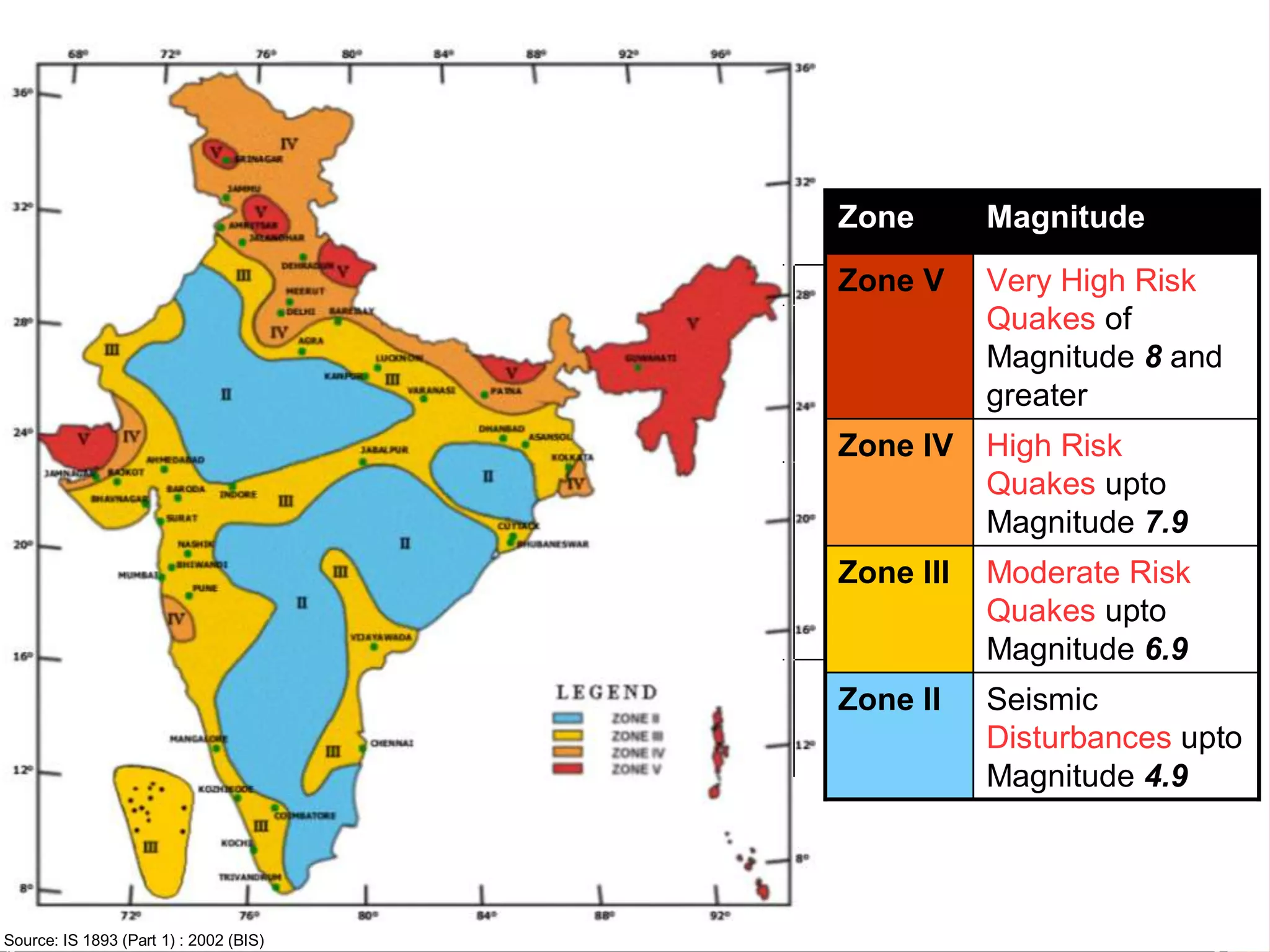
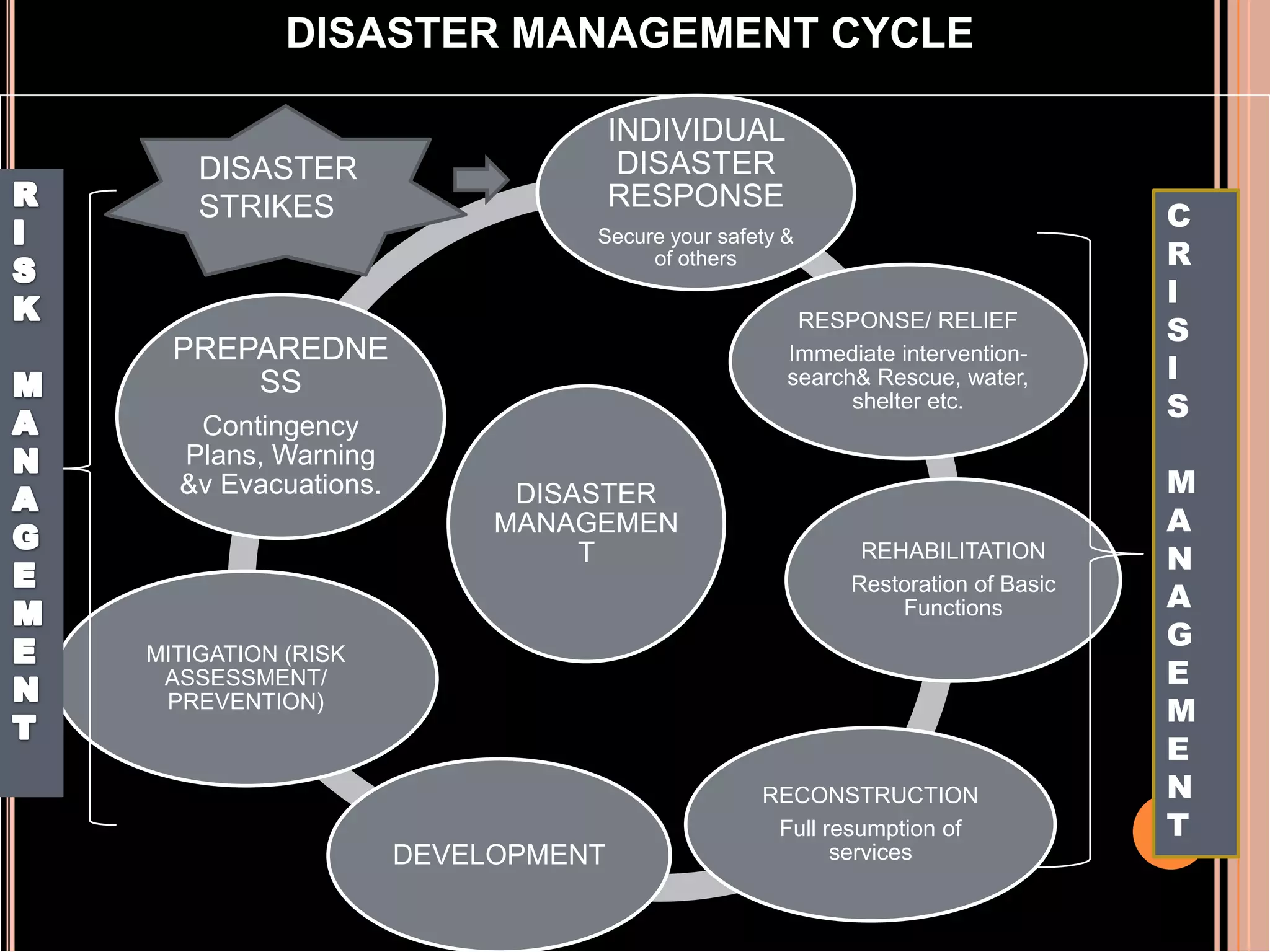
This document discusses the concept of disaster risk management. It begins by showing pictures of recent disasters in India to illustrate the risks faced. It then defines key terms like hazard, vulnerability, capacity and disaster risk. Disaster risk is explained as being a function of hazard x vulnerability - capacity. Recent examples of disasters across India from 2011-2012 are provided, including earthquakes, floods, cyclones and landslides. The document emphasizes that communities must be aware and prepared in order to minimize losses from disasters. It outlines the disaster management cycle and different approaches like emergency management and disaster risk management.