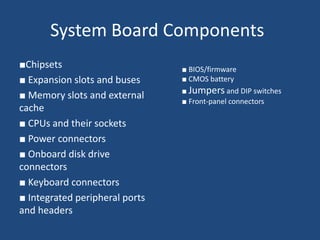
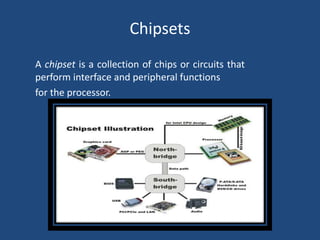
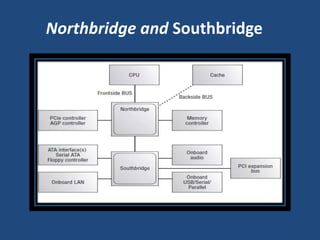
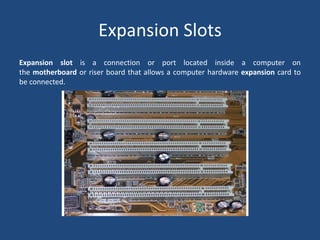
A motherboard is the main circuit board in a computer that connects the central processing unit and RAM to other components like expansion cards and ports. It contains chipsets to interface with peripherals and components like the CPU socket, memory slots, expansion slots for graphics and other cards, and front panel connectors. Key factors in motherboards include the form factor like ATX or Mini-ITX and components like the northbridge and southbridge chips that connect different parts of the system.