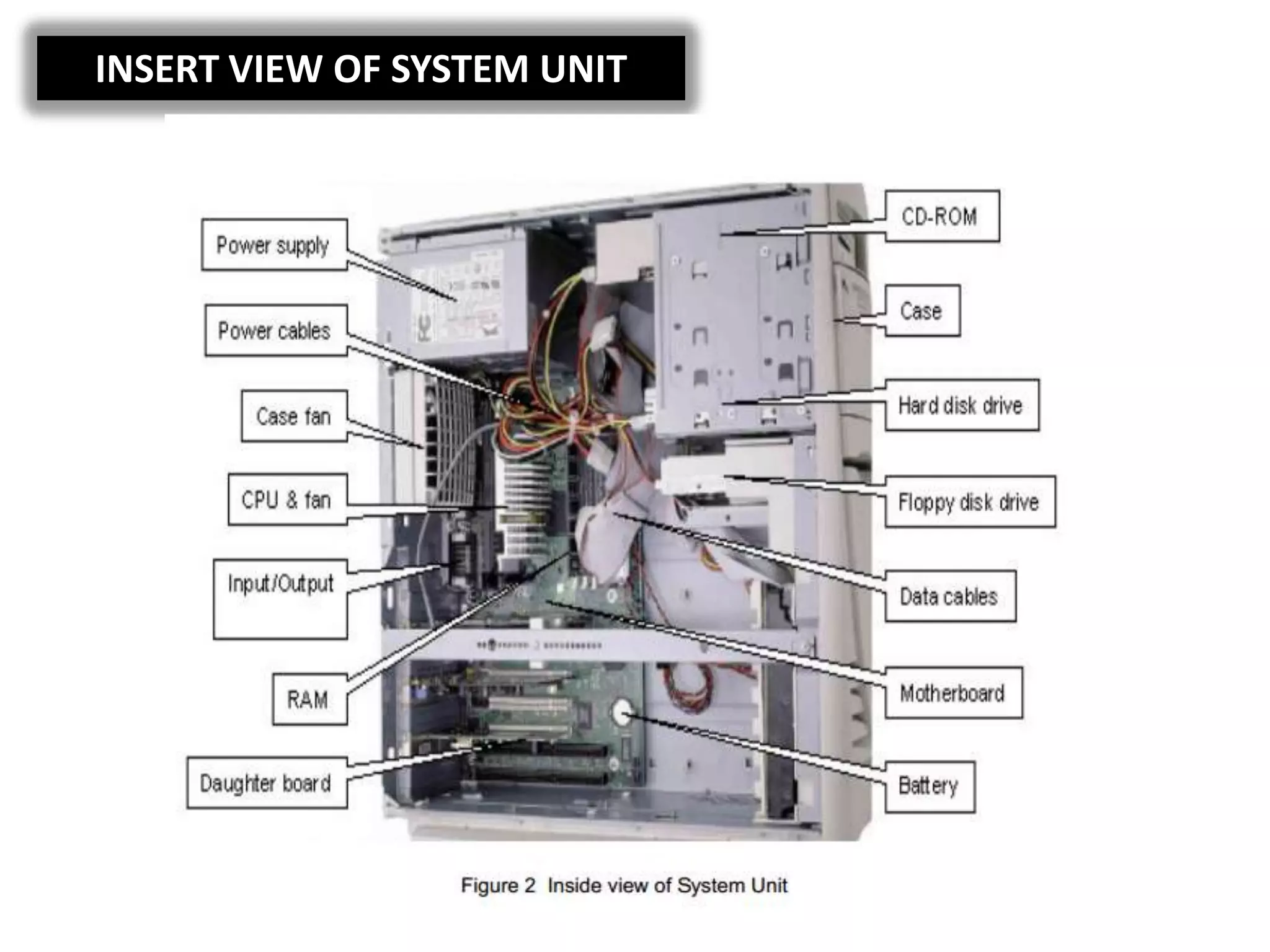
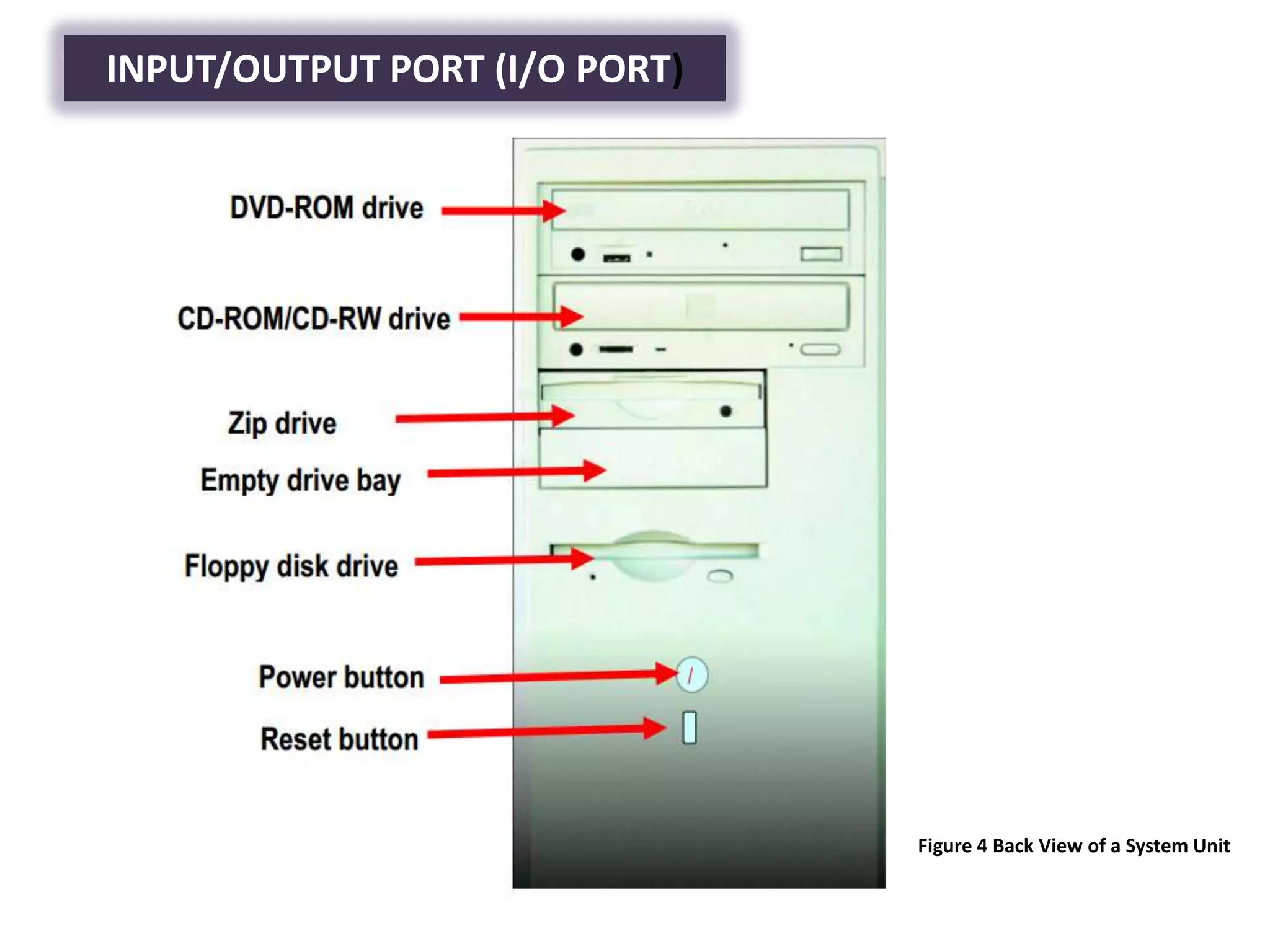
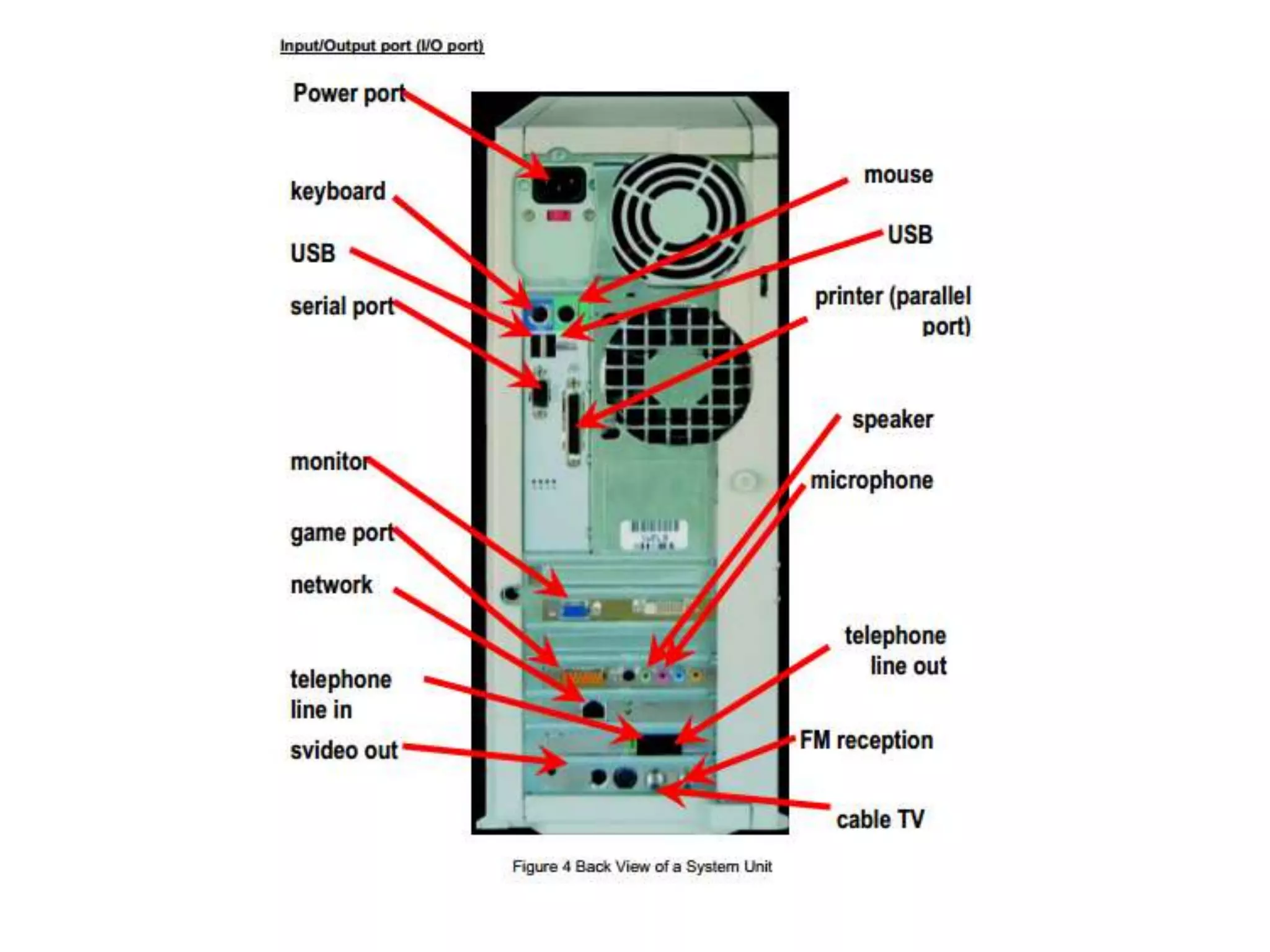
