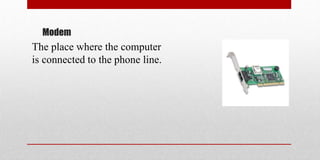
This document provides an overview of computer hardware and the evolution of computer generations from the first to fifth. It details the key components of a computer, including input/output devices, CPU, and various storage media. Additionally, the document outlines the technological advancements associated with each generation and introduces concepts related to artificial intelligence.