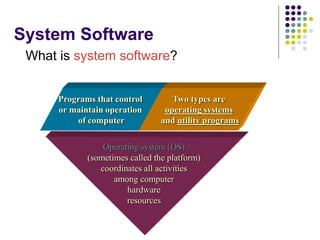
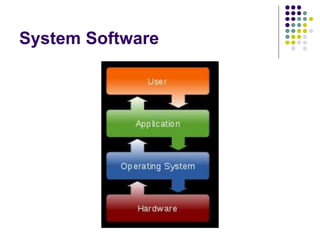
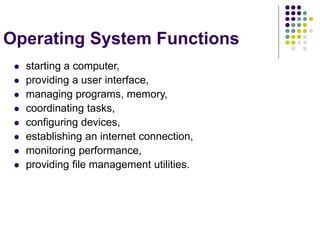
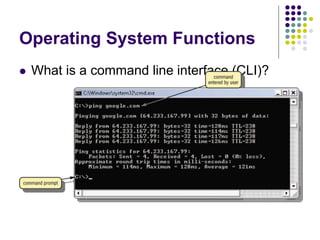
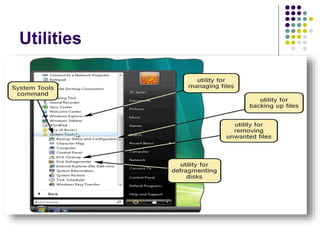
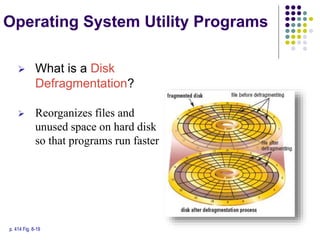
This document provides an overview of different types of software, with a focus on system software. It defines software and discusses the two main categories: system software and application software. System software includes operating systems, utility programs, and device drivers. An operating system coordinates activities between the computer hardware and user programs. It provides functions like starting the computer, managing memory and tasks. Device drivers allow hardware components to interface with the computer system. Utility programs perform maintenance tasks related to files, disks, backups and more. Specific examples of utility programs discussed include file managers, disk defragmenters, backup utilities and antivirus software.