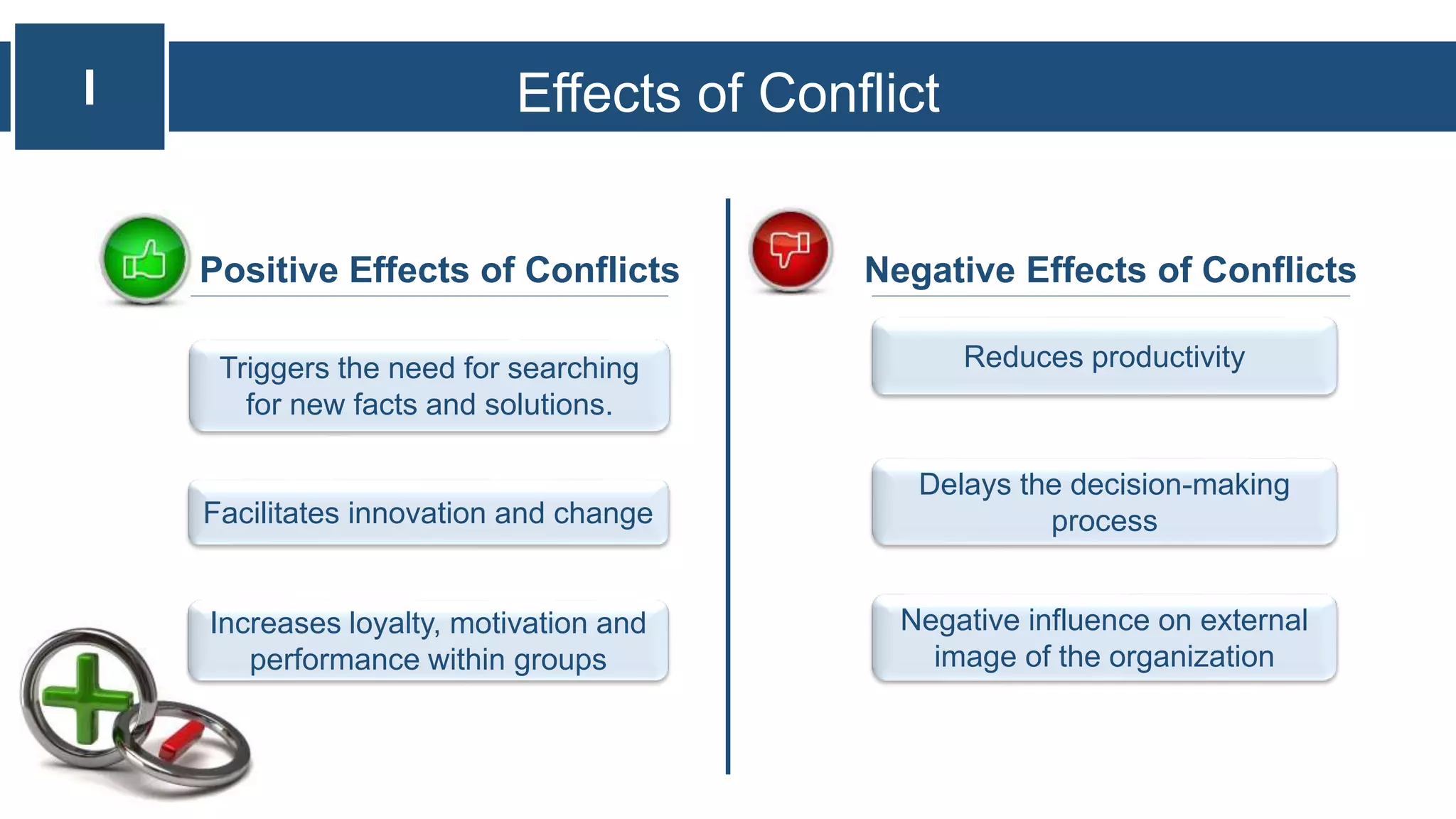
The document presents an exploration of conflict and conflict management, outlining its definitions, causes, effects, and various management styles. It discusses traditional, human relations, and integrationist views of conflict, emphasizing its inevitability and potential positive effects. Strategies for managing conflict are presented, highlighting preventive and curative measures essential for effective workplace interactions.