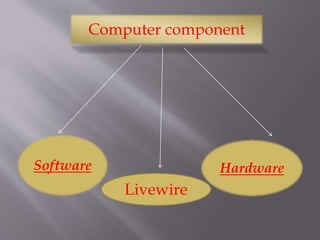
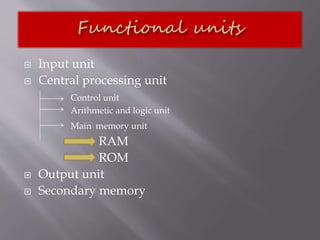
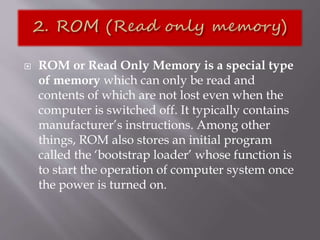
A computer is a programmable machine that performs arithmetic and logical operations on input provided by the user to produce desired output. It consists of both hardware and software components. The hardware includes physical parts like the central processing unit, memory, input/output devices, while software refers to programs and instructions. A computer accepts data as input, processes it, stores results, and provides output according to programmed instructions at high speed, accuracy, and capacity.