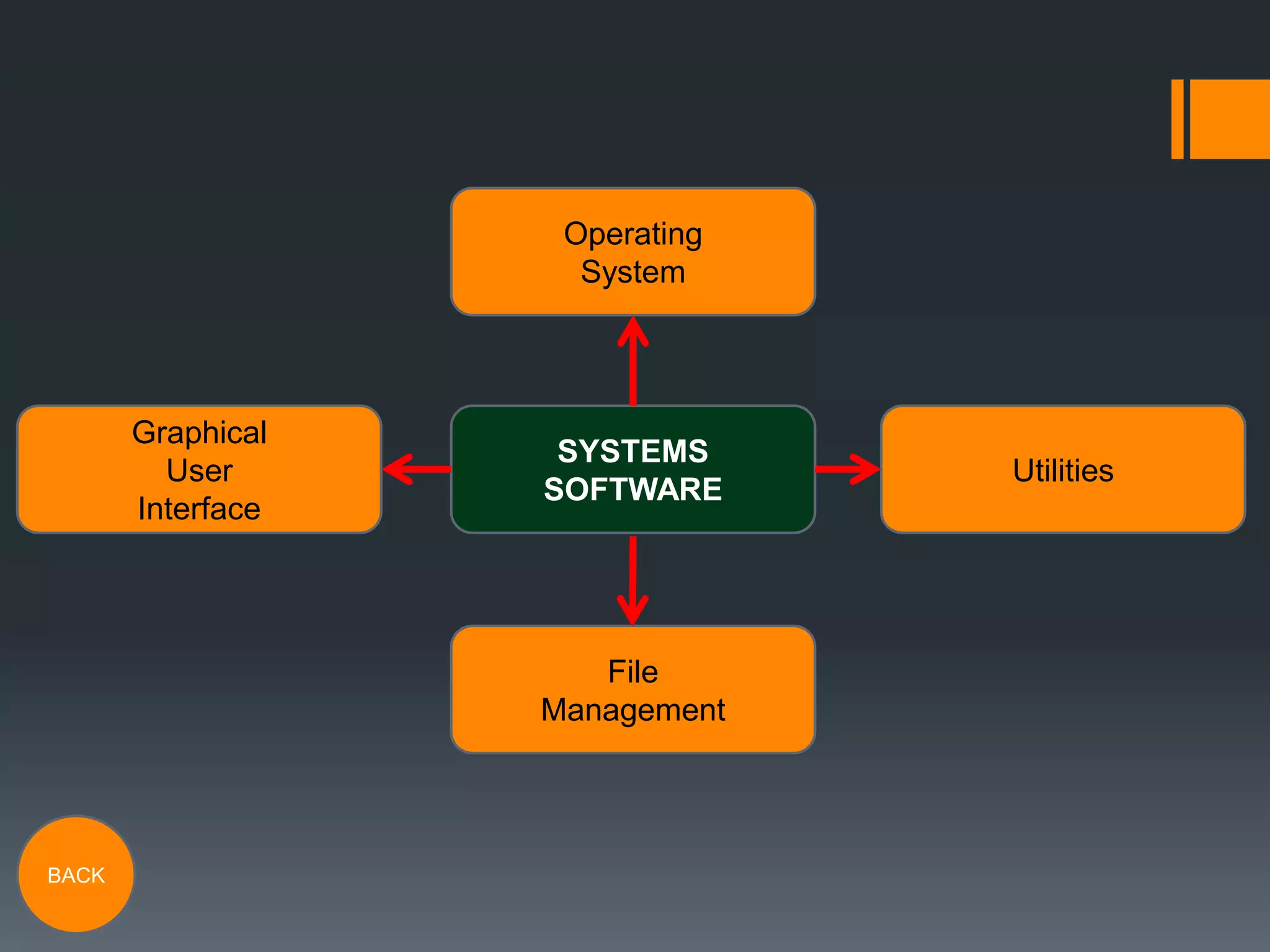
The document discusses the distinction between application software and system software, outlining that application software serves specific tasks while system software governs hardware functionality. It highlights the responsibilities of operating systems, including input/output management, memory management, and security, as well as the roles of utilities like antivirus programs and file management systems. The document also describes graphical user interfaces (GUIs) designed to simplify user interaction with computer systems.