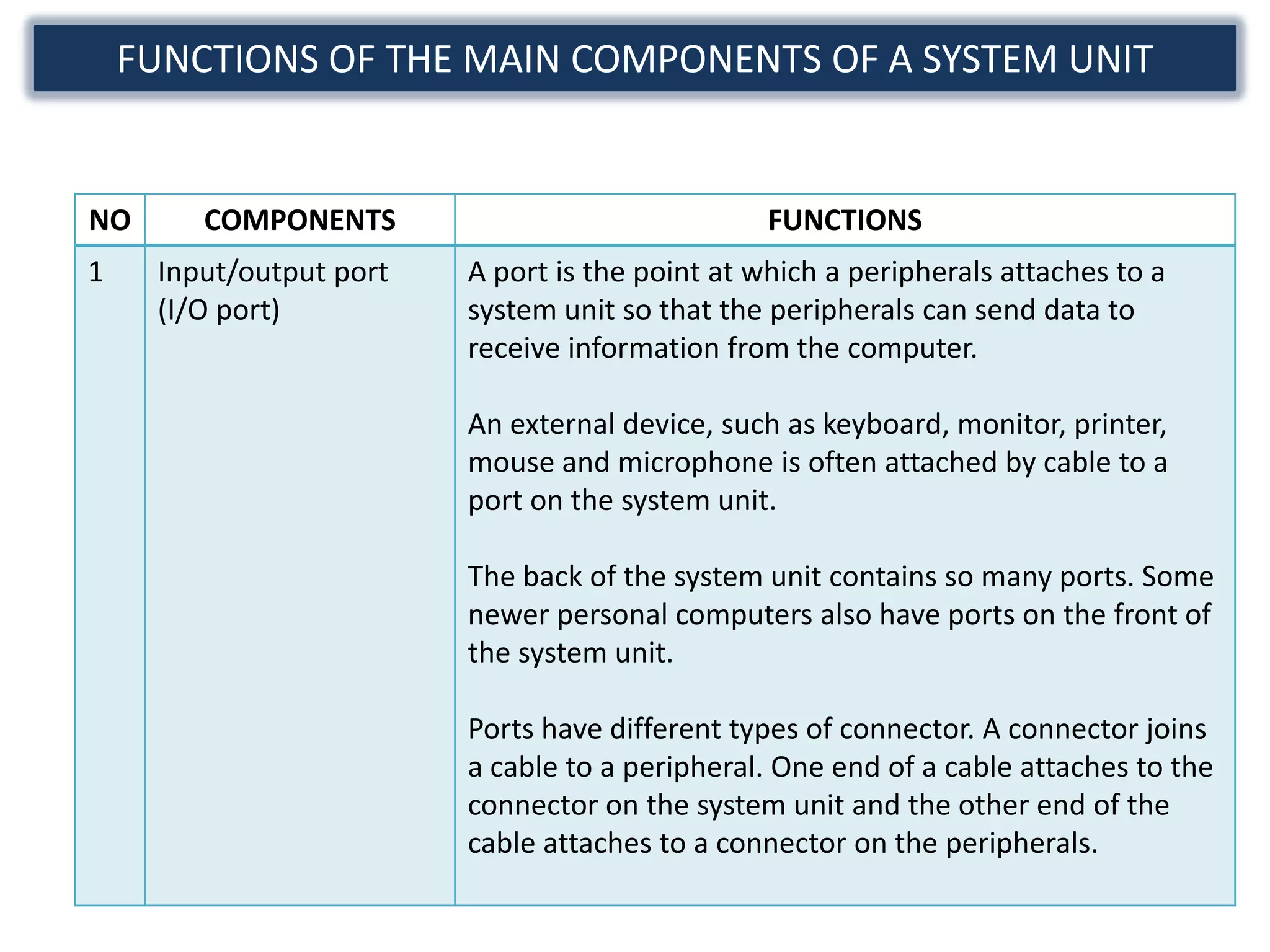
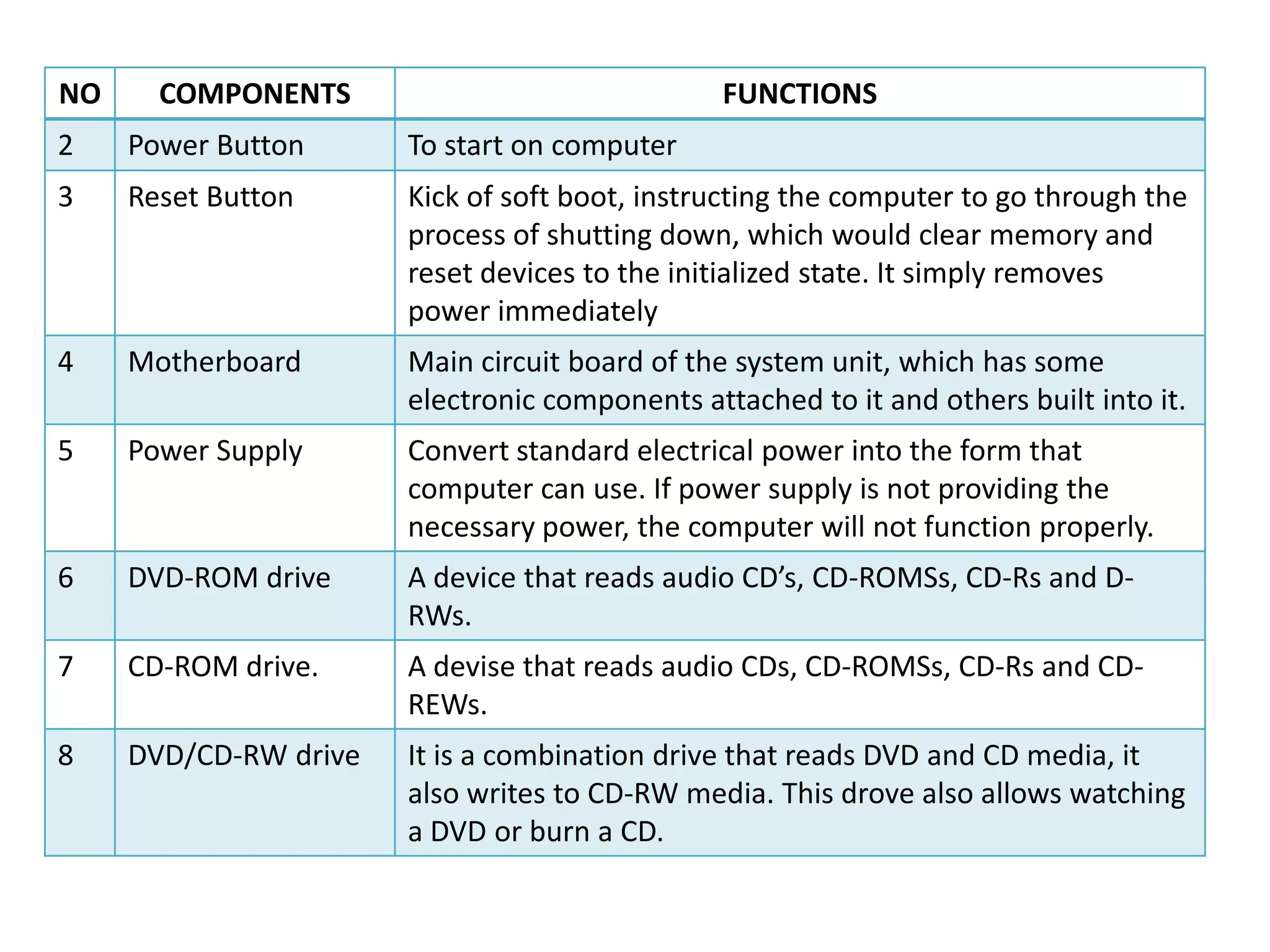
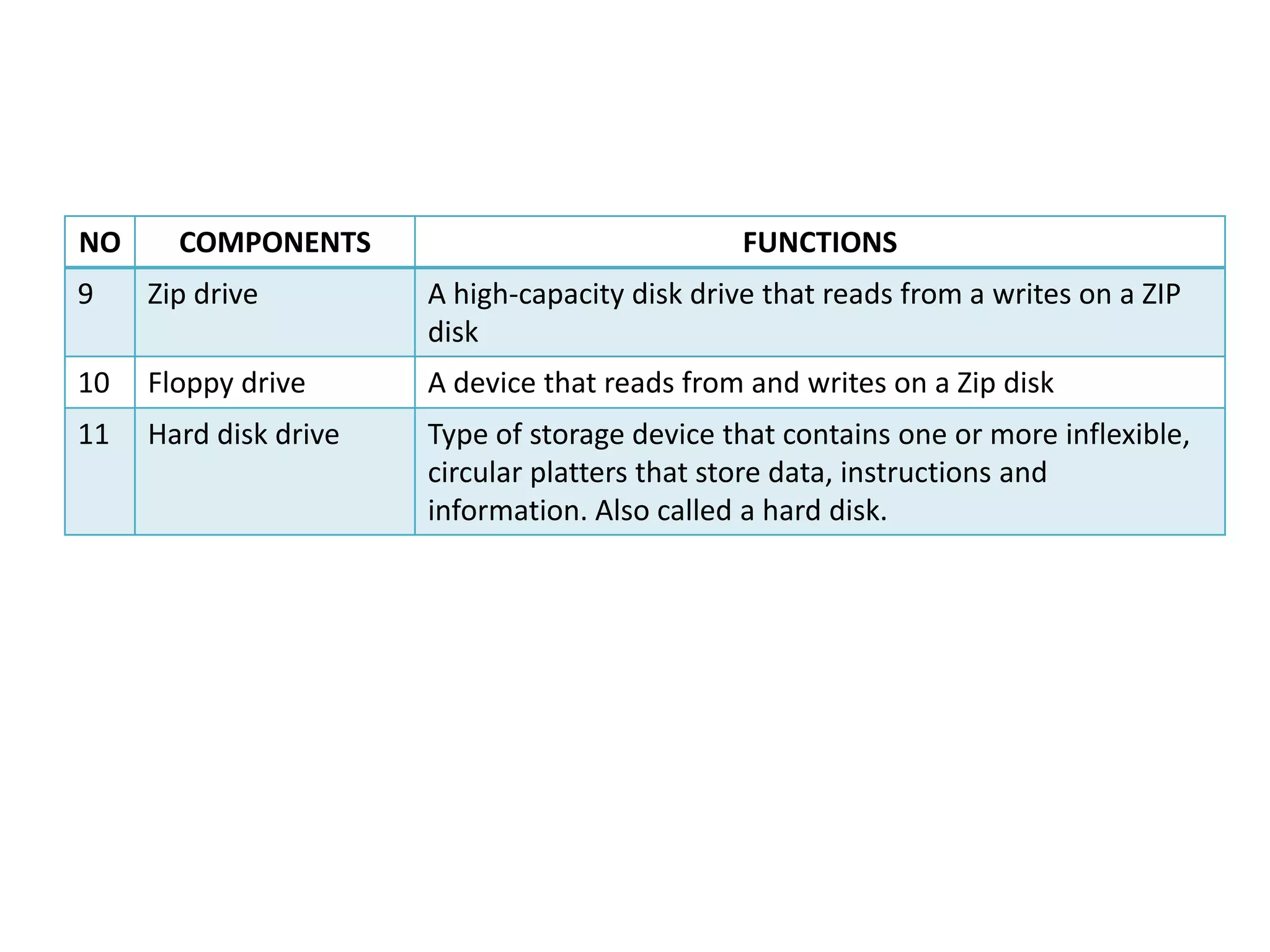
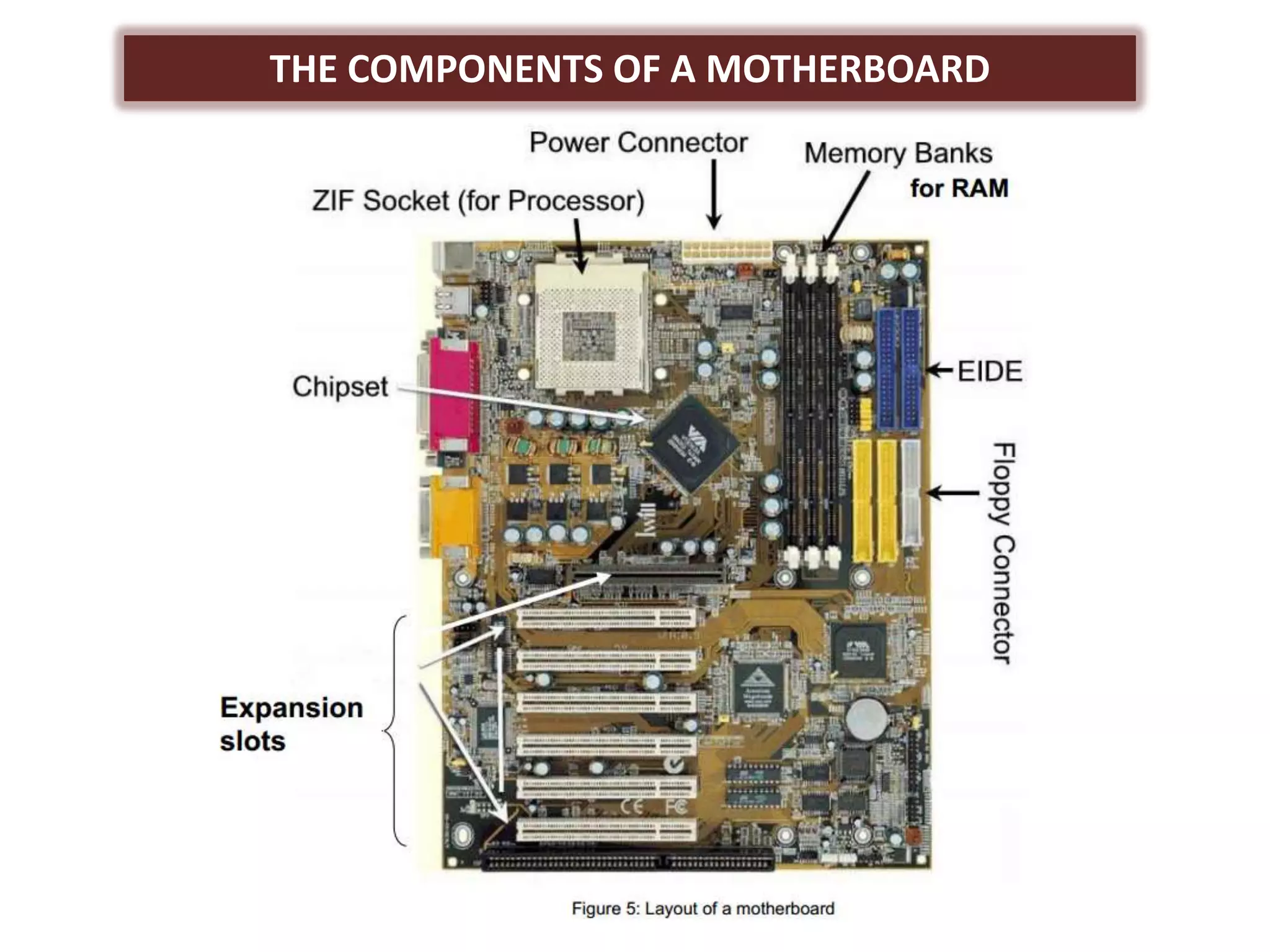
