Pacg
- 1. PRIMARY ANGLE CLOSURE GLAUCOMA MAJ F M ASHEKULLAH FCPS PART-11 TRAINEE IN OPHTHALMOLOGY
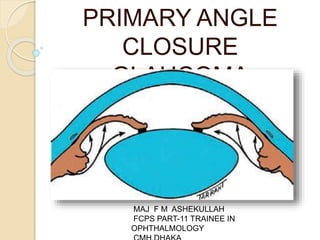
- 2. The term ‘angle closure’ refers to occlusion of the trabecular meshwork by the peripheral iris (iridotrabecular contact – ITC), obstructing aqueous outflow. PACG may be responsible for up to half of all cases of glaucoma globally
- 3. Classification • Primary angle closure Suspect( PAC-Suspe • Primary angle Closure (PAC) • Primary Angle-Closure Glaucoma(PACG)
- 4. Primary angle closure suspect (PACS) ○ Gonioscopy shows posterior meshwork ITC in three or more quadrants but no PAS. ○ Normal IOP, optic disc and visual field. - The risk of PACG at 5 years may be around 30%.
- 6. Primary angle closure (PAC) ○ Gonioscopy shows three or more quadrants of ITC with raised IOP and/or PAS or excessive pigment smudging on the TM. ○ Normal optic disc and field.
- 8. Primary angle-closure glaucoma (PACG) ○ ITC in three or more quadrants, with glaucomatous optic neuropathy. ○ Optic nerve damage may not appear as typical glaucomatous cupping.
- 9. Mechanism Relative pupillary block ○ Failure of physiological aqueous flow through the pupil leads to a pressure differential between the anterior and posterior chambers anterior bowing of the iris . ○ The lens vault quantifies the portion of the lens located anterior to the anterior chamber angle
- 11. Non-pupillary block ○ Far Eastern patients. ○ deeper anterior chamber (AC) than pure pupillary block. ○ younger than those with pure pupillary block. ○ angle closure is not fully relieved by iridotomy. ○ plateau iris, and a thicker or more
- 12. ○ Plateau iris configuration is characterized by a flat or only slightly convex central iris plane. A characteristic ‘double hump’ sign is seen on indentation gonioscopy. ○ Plateau iris syndrome describes the persistence of gonioscopic angle closure despite a patent iridotomy in a patient with morphological plateau iris
- 14. • Reduced aqueous outflow in angle closure caused by the following mechanisms : ○ Appositional obstruction by the iris. ○ Degeneration or damage of the TM itself ○ Permanent occlusion of the TM by PAS
- 15. Risk factors • Age • Family history • Gender. Females >males. • Axial length • Race.Far Eastern and Indian Asians • Refraction.Up to one in six patients with hypermetropia of one dioptre or more are primary angle closure suspects - so routine gonioscopy should be considered in all hypermetropes.
- 17. Diagnosis Symptoms • Most are asymptomatic. • intermittent mild symptoms of blurring (‘smoke-filled room’) and haloes (‘rainbow around lights’) or acutely with markedly decreased vision, redness and ocular/periocular pain and headache etc.
- 18. • Precipitating factors include - watching television in a darkened room, - pharmacological mydriasis - semiprone position (e.g. reading) - acute emotional stress and -occasionally systemic medication
- 19. Signs • Chronic presentation ○ VA is normal unless damage is advanced. ○ The AC is usually shallower in relative pupillary block than non-pupillary block. ○ IOP elevation may be only intermittent. ○ ‘Creeping’ angle closure ○ Intermittent ITC with discrete PAS ○ Optic nerve signs
- 20. • Acute primary angle closure (APAC) - VA is usually 6/60 to HM. - The IOP is usually very high (50–100 mmHg). - Conjunctival hyperaemia with violaceous circumcorneal injection. - Corneal epithelial oedema -The AC is shallow, and aqueous flare is usually present. - An unreactive mid-dilated vertically oval pupil
- 21. • Resolved APAC ○ Early: -low IOP -folds in Descemet membrane - optic nerve head congestion -choroidal folds.
- 22. ○ Late: -iris atrophy with a spiral-like configuration -glaukomflecken and other forms of cataract -irregular pupil due to iris sphincter/dilator damage -posterior synechiae - optic nerve may be normal or exhibit pallor and/or cupping
- 23. ○ The greater (i) the duration of an attack of APAC and (ii) the extent of post-APAC PAS the lower the likelihood of IOP control with medical treatment alone.
- 26. Investigation • Anterior segment OCT • Anterior chamber depth measurement • Biometry if lens extraction is considered. • Posterior segment ultrasonography • Provocative testing. ○ Pharmacological mydriasis ○ Dark room/prone provocative test (DRPPT):
- 27. Differential diagnosis of acute IOP elevation • Lens-induced angle closur • Malignant glaucoma • Neovascular glaucoma • Hypertensive uveitis • Scleritis (rarely episcleritis) • Pigment dispersion. • Pseudoexfoliation. • Orbital/retro-orbital lesions
- 28. Treatment PACS • Laser iridotomy • If significant ITC persists after iridotomy, options include observation (most), laser iridoplasty, and long-term pilocarpine prophylaxis, If symptomatic cataract is present, lens extraction PAC and PACG • Management is as for PACS • Medical treatment as for POAG may be
- 30. APAC • Initial treatment ○ supine position ○ Acetazolamide 500 mg intravenously if IOP >50 mmHg, and orally if IOP is <50 mmHg. ○ If treatment is intravenous an additional oral dose of acetazolamide 500 mg ○ A single dose of each of apraclonidine 0.5% or 1%, timolol 0.5%, and prednisolone 1% or dexamethasone 0.1% ○ Pilocarpine 2–4% one drop to the affected eye, repeated after half an hour; one drop of 1% into the fellow eye
- 31. • Resistant cases ○ Central corneal indentation ○ Further pilocarpine 2–4%, timolol 0.5%, apraclonidine 1% and topical steroid. ○ Mannitol 20% 1–2 g/kg intravenously over 1 hour ○ Early laser iridotomy or iridoplasty ○ Paracentesis can be performed ○ Surgical options: peripheral iridectomy, lens extraction, goniosynechialysis, trabeculectomy and cyclodiode.
- 34. • Subsequent medical treatment ○ Pilocarpine 2% four times daily to the affected eye and 1% four times daily to the fellow eye. ○ Topical steroid four times daily ○ Any or all of the following should be continued as necessary according to response: timolol 0.5% twice daily, apraclonidine 1% three times daily and oral acetazolamide 250 mg four times daily.
- 35. • Bilateral laser iridotomy is performed once an attack has been broken. • Trabeculectomy is occasionally necessary.
- 36. Follow up Repeat gonioscopy to look for chronic angle closure.
- 37. reference 1.Kanski’s clinical ophthalmology 2.American academy section 10 3.Parson’s diseases of the eye 4.Wilis eye manual