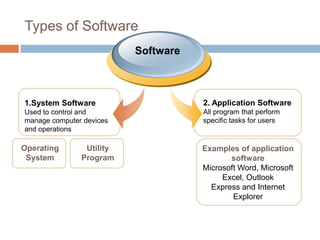
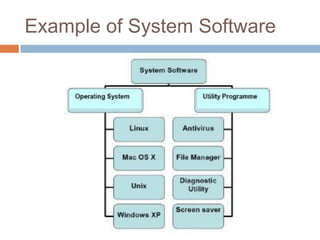
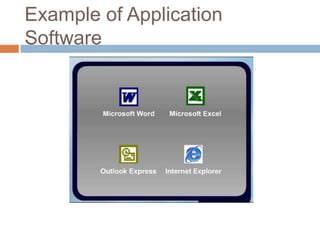
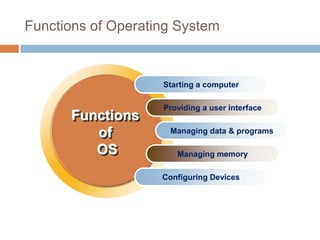
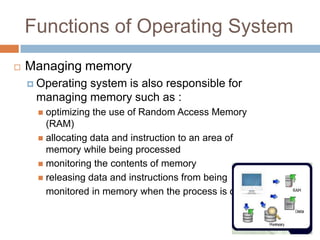
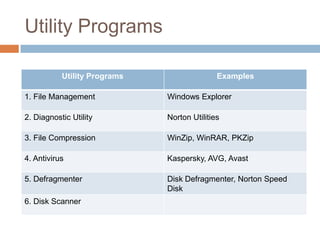
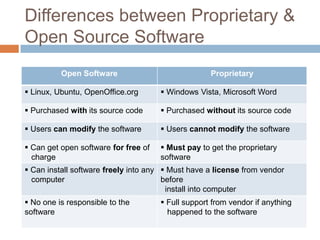
Software consists of instructions that tell a computer's hardware what to do. There are two main types of software: system software that controls computer operations, and application software that performs specific tasks for users. An operating system is system software that coordinates hardware, manages memory and files, and provides a user interface. Application software includes programs for word processing, spreadsheets, presentations, graphics editing, and more. Utility programs allow users to perform maintenance tasks like file compression. Software can be proprietary, where users pay for a closed source, or open source, where users can freely modify free software.