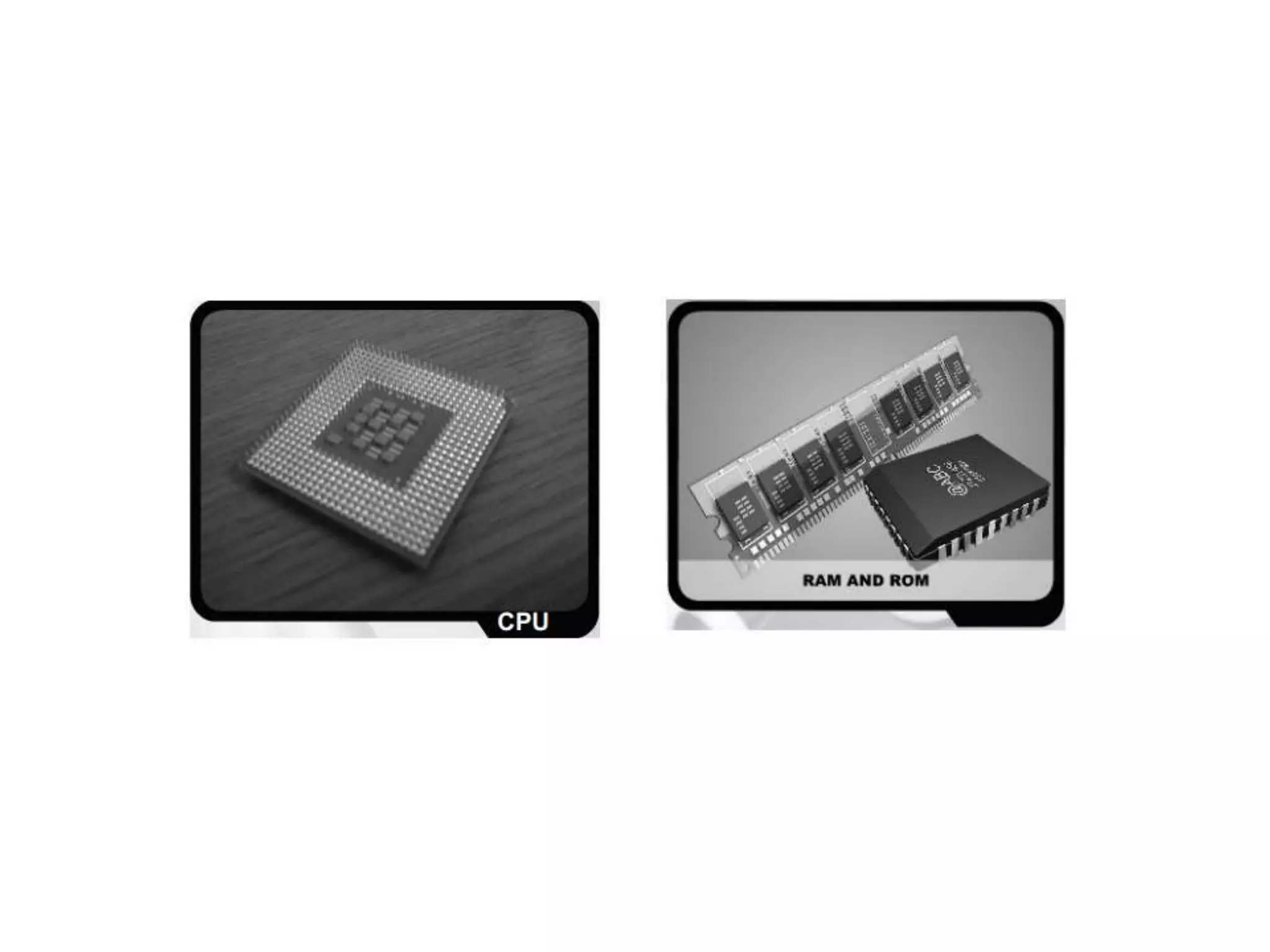
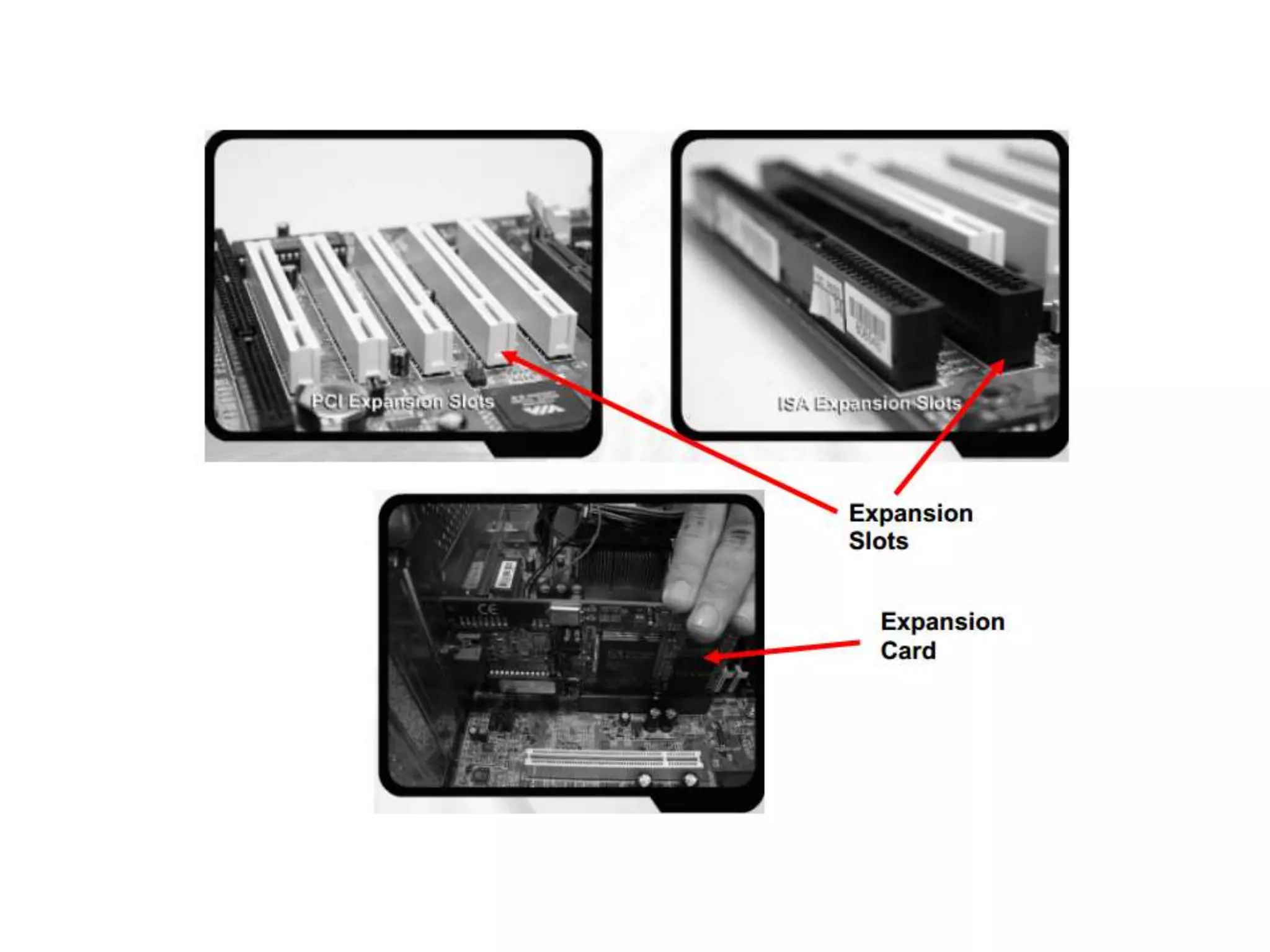
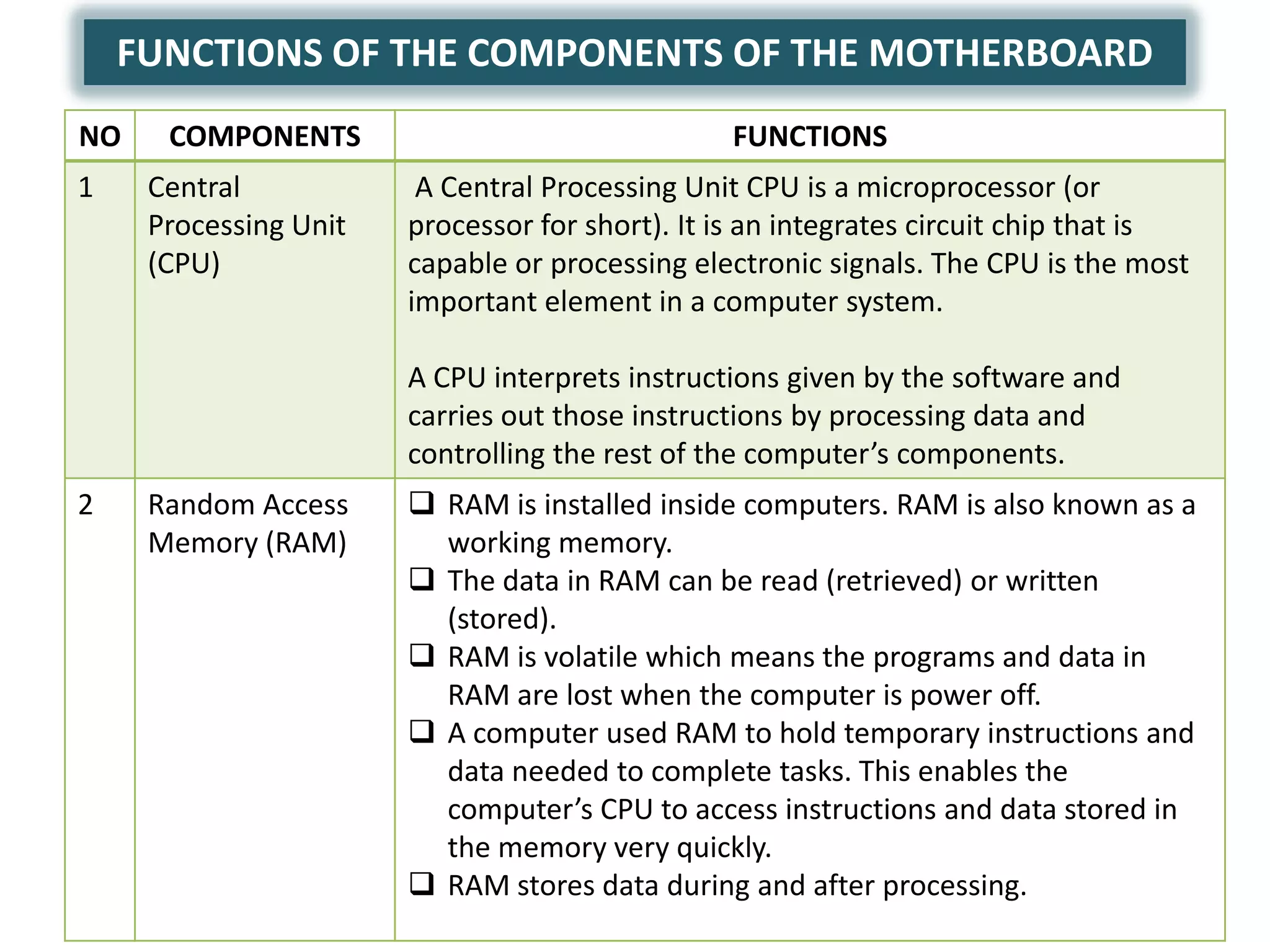
