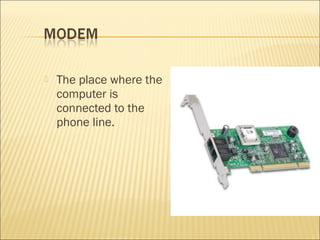
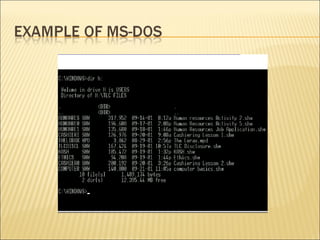
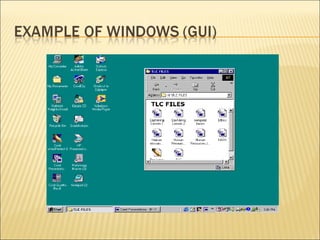
This document discusses the major components that make up a basic computer system. It explains that a computer contains physical parts like the central processing unit (CPU) and memory chips that work together to process instructions. It also describes common input/output devices like a monitor, mouse, keyboard, printer, and speakers that allow a user to interact with and receive output from the computer. The document provides brief explanations of what each component does and its role in the overall functioning of the computer.