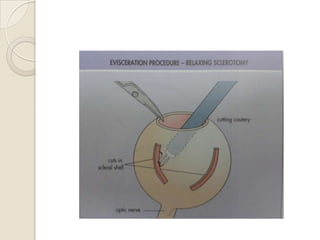
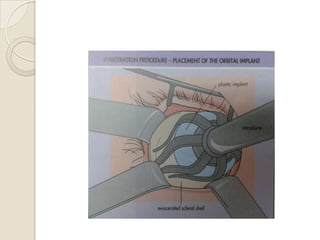
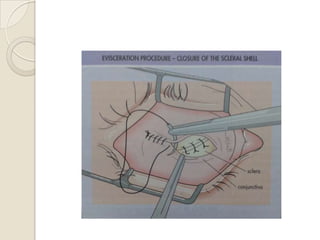
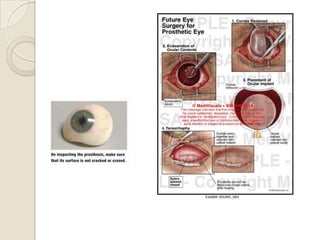
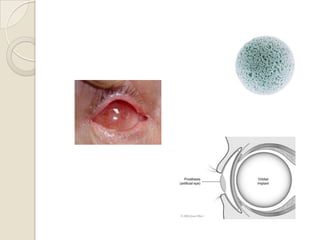
This document discusses congenital anophthalmia and recent advances in its management. It describes how the introduction of hydrogel socket expanders and orbital expanders has modified the rehabilitation approach. The goals of treatment are to simultaneously expand soft tissues and orbital bones to replace lost volume, maintain orbital structure, and allow prosthesis motility. Various types of orbital implants and expanders are discussed, including advantages and disadvantages. Guidelines for successful socket reconstruction with adequate volume, fornices, eyelid tone and prosthesis motility and comfort are provided.