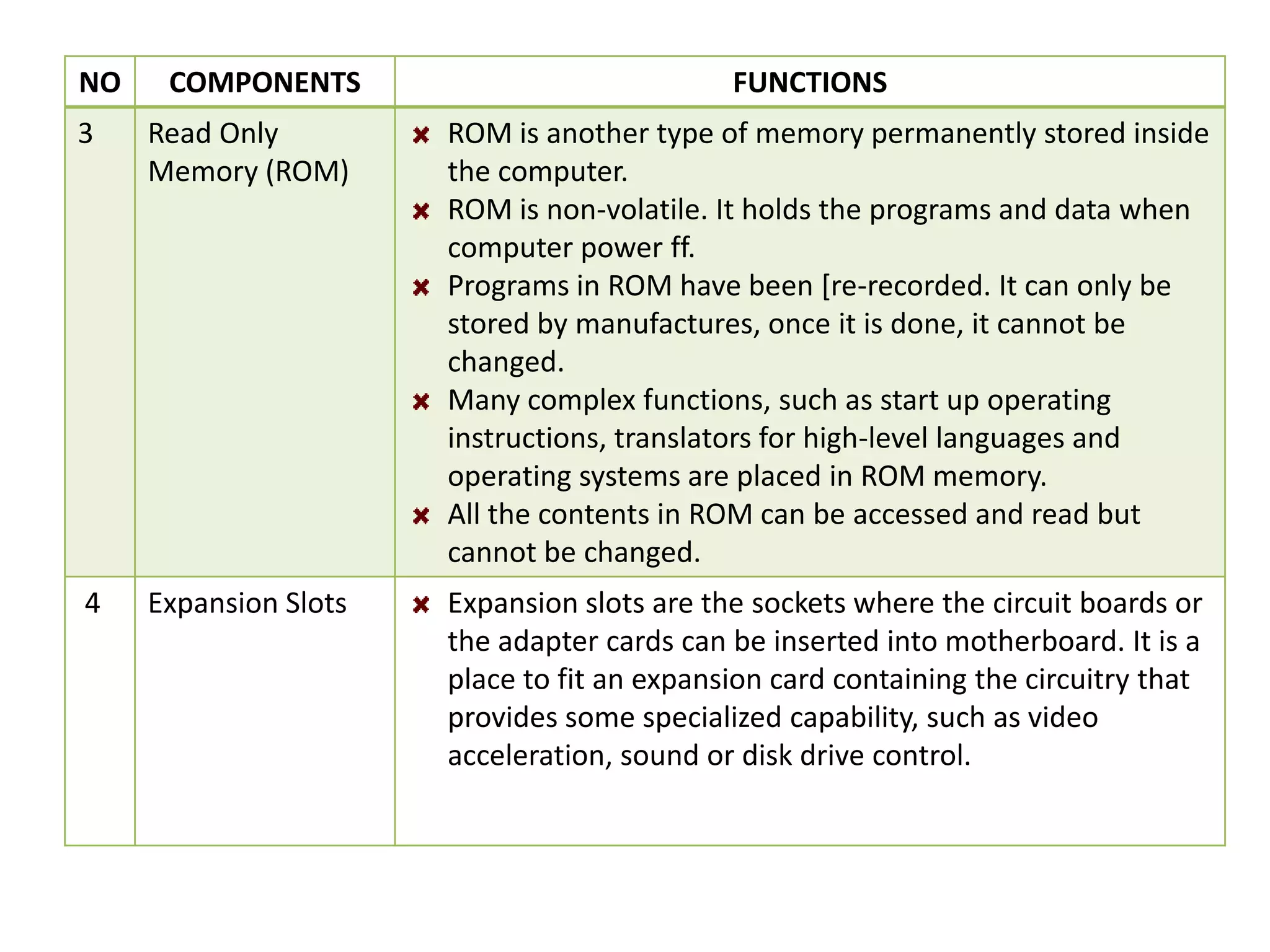
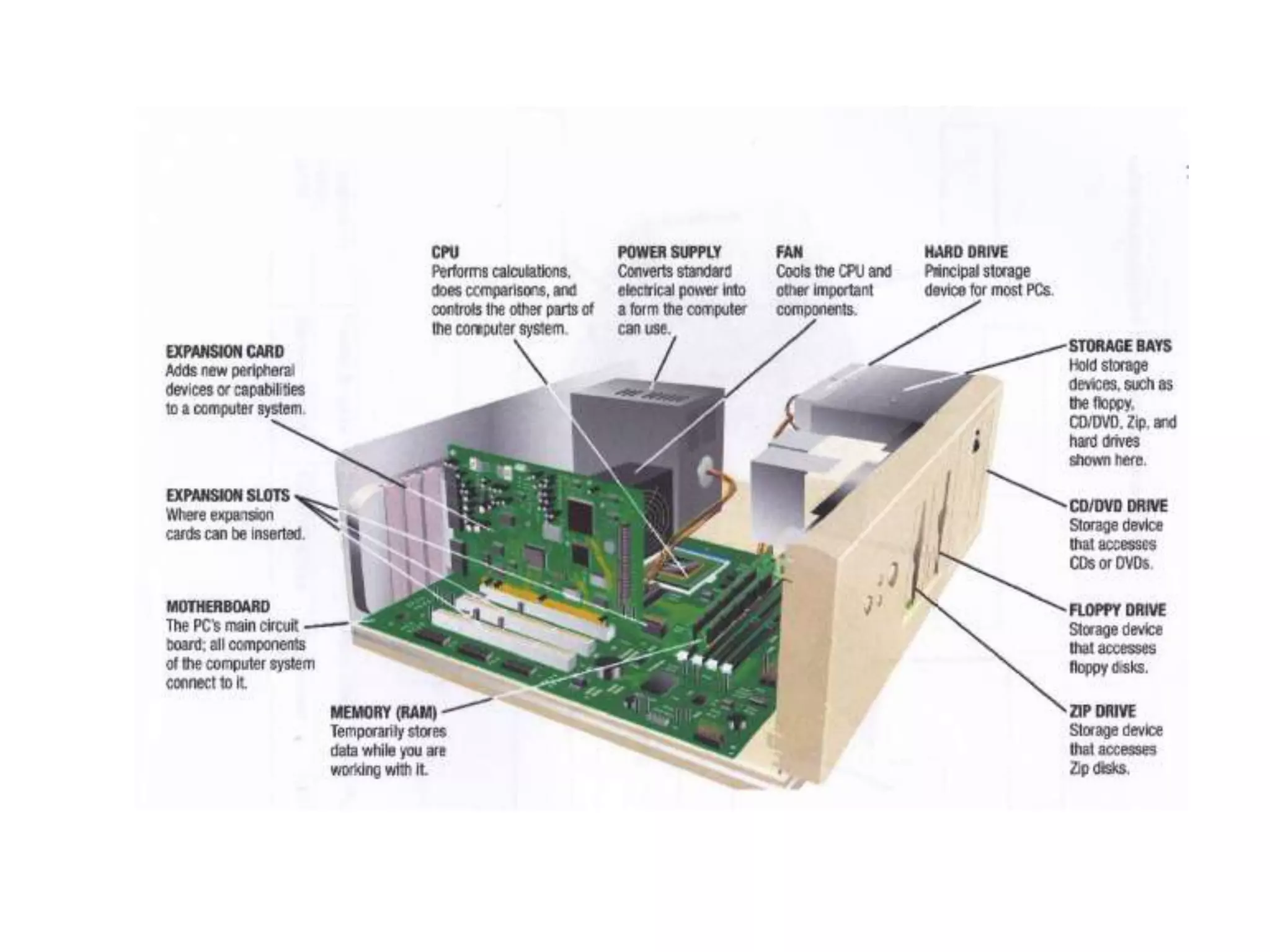
The document discusses the components and functions of a computer system unit. It describes the system unit as the box-like case that contains the computer's electronic components. The main components include the motherboard, CPU, RAM, ROM, power supply, and input/output ports. The motherboard is the main circuit board that has electronic components attached or built into it. The CPU interprets instructions and processes data. RAM is used for temporary storage while programs are running, and ROM permanently stores basic startup instructions. Expansion slots allow additional capabilities to be added via circuit